What Is AI and How It Transforms Technology: The Engine Behind Innovation
What Is AI and How It Transforms Technology: The Engine Behind Innovation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer the futuristic concept of science fiction—it is the core driver reshaping industries, automating tasks, and redefining human-machine interaction across the globe. From powering personalized recommendations on streaming platforms to enabling autonomous vehicles and revolutionizing healthcare diagnostics, AI operates at the intersection of data, algorithms, and real-world application. Understanding what AI truly is—and how it functions—reveals not just a technological marvel, but a transformative force reshaping daily life and economic systems.
This article unpacks AI’s fundamental principles, operational mechanics, key types, and its expanding role in modern society.
At its essence, Artificial Intelligence refers to computer systems designed to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. These include pattern recognition, decision-making, language understanding, and problem-solving—capabilities once thought exclusive to human cognition. Unlike traditional software following rigid instructions, AI systems learn from data, adapt to new inputs, and improve performance over time.
As Andrew Ng, pioneer in machine learning, notes, “AI is really about designing systems that learn how to make better decisions with experience.” This adaptive learning forms the foundation of modern AI, enabling machines to evolve beyond programmed responses into dynamic, context-aware agents.
Core Mechanisms: How AI Learns and Reasoning in Action
AI operates through structured frameworks built on data, algorithms, and computational models. At the heart of most AI systems lies machine learning (ML), where algorithms parse vast datasets to detect patterns and make predictions or decisions without explicit programming. Supervised learning, a common approach, trains models on labeled data—such as customer purchase histories tagged with outcome labels—so the system learns to predict future behaviors.
Unsupervised learning, by contrast, identifies hidden structures within unlabeled data, uncovering clusters or insights without predefined outputs.
Technical Foundations: Neural Networks and Deep Learning
Modern AI has been profoundly advanced by neural networks—inspired by the human brain’s architecture—capable of handling complex, high-dimensional data. Deep learning, a subset of ML powered by multi-layered artificial neural networks, excels at tasks like image recognition, speech processing, and natural language understanding. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) analyze visual data by detecting edges, textures, and shapes, enabling applications such as facial recognition and medical imaging analysis.
Meanwhile, Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) manage sequential data, making breakthroughs in language translation and time-series forecasting.
The Role of Training Data and Continuous Improvement
AI systems depend heavily on training data quality and diversity. Garbage in, garbage out remains a critical principle—biased, incomplete, or noisy data can distort model behavior and lead to inaccurate, unfair outcomes. Successful AI deployment requires rigorous data curation, preprocessing, and validation.
Furthermore, AI models undergo iterative refinement through feedback loops: real-world performance data fine-tunes algorithms, reducing errors and enhancing accuracy. This continuous learning cycle ensures AI evolves alongside changing environments and user needs.
Types of AI: From Narrow Tools to General Capabilities
AI manifests in multiple forms, each serving distinct functions across industries. Recognizing these variations clarifies AI’s current scope and future potential:
- Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI): The most prevalent form today, ANI excels at specific tasks—such as chatbots answering FAQs, recommendation engines suggesting products, or fraud detection systems.
It operates within a defined domain without broader comprehension or consciousness.
- Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): A hypothetical future milestone, AGI would possess human-like cognitive flexibility—understanding and applying knowledge across diverse, novel contexts. While widely speculated, AGI remains theoretical, requiring breakthroughs in reasoning, emotions, and self-awareness.
- Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI): Even more speculative, ASI surpasses human intelligence across all domains, raising profound ethical questions about control, autonomy, and societal impact.
As AI matures, its applications span sectors: healthcare utilizes AI for diagnostics and drug discovery; finance leverages predictive analytics and risk modeling; manufacturing employs AI-driven robotics for precision and efficiency; customer service deploys virtual assistants to enhance user experience.
Real-World Impact and Ethical Considerations
The integration of AI
![[Webinar] Prototyping, the Driver Behind Innovation](https://cdn.sanity.io/images/qyzm5ged/production/dc3464b2628cfbd7c706a79a765294c9941d7a08-2138x1200.png)

Related Post
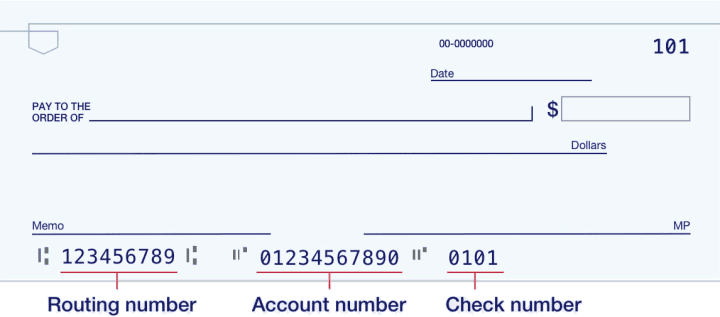
Unlocking Your Financial Flow: Td Bank Routing Numbers in New Jersey
Call To Whomever NY Panders Are They Selling Out America?

