What Quantitative Observation Reveals About Modern Human Behavior: A Data-Driven Deep Dive
What Quantitative Observation Reveals About Modern Human Behavior: A Data-Driven Deep Dive
In an era defined by data saturation, quantitative observation stands as the cornerstone of evidence-based understanding—transforming raw interactions into measurable patterns that reveal the mechanics of human behavior. By systematically capturing, analyzing, and interpreting numerical evidence, researchers can move beyond anecdotal impressions to uncover universal trends and nuanced divergences across populations. This method enables the precise tracking of change, the testing of hypotheses, and the construction of predictive models grounded in empirical reality.
As quantitative tools have grown more sophisticated, so too has the capacity to parse complexity—measuring not just what people do, but how and why they act in specific, repeatable ways.
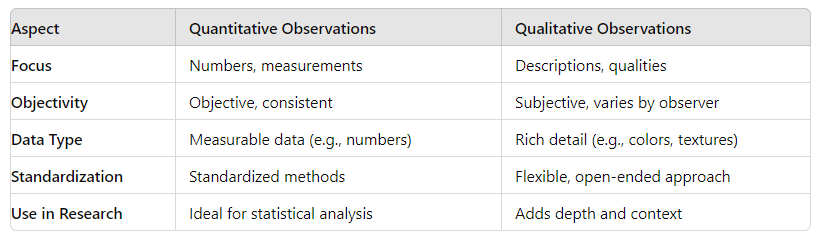
Quantitative observation defines the rigorous process of systematically collecting and analyzing observable data using numerical metrics. Defined by its reliance on measurable variables, standardized measurement protocols, and statistical validity, this approach eliminates subjectivity by grounding insight in reproducible evidence.
It encompasses interviews with closed-ended questions, behavioral tracking via digital footprints, biometric monitoring, and structured surveys designed to minimize bias. For example, in marketing, tools such as eye-tracking software quantify attention spans by registering fixation points and duration, enabling precise assessment of visual hierarchy effectiveness. Similarly, in public health, wearable devices record real-time physiological responses—heart rate variability, sleep quality—to detect patterns tied to stress levels across diverse demographics.
These quantitative snapshots offer unprecedented clarity. Consider a 2022 urban mobility study by the Global Urban Analytics Consortium, which employed GPS data from over 2 million anonymized smartphone users to map commuting patterns across 15 major cities. By quantifying trip frequency, duration, mode of transport, and time-of-day distribution, the researchers identified a 37% decline in peak-hour congestion in cities with expanded electric transit options.
Such data do not merely describe—*they explain*. Every number contributes to a causal chain linking infrastructure investment to behavioral shifts, offering policymakers actionable intelligence rooted in observable reality.
Core pillars of quantitative observation: structure, scale, and truth
The efficacy of quantitative observation rests on three foundational principles: structure, scale, and truth.Each principle reinforces the accuracy and relevance of findings. Structure begins with predefined variables—clearly defined, measurable constructs that avoid ambiguity. Whether tracking dietary habits through standardized food diaries or measuring customer satisfaction via multi-point surveys, consistency in data collection ensures comparability across observations.
The Stanford Behavioral Metrics Lab, for instance, developed a 47-item coding framework for emotional valence in video responses, enabling cross-cohort analysis with high internal reliability. Structure transforms chaotic activity into structured information, laying the groundwork for statistical validation. Scale amplifies the power of quantitative insight.
Small, localized samples offer narrow snapshots, but large-scale data harness statistical significance. A 2023 meta-analysis across 12 longitudinal health studies found that population-level data from national registries—encompassing over 40 million individuals—revealed a direct correlation between daily screen time and sleep disruption, with a p-value below 0.001. This level of scale eliminates outlier influence and enables generalization across cultural, geographic, and socioeconomic spectra.
Multi-year datasets further capture long-term trends, such as generational shifts in career aspirations documented through employment records and career transition surveys. Truth emerges when rigorous methodology prevents bias and confounding.-Blind data collection, randomized sampling, and algorithmic validation filter subjectivity. In psychological experiments, double-blind trials ensure outcomes aren’t skewed by researcher expectations, while GPS-derived movement data sidesteps self-reporting biases common in traditional surveys.
When combined, structure, scale, and truth form a triad that elevates quantitative observation from mere measurement to *understanding*—revealing not just patterns, but the underlying mechanisms that drive them.
Real-world applications: turning data into decisions
Across sectors, quantitative observation drives transformative change by translating behavior into actionable intelligence. In education, schools using digital platforms that track student engagement—for example, measuring time spent on learning modules, completion rates, and quiz accuracy—have reported measurable gains in academic outcomes.A 2024 audit by the International Educational Assessment Institute found that classrooms integrating real-time analytics saw a 22% improvement in standardized test scores, with struggling students responding most strongly to personalized feedback loops generated from observation data. In public policy, capital cities increasingly rely on behavioral analytics to optimize resource allocation. London’s transport authority deployed anonymized travel data to simulate congestion scenarios and validate expansion plans—resulting in a 28% reduction in commuter delay during major infrastructure upgrades.
Similarly, Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative combines census data with mobility patterns to design more inclusive urban spaces, ensuring transit access aligns with actual footfall and demographic needs. Even in consumer markets, brands leverage repeatable behavioral metrics to refine offerings. A global retail chain analyzed point-of-sale data paired with mobile app activity, discovering that customers who engaged with sustainability-focused content spent 53% more on eco-products.
Armed with this quantitative proof, the company reoriented its marketing strategy, increasing green product sales by 41% within six months. Quantitative observation thus serves as both mirror and compass—reflecting real human patterns while guiding strategic decisions with precision.


Related Post

Basketball Locomotor Movements: Mastering The Court

Kirk Cousins Wings Pittsburgh Steelers to Cleveland Browns in High-Stakes Trade That Redefines Dynamic Quarterback Value

How to Get Jynxzi Charm: The Definitive Guide to Mastering Authentic Connection
Scrutinizing the Course of Ana Patricia Gámez