What Is the Time in USA Ohio? A Precise Guide to Eastern Time Standards
What Is the Time in USA Ohio? A Precise Guide to Eastern Time Standards
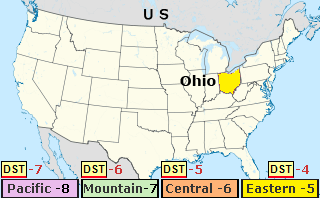
The time in Ohio is defined by Eastern Time—specifically Eastern Standard Time (EST) and Eastern Daylight Time (EDT)—making the state a key node in the timekeeping network of the American Midwest. With no daylight saving time observed in winter, Ohio remains synchronized to Eastern Time year-round in its standard window, while switching to EDT during the spring and fall months. This consistent rhythm aligns Ohio with major East Coast cities like New York and Washington, D.C., enabling seamless coordination across business, transportation, and daily life.
Ohio’s timekeeping follows the synchronized pattern of most U.S. states outside the Pacific and Mountain Time zones. From the last Sunday in October to the second Sunday in March, Ohio observes Eastern Standard Time (EST), uniformly set at UTC-5.
Between March and November, the state shifts to Eastern Daylight Time (EDT), advancing clocks one hour forward to UTC-4. This biannual shift is driven by federal standard time regulations, ensuring nationwide time cohesion.
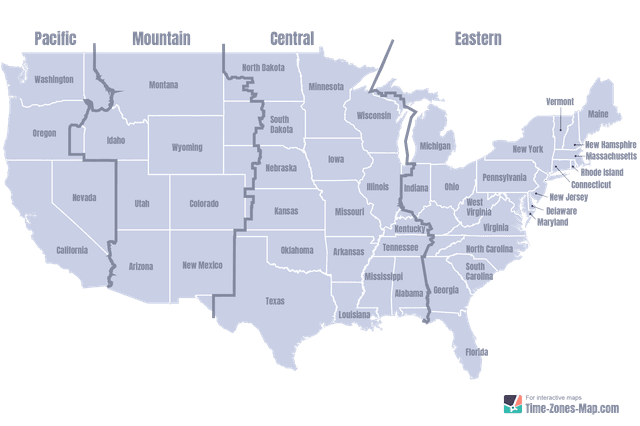
At the core of Ohio’s time system lies its geographic placement within the Eastern Time Zone, a region spanning 19 states and estimated populations of over 70 million.
Unlike regions using independent time schemes—such as Alaska’s non-DST schedule or Arizona’s year-round standard time—Ohio remains locked to the continental Eastern Time framework. This alignment supports synchronized operations across the nation’s economic and institutional sectors, including finance, broadcasting, and interstate travel. Despite minor daily fluctuations tied to daylight saving, the transition remains predictable and standardized, minimizing confusion for residents and visitors alike.
Time Zones and Daylight Saving in Ohio
Ohio resides entirely within the Eastern Time Zone, a harmonic division that smooths time transitions between neighboring regions.Eastern Time divides the U.S. into three quarter-hour sub-regions—EST (UTC-5), EDT (UTC-4), and, temporarily, the Central Time Zone during daylight saving pivots—but Ohio never crosses into either. Unlike states further south such as Florida or Georgia, where time adjustments follow broader state policies, Ohio strictly adheres to the Eastern Time Zone’s rules codified by federal law.
Daylight Saving Time begins formally the second Sunday in March, when clocks advance from 2:00 AM to 3:00 AM—to capture more daylight in the evenings. In Ohio, this shift to EDT typically affects schools, workplaces, and public services within hours, prompting immediate updates in digital systems, flight schedules, and broadcast timelines. Conversely, on the first Sunday in November, clocks revert back to EST, restoring the fixed standard time.
This biannual rhythm affects everything from internet time stamps to international meeting coordination, requiring awareness but never disruption to Ohio’s daily rhythm.
While daylight saving boosts evening daylight, it also introduces temporary interruptions in timekeeping—short switches that are broadly observed but not mandated beyond the federal mandate. Ohio does not observe permanent daylight saving; like most of the U.S.
East Coast, it follows the two-timesheet transition governed by the Energy Policy Act of 2005. This synchronization preserves reliable alignment with time-sensitive activities across industries and communities.
Impact on Daily Life and Infrastructure
For Ohio’s 11.8 million residents—largely clustered in urban corridors like the Columbus-Cincinnati-Louisville axis and the Cleveland-Akron-Garage triangle—consistent timekeeping enhances coordination across education, commerce, and transportation. Public school calendars, business hours, and broadcast schedules align precisely with Eastern Time standards, enabling synchronized commutes, national programming, and federal appointments.The state’s reliance on Eastern Time extends to critical infrastructure. Air traffic control, railway networks, and telecommunications all depend on a unified temporal framework to manage cross-state operations. During daylight saving transitions, digital systems—from atomic clocks to software applications—undergo rigorous timestamps to prevent data discrepancies.
While minor timing shifts occasionally draw attention, especially among travelers unfamiliar with the change, Ohioans and visitors alike depend on the predictability of Eastern Time’s schedule to navigate daily routines.
In practical terms, living in Ohio means no need to adjust clocks twice a year—one hour behind in winter, one hour ahead in summer. This consistency benefits not only individual routines but also regional business strategies tied to time-sensitive markets.
Manufacturers, financial services, and logistics firms operate within a stable temporal zone, reducing friction in interstate coordination. Even modest seasonal shifts in sunrise and sunset times are accounted for in public summer lighting and energy usage planning, demonstrating how timekeeping integrates with broader civic life.
Historical Context and Standardization
Ohio’s time standard evolved alongside national time conventions, beginning in the 19th century when railroads demanded coordinated schedules across vast distances.Initially, local towns set their own times, leading to chaos. In 1883, standard time zones were established nationwide, with Eastern Time introduced as a formal region. Ohio’s adoption of this system reflected its growing economic integration with the Northeast and mid-Atlantic states.
Federal regulation strengthened this structure in the 20th century—a mandate solidified by the Uniform Time Act of 1966 and later extended by the Energy Policy Act of 2005. Rather than granting flexibility, these laws unified the Eastern Time Zone, ensuring Ohio’s clocks align with Washington, D.C., and other major cities. Even amid debates over year-round daylight saving, Ohio remains committed to the standard Eastern Time pattern, reinforcing its role as a consistent temporal anchor in the U.S.
Midwest.
This institutional stability contrasts sharply with regions that manipulate time schedules for energy or seasonal adaptation. Ohio’s steadfast use of Eastern Time underscores a pragmatic approach: balance between natural sunlight and societal efficiency.
While some countries around the world experiment with variable time zones, within the continental U.S., Ohio’s alignment with Eastern Time represents both continuity and coordination—a cornerstone of regional order in a connected nation.
Navigating Time in Ohio: Practical Tips and Common Questions
For residents and visitors, understanding Ohio’s time framework simplifies scheduling and travel. Since the state does not participate in permanent daylight saving policy, clocks follow a consistent biannual shift—not permanent fast or slow time—but retains the same time each year within each season.To track the current time in Ohio: - Eastern Standard Time (EST, UTC-5): from early November to late March - Eastern Daylight Time (EDT, UTC-4): from late March to early November Public clocks, digital devices, and official timestamps update automatically across time zones.
For precise coordination—especially during business meetings or cross-state travel—use the beginning and end dates of daylight saving as reference points. Many mobile apps and smart devices prompt automatic updates, reducing manual checking. Some visitors confuse Ohio’s annual rhythm with states practicing permanent DST or permanent standard time.
Educating travelers on the two-phase system prevents missteps: remember, no permanent shift—only a one-hour change per season. Residents, meanwhile, typically grow accustomed to minor sleep adjustments each spring and fall, knowing the 60-minute shift ultimately supports predictable routines.
Timekeeping in Ohio, though unremarkable in daily headlines, plays a vital unifying role.
It binds cities, industries, and communities into a shared temporal framework—one that supports both individual habits and the broader tempo of regional life. For Ohioans, time


Related Post
Understanding Time Zones: What Is The Time In USA Ohio Right Now?

Revolutionizing Workflow Efficiency: How Nin Apps Transforms Team Collaboration

Organized Government Defined: The Backbone of Modern Governance

