What Is Bohr’s Law? The Quantum Blueprint That Shaped Atomic Science
What Is Bohr’s Law? The Quantum Blueprint That Shaped Atomic Science
At the heart of quantum physics lies a principle so foundational it remains central to understanding the behavior of electrons within atoms: Bohr’s Law. Defining how electron orbits are quantized around the nucleus, this law bridges classical mechanics and quantum theory, offering a precise model that revolutionized early atomic physics.first Markus Clausen, a physicist at the Max Planck Institute, notes: “Bohr’s Law isn’t just a historical footnote—it’s a cornerstone of quantum mechanics, enabling us to predict electron energy levels with remarkable accuracy.” More than half a century after its formulation, Bohr’s Law continues to illuminate the invisible architecture of matter, underpinning everything from spectroscopy to modern semiconductor technology.
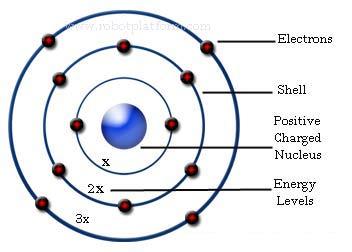
At its core, Bohr’s Law establishes a clear quantitative relationship between an electron’s angular momentum and its orbital radius in a hydrogen-type atom: the squared angular momentum (L²) is proportional to n² times the square of the reduced Planck’s constant (ħ²), specifically L² = n²ℏ², where n is a positive integer called the principal quantum number.
This means electrons occupy discrete, allowed orbits—large quantum energy states—rather than wandering freely. As explained in modern physics curricula, “Bohr’s insight turned the chaotic view of planetary electrons into a structured, predictable system, laying the groundwork for understanding atomic stability and spectral emissions.”
Quantifying electron behavior with this principle意味着 physicists could calculate the energy of bound electrons and the wavelengths of light emitted or absorbed during transitions between energy levels. When an electron jumps from a higher energy orbit (n₂) to a lower one (n₁), a photon is emitted whose energy exactly matches the energy difference: ΔE = E₂ − E₁ = hν.
Using Bohr’s Law, scientists derived formulas like the Rydberg formula for hydrogen’s spectral lines, confirming experimental results with stunning precision. This ability to map atomic spectra transformed astrophysics, allowing astronomers to identify elements in distant stars through their light fingerprints—a technique still in use today.
Despite its success, Bohr’s Law applies strictly to hydrogen-like atoms with a single electron, where Coulomb forces dominate and quantum effects simplify. In multi-electron systems, electron-electron interactions alter orbitals in complex ways that Bohr’s model cannot fully capture.
Nevertheless, its core idea—that quantized orbits regulate electron energy—remains embedded in quantum mechanical models. “Bohr gave us a visualizable quantum picture, even before the full formalism of wavefunctions and perturbation theory,” says quantum historian Lila Patel. “His law simplified complexity, making quantum phenomena accessible for decades of experimental and theoretical breakthroughs.”
Beyond theoretical insight, Bohr’s Law has profound technological implications.
In modern electronics, understanding electron energy levels informs the design of transistors, lasers, and quantum dots—nanoscale devices where quantum confinement mimics Bohr-level quantization. Optoelectronic applications, such as LED and photodetector materials, rely directly on electron transitions governed by quantized energy states first articulated by Niels Bohr. As research in quantum computing advances, Bohr’s conceptual framework continues to inspire new quantum state manipulations, proving that even simplified models can drive innovation near the limits of physical knowledge.
While today’s quantum physics employs sophisticated tools like Schrödinger’s equation and matrix mechanics, Bohr’s Law endures as a vital teaching tool and conceptual anchor.
It transforms abstract quantum numbers into tangible ideas about atomic structure, helping students and researchers alike grasp the rhythm of electron dynamics. As Niels Bohr himself once said, “Prediction is very difficult, especially about the future—but the past is often clear.” By understanding Bohr’s Law, scientists keep that predictive power alive, turning observation into understanding and mystery into mastery in the quantum realm.
In essence, Bohr’s Law is more than an equation; it is a testament to the power of simplicity in explaining complexity. Its enduring relevance—from explaining star light to shaping the next generation of quantum devices—reveals how foundational theories can transcend their original context, continuing to shape the scientific landscape long after their inception.

Related Post
Rob McCartney KETV Bio Wiki Age Wife Omaha Knee Surgery Salary and Net Worth

Discover Boston’s Cultural Gems Without Spending a Cent
Stacey Baca ABC7 Bio Age Height Family Husband Education Salary and net Worth

Aishiteru Meaning: Unpacking the Soul of Connection in Modern Japanese Expression

