Volume in Chemistry: The Silent Architect of Chemical Systems
Volume in Chemistry: The Silent Architect of Chemical Systems
volume in chemistry is far more than a simple measurement—it is a foundational concept that governs how substances interact, react, and behave in real-world applications. Defined as the three-dimensional space occupied by a substance, volume influences density, concentration, and phase behavior, shaping everything from industrial manufacturing to biological processes. As a central pillar in chemical science, understanding volume requires examining its physical definition, its role in quantifying matter, and its practical impact across diverse fields.
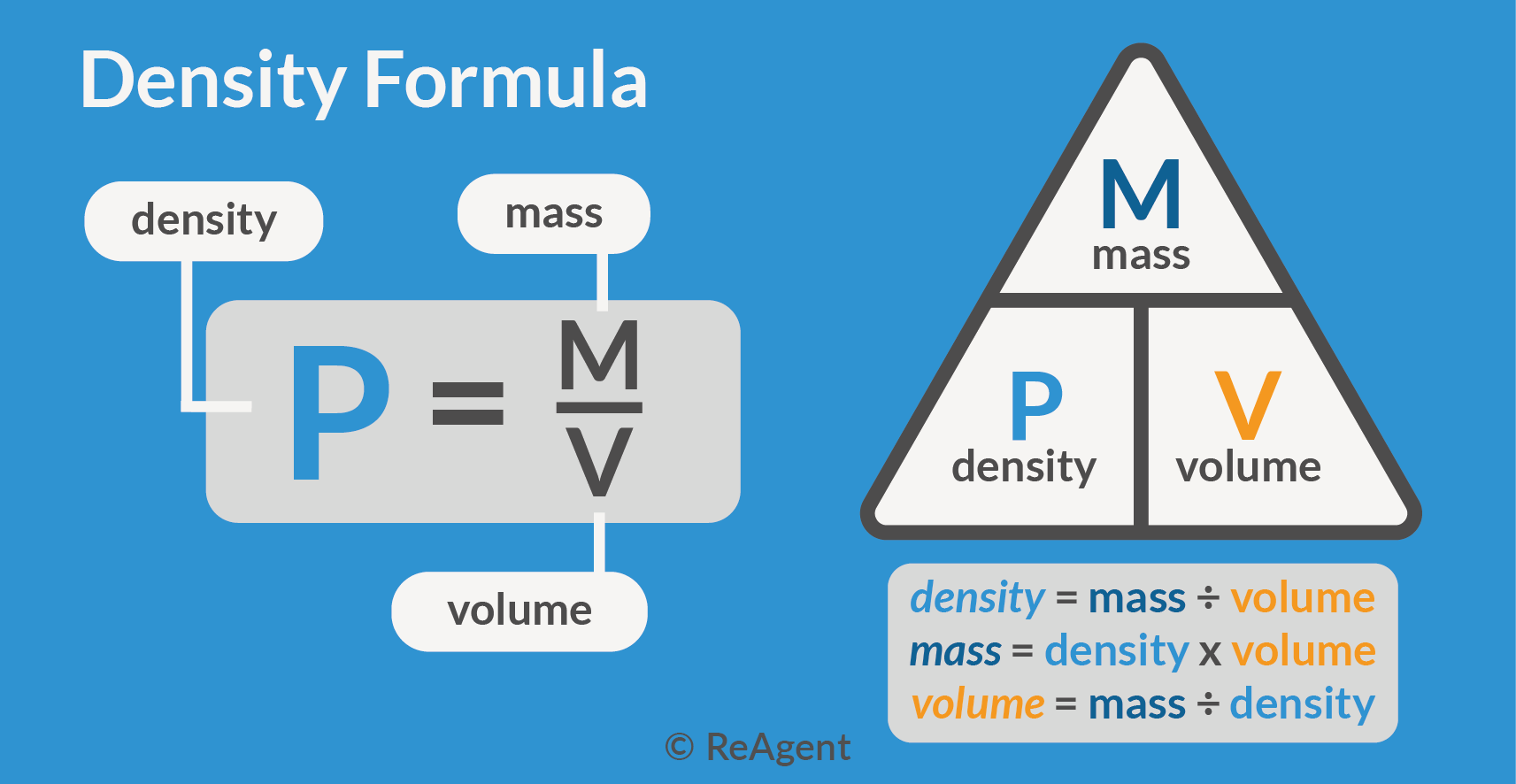
At its core, volume is the capacity of a substance to occupy space, typically measured in liters (L), milliliters (mL), or cubic centimeters (cm³). In chemistry, volume is indispensable for calculating concentration—most notably via molarity, where volume directly determines the ratio of solute to solvent. As chemist David Attenborough once noted, “volume is not just a number; it’s the window through which chemical relationships reveal themselves.” Molarity (M), expressed as moles of solute per liter of solution, hinges on precise volume measurements, enabling accurate reproducibility in lab experiments and industrial processes alike.
Without correct volume data, even the most sophisticated chemical equations lose their predictive power.
Molecular Volume and the Fabric of Substances
Beyond bulk measurements, volume manifests at the molecular scale, where the size and arrangement of atoms define a substance’s physical and chemical properties. The molecular volume—a concept often derived from crystallography and quantum chemistry—describes the spatial extent of individual molecules and their packing efficiency in solids and liquids.This microscopic volume influences solubility, melting points, and reactivity, dictating how molecules interact in solution or during chemical reactions.
“A molecule’s volume reflects its spatial footprint in space,” explains Dr. Lena Müller, a materials physicist at ETH Zurich.
“In dense crystalline structures, for instance, molecules pack tightly, leaving less volume for solvent infiltration—directly affecting reaction kinetics and diffusion rates.” Molecular volume also plays a critical role in polymer science, where the size of monomer units determines polymer chain flexibility and material strength. Thus, volume measurements at the molecular level bridge the gap between atomic structure and macroscopic behavior, enabling scientists to tailor substances for specific applications, from drug delivery systems to high-performance coatings.
Volume and Phase Behavior: From Liquids to Gases
The influence of volume extends to phase transitions—transformations between solid, liquid, and gaseous states—where volume changes dramatically and govern process efficiency.During melting or vaporization, a substance’s volume expands or contracts, a phenomenon rooted in differences in molecular packing. For example, water expands by about 9% when freezing, a rare behavior among liquids that profoundly impacts natural and engineered systems, from winter road salt management to industrial refrigeration cycles.
Understanding volume changes during phase shifts is essential in chemical engineering and thermodynamics.
The ideal gas law—PV = nrt—explicitly ties volume (V) to pressure (P), temperature (T), and the amount of substance (n)—underscoring volume’s pivotal role in predicting gas behavior. “Volumetric changes during phase transitions dictate everything from boiler design to atmospheric modeling,” notes Dr. James Chen, a thermal dynamics specialist.
In real-world applications such as liquefied natural gas (lng) storage, precise volume control prevents pressure surges and ensures safe transport. Thus, volume is not static but a dynamic parameter essential for managing chemical transformations across scientific and industrial frontiers.
Practical Applications and Innovations Driven by Volume
In modern chemistry and engineering, volume measurements underpin countless technological advancements.In pharmaceuticals, accurate volume determination is critical during drug formulation, ensuring correct dosing and stability. In environmental chemistry, knowing the volume of industrial effluents aids in dilution calculations, protecting ecosystems from hazardous concentrations. Fuel efficiency in transportation hinges on volumetric energy density—the volume occupied by a given energy output, a key metric in evaluating alternative fuels and battery technologies.
Recent breakthroughs showcase volume’s expanding role. Supercritical fluids, where liquid and gas phases blur, exploit volume-dependent density shifts for green solvents in extraction processes, reducing reliance on toxic chemicals. Similarly, in microfluidics, engineered channels manipulate minute volumes—down to picoliters—to conduct rapid biochemical analyses, revolutionizing diagnostics and drug discovery.
“We’re now manipulating volume at micro- and nanoscales to unlock unprecedented precision,” remarks Dr. Amira Hassan, leading researcher in lab-on-a-chip technology. These innovations illustrate how volume, once viewed merely as a static quantity, is now a dynamic enabling force in chemical design.
Analyzing volume through both macroscopic and molecular lenses reveals its profound significance in chemistry. From dictating concentration and phase behavior to enabling cutting-edge applications, volume remains a silent yet central architect of chemical systems—guiding reactions, shaping materials, and advancing technology with quiet precision.
Yet, mastering volume demands rigor: measurement errors, phase-dependent variations, and interfacial effects can skew results by significant margins.
Modern laboratories employ advanced tools—such as laser volume measurement and high-resolution imaging—to capture volume with nanoscale accuracy, ensuring data reliability across scales. As chemical science evolves, volume continues to bridge theory and application, proving that in chemistry, even the smallest spaces hold transformative power.



Related Post
Kevin Alejandro Movies Bio Wiki Age Wife Arrow True Blood and Net Worth
Chronological Examination: Investigating the Pivotal Achievements of Drake's Lifetime and Enduring Cultural Impact

Bob Seger’s Health: Vital Updates and Fan Concerns Spark Urgency
Unlock Next-Level Graphics: The Power of DirectX 12 Download for Developers and Gamers

