Uranium-235: The Key to Nuclear Power and Weighted Global Security
Uranium-235: The Key to Nuclear Power and Weighted Global Security
From powering entire nations to shaping the delicate balance of global military power, uranium-235 stands at the heart of modern energy and defense. This rare, fissile isotope drives nuclear reactors that supply nearly 10% of the world’s electricity and fuels sophisticated arsenals worldwide. Its unique nuclear properties—enabling sustained chain reactions—make it both a cornerstone of clean energy innovation and a focal point in nuclear non-proliferation debates.
Understanding uranium-235 means unraveling the dual nature of atomic science: a promise of sustainable power intertwined with complex geopolitical stakes.
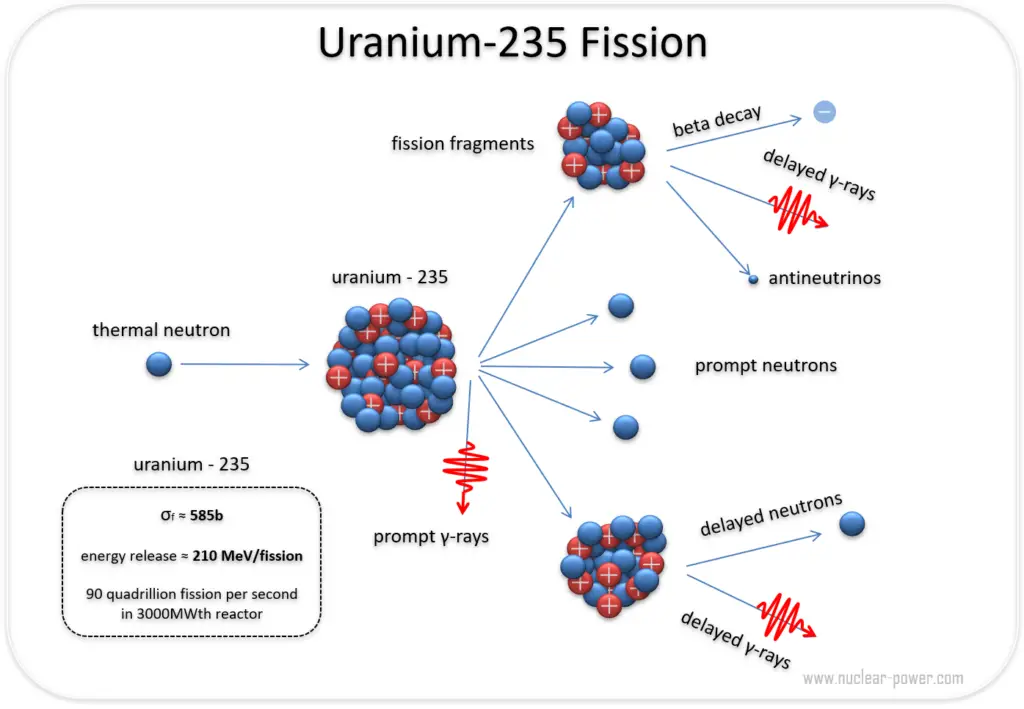
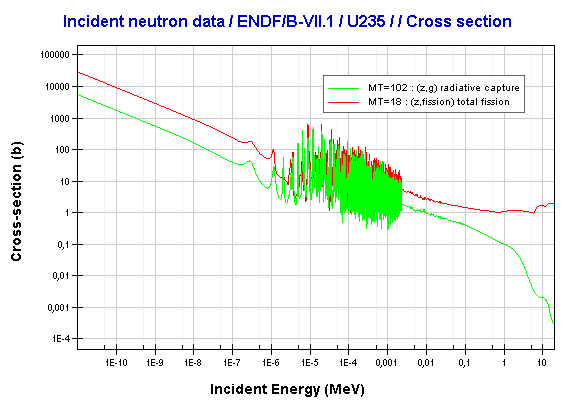
At the core of uranium-235’s utility is its fissile nature—unlike most thorium-232 or natural uranium-238, which resist immediate chain reactions, uranium-235 readily splits when struck by a low-energy neutron. This characteristic allows it to sustain a chain reaction, the fundamental principle behind nuclear reactors and atomic bombs.
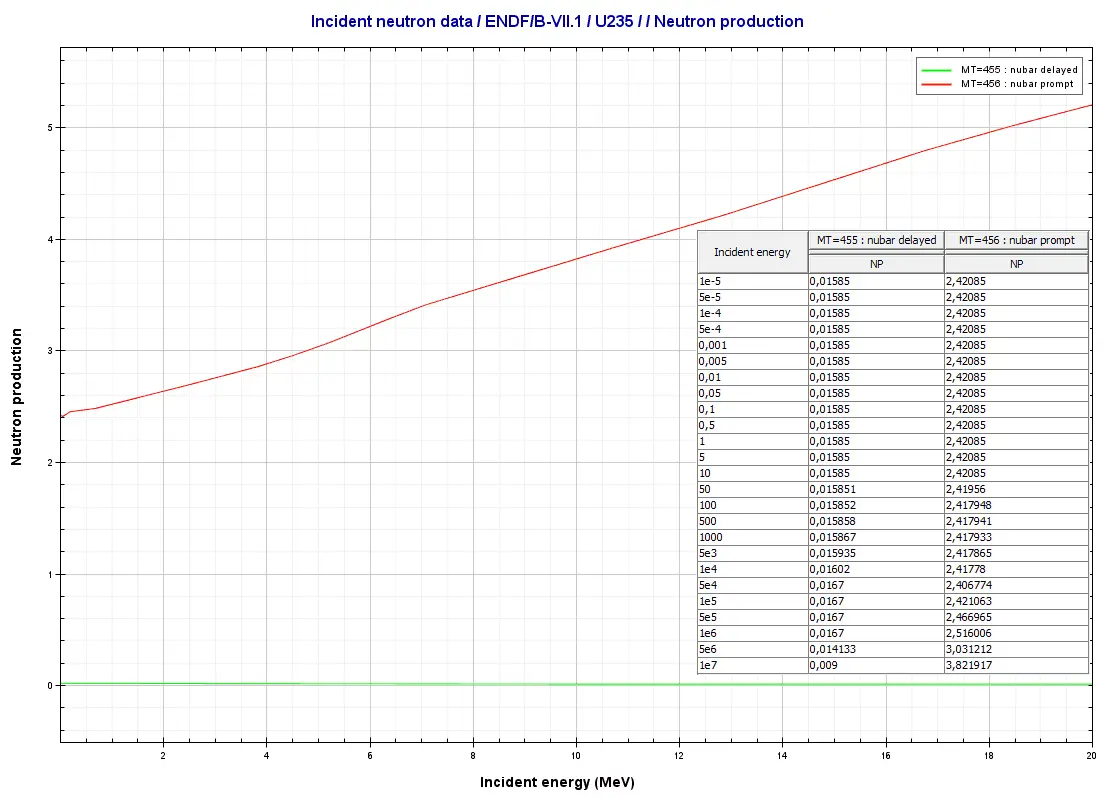
When a single neutron hits a U-235 nucleus, it fractures, releasing an average of 200–240 additional neutrons per fission event. These neutrons can then trigger further splits, multiplying energy output exponentially. “Each fission in a uranium-235 chain release is like a microexplosion—efficient, powerful, and precisely harnessed,” explains Dr.
Elena Markov, a nuclear physicist at the International Atomic Energy Agency. This controlled chain reaction powers commercial reactors, producing heat that drives turbines and generates carbon-free electricity.
Globally, uranium-235 accounts for approximately 0.7% of naturally occurring uranium by mass, making it significantly rarer than uranium-238.
Natural uranium consists of about 99.28% U-238 and 0.72% U-235, meaning vast enrichment processes are required to boost its concentration. In power plants, enriched uranium typically reaches 3–5% U-235—sufficient to maintain criticality without excessive risk. Yet even trace enriched uranium powers satellites, research laboratories, and defense systems, underscoring its strategic value.
The need for enrichment transforms U-235 from a passive component into an active resource, tightly managed through technical and regulatory frameworks.
In civilian energy, uranium-235 has revolutionized electricity generation. Nuclear reactors fueled by enriched uranium now supply about 10% of global power, with countries like France—where nuclear generates over 70% of electricity—relying deeply on this isotope.
The efficiency of uranium-235-based fission allows reactors to operate for years on minimally enriched fuel, with modern designs pushing enrichment levels to 5%
Related Post

PSE PSE Wallet Meets Polygon: A Deep Dive into Scalable Blockchain Fusion
Christopher Nolan Oppenheimer Bio Age Wife Movies and Salary
The Analysis into Our Vincent: Profession and Effect

How Canada’s 2022 Energy Shift Reshaped Rural Economies — A Post-CBC Deep Dive

