Unlocking the Spinal Puzzle: How Dorsal Ramus Units Shape Nerve Function
Unlocking the Spinal Puzzle: How Dorsal Ramus Units Shape Nerve Function
Below the spinal cord’s intricate network lies a critical yet underappreciated structure: the dorsal ramus of spinal nerves—branching off to deliver precise sensory and motor innervation to the back, limbs, and torso. These small but vital nerve branches are essential for pain signaling, muscle control, and reflex coordination, forming a silent workforce beneath the skin’s surface. Understanding their anatomy, pathways, and functional roles reveals the intricate logic behind spinal nerve physiology and its clinical relevance in pain management and neuromuscular disorders.
Anatomy of the Dorsal Ramus: Branch-specific Pathways and Origins
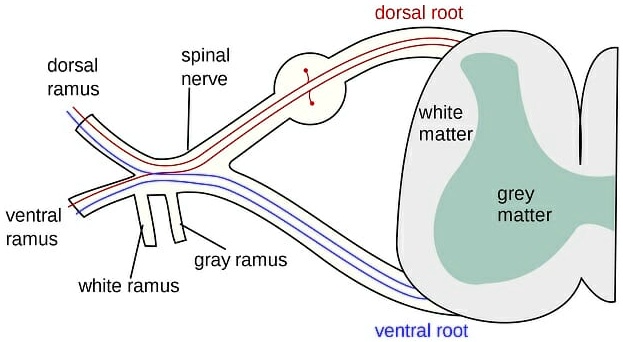
The dorsal ramus arises as a lateral division from each segmental spinal nerve just as it exits the intervertebral foramen. Each dorsal ramus can be subdivided into dorsal (posterior) and ventral (anterior) branches, extending medially toward their target tissues. Originating from specific spinal levels—typically matching that of the parent spinal nerve—the dorsal rami course parallel to the vertebral column before diverging to innervate paraspinal muscles, skin, and deeper structures.- **Dorsal Ramus Pathway:** - Emerges after the spinal nerve exits the spine. - Travels posteriorly along the laminae or spinous process. - Varies in size and direction based on the spinal segment, notably decreasing in length from cervical to lumbar regions.
- Arrives at thin rami that fan outward to connect with back and limb tissues. The dorsal ramus of C1 primarily supplies the cervical region and neighboring tissues, while higher-level rami—such as those from L1—extend to the lumbar back and pelvic girdle. The ventral ramus, though重要于frontal musculature, is distinct in function.
The dorsal branch’s precise targeting underscores a finely tuned anatomical organization designed for segmental control.
Sensory and Motor Contributions: The Dual Role of Dorsal Ramus Fibers
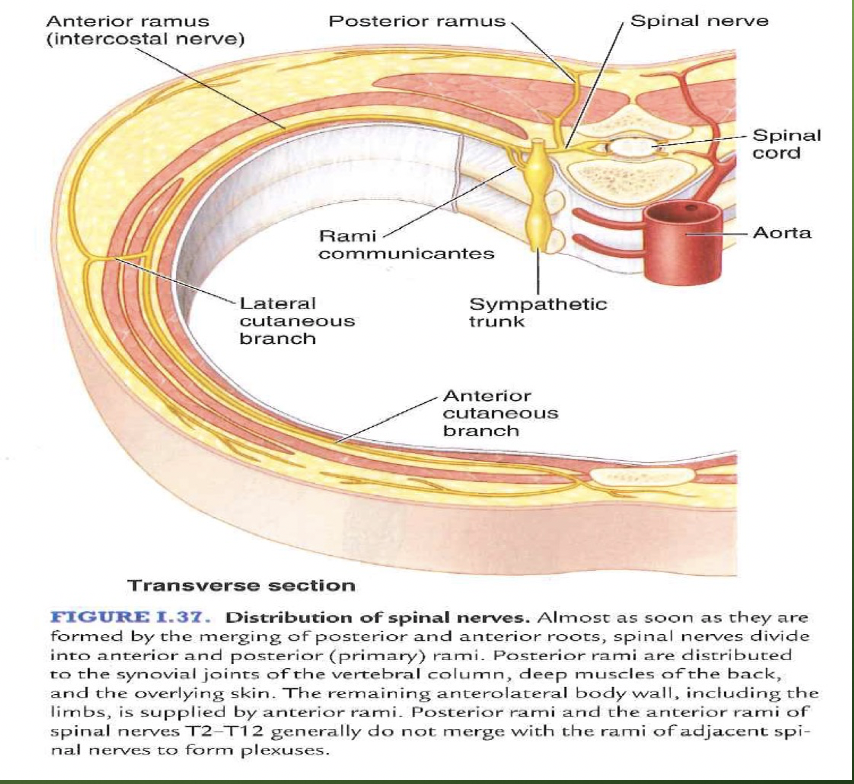
The dorsal ramus plays a dual role in both sensory perception and motor execution, mediating critical communication between the central nervous system and the body’s posterior regions. As afferent fibers, the dorsal rami transmit sensory signals—particularly sharp, localized pain—from the back, skin, and deeper musculoskeletal structures.This sensory input is vital for protective reflexes, posture regulation, and awareness of injury. Concurrently, efferent (motor) fibers from the dorsal ramus drive spinal muscle activation, primarily targeting the paraspinal muscles that stabilize the spine and assist in movement. These motor signals enable fine-tuned adjustments to posture and movement, reinforcing spinal integrity.
- **Sensory Functions:** - Conveys nociceptive and proprioceptive inputs from dorsal and lateral body regions. - Essential for detecting strain, injury, or abnormal load on the spine. - Mediates segmental pain responses, pivotal in spinal pathologies.
- **Motor Functions:** - Innervates interspinous and multifidus muscles. - Coordinates muscle tone to maintain spinal alignment. - Facilitates fine, segmental control of back musculature.
Notably, dorsal ramus innervation does not overlap completely with adjacent dermatomes, creating a somatotopic map that allows precise localization of sensory inputs. This distinct coverage explains why pain in a specific spinal region often traces to a targeted ramus, a concept central to clinical assessment.
The dorsal ramus’s anatomical precision and dual functional capacity highlight its indispensable role in spinal homeostasis.
By integrating sensory feedback with motor output, these nerve branches support both protective reflexes and voluntary movement, making them essential to the spine’s physiological complexity.
Clinical Significance: Dorsal Ramus Involvement in Pain and Injury
Given their focus on the back and deep musculature, dorsal rami are frequent targets in chronic pain syndromes. Conditions such as radiculopathy, facet joint syndrome, and mechanical low back pain often trace their origin to dorsal ramus irritation or damage. Nerve entrapment, post-surgical changes, or degenerative spine disorders can cause hyperactivity or inflammation within these branches, leading to neuropathic pain and muscle spasm.Diagnostic imaging—particularly fluoroscopy-guided targeted injections—leverages anatomical knowledge of dorsal ramus pathways to deliver nerve blocks with high precision. These interventions not only confirm the ramus as a pain source but also offer therapeutic relief by interrupting pain signaling without systemic side effects. “Understanding dorsal ramus anatomy is key for achieving effective neuromodulation,” notes Dr.
Elena Torres, a pain management specialist. “Accurate localization of the affected branch transforms diagnostic uncertainty into actionable treatment.” Ligamentous injuries, spinal stenosis, and disc herniation frequently impinge upon dorsal rami, disrupting their sensory-motor balance. Patients may experience localized back pain refractory to conventional therapy, emphasizing the need for clinicians to recognize ramus involvement.
Dorsal ramus targeting represents a cornerstone in modern interventional pain strategies, merging anatomical insight with clinical practice to restore function and alleviate suffering.
The Enduring Relevance of Dorsal Ramus Physiology
The dorsal ramus of spinal nerves stands as a masterclass in neural design—segmented, segment-specific, and exquisitely functional. From their emergence just beyond the spinal cord to their dual roles in sensation and movement, these nerve branches exemplify the spine’s sophisticated control mechanisms. Their clinical importance continues to grow as diagnostic and interventional techniques advance, offering new pathways for pain relief and mobility restoration.Recognizing the dorsal rami’s contributions transforms our approach to back health, elevating both diagnosis and therapy in spinal care.


Related Post

Unlocking the Potential of Stw VCS: The Comprehensive Guide That Transforms Development Workflows

Joe Bonamassa’s Family Reveals the Human Heart Behind the Blues Legend’s Legacy