Unlocking the Secrets of Change: How the Derivative of an Inverse Function Shapes Mathematics and Engineering
Unlocking the Secrets of Change: How the Derivative of an Inverse Function Shapes Mathematics and Engineering
When exploring the hidden connections within calculus, few tools are as powerful—and underutilized—as the derivative of an inverse function. This concept bridges the familiar worlds of functions and their inverses, revealing dynamic insights into rates of change, optimization, and system behavior. From restoring lost variables in cryptography to modeling population dynamics, the derivative of an inverse function is not just a theoretical curiosity—it’s a practical engine driving innovation across science and engineering.
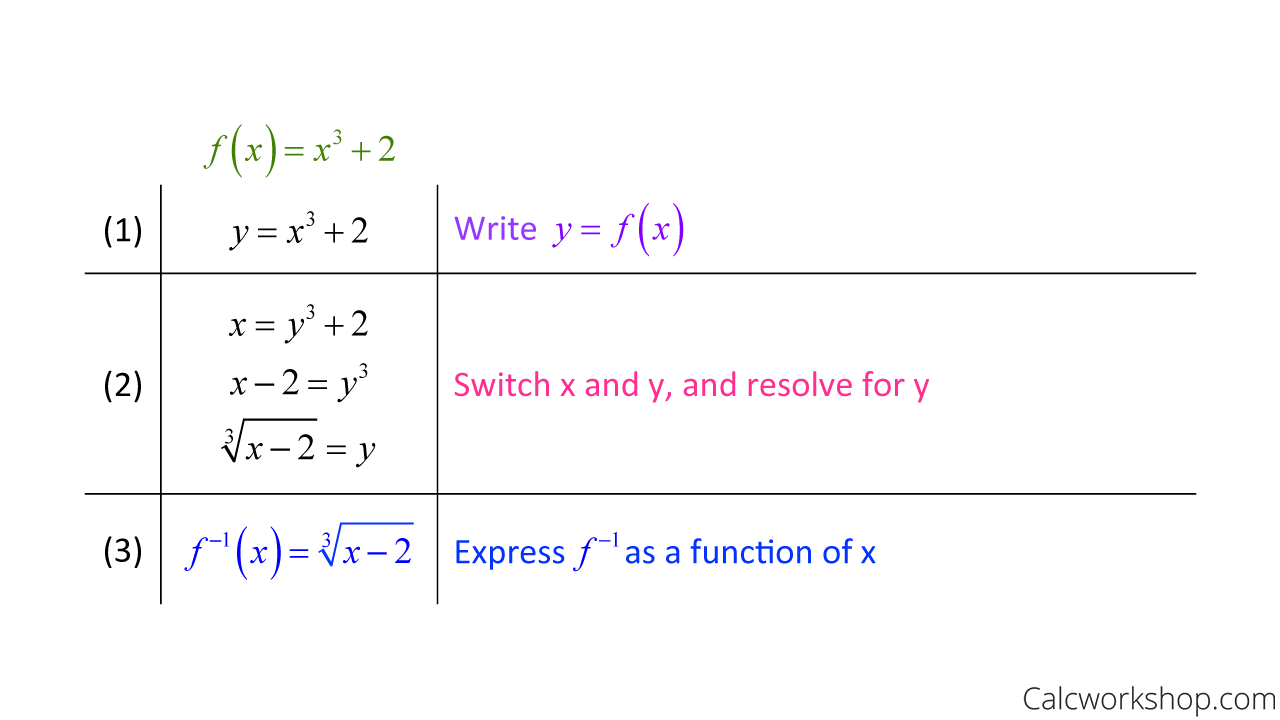
At its core, the derivative of an inverse function arises when one function “undoes” another. If a bijective function $ f $ maps inputs $ x $ to outputs $ y = f(x) $, then its inverse $ f^{-1} $ reverses this mapping: $ x = f^{-1}(y) $. But what happens when we seek how $ f^{-1} $ changes as $ y $ evolves?
This is precisely where the derivative of the inverse steps in—a function defined by $ (f^{-1})'(y) = \frac{1}{f'(f^{-1}(y))} $, provided $ f $ is differentiable and strictly monotonic. This elegant formula unlocks instantaneous rates of change for inverse relationships, transforming abstract ideas into calculable real-world tools.
From Function to Rate: The Formula That Transforms Calculation
The formula for the derivative of an inverse function—$ (f^{-1})'(y) = \frac{1}{f'(f^{-1}(y))} $—is deceptively simple, yet profound in scope. Let us unpack its components: - $ f $ is a differentiable and strictly monotonic function (ensuring a unique inverse), - $ f^{-1} $ is its inverse, solving for $ x $ in $ y = f(x) $, - The derivative of the inverse at point $ y $ depends on both how fast $ f $ is changing at $ x = f^{-1}(y) $, and how steeply $ f^{-1} $ steeply inverts that change.This interdependence reveals a key insight: even negligible changes in the output of $ f $ translate into abrupt shifts in the input of $ f^{-1} $, scaled by the rate at which $ f $ grows. For example, in physics, if $ f(t) $ describes displacement over time, then $ f^{-1}(s) $ yields time for a given distance—its derivative reveals how quickly time advances with position, a crucial factor in designing responsive systems. Why This Formula Matters Beyond textbooks: - In optimization, it enables solving for stationary points of composite inverses efficiently.
- In machine learning, inverse derivatives inform gradient updates in model parameter tuning. - In control theory, they stabilize feedback loops where outputs must be rapidly inverted.
To grasp the power of this concept, consider a concrete example: let $ f(x) = e^x $, a strictly increasing, differentiable function with derivative $ f'(x) = e^x $.
Its inverse is $ f^{-1}(y) = \ln(y) $. Applying the inverse derivative rule: (ln(y))' = 1 / f'(ln(y)) = 1 / e^{ln(y)} = 1 / y. Thus, the derivative of the natural logarithm is simply $ 1/y $—a result students learn early, but often underappreciate in real-world application.
This formula didn’t compute instantaneous growth rate; it revealed it with elegance, turning a limit into a tool.
Applications That Shape Modern Technology and Science
The derivative of an inverse function permeates diverse fields, often behind the scenes. In cryptography, decryption depends on inverting encoded data; knowing $ (f^{-1})' $ helps analyze resistance to differential attacks by modeling how small input perturbations propagate through encryption layers.In control systems, feedback controllers use inverse mappings to predict system responses—whether adjusting temperature in a reactor or steering an autonomous vehicle—where rapid inversion ensures real-time corrections. In optimization, consider a constrained minimization problem requiring inversion. For instance, if a cost function $ y = f(x) $ defines constraints, inverting $ f $ to find feasible $ x $ values efficiently often relies on understanding derivative behavior.
The rule $ (f^{-1})'(y) $ quantifies sensitivity: small changes in $ y $—say, resource targets—induce precise shifts in $ x $, vital for precision in engineering designs. In population modeling, inverse functions map ordination metrics (e.g., survival rates) back to time projections. Its derivative reveals how sensitive future estimates are to current data points—critical for policy planning under uncertainty.
Brilliance in the Derivative: - Energy systems use inverse derivatives to optimize power flow, adjusting voltage/current mappings dynamically. - Signal processing leverages inverse rate relationships to filter noise and reconstruct original data streams efficiently. - Finance applies these insights in option pricing models, where inverse changes in volatility dictate risk exposure.
What all these applications share is a reliance on rapid, accurate inversion of change—exactly what the derivative of an inverse function provides. It transforms qualitative understanding into quantitative precision, enabling software, algorithms, and hardware to respond with agility.
The Mathematical Beauty and Practical Precision
The elegance of $ (f^{-1})' = 1/f'(f^{-1}(y)) $ lies not only in its form but in its universality.It applies across any smooth, invertible function, from elementary curves to complex multivariate systems encoded in partial derivatives. Calculating inverse rates—whether through symbolic derivation or numerical approximation—unlocks sensitivity analysis critical for robust design. Engineers use this to stress-test prototypes; economists use it to model elasticity; physicists use it to track quantum state transitions.
Mathematicians recognize this as a gateway concept: once internalized, it deepens comprehension of function inversion and chain rule applications. For students, mastering this tool shifts problem-solving from brute computation to insightful interpretation, where every derivative tells a story of transformation.
Mastering the Derivative of Inverses: A Skill for the Future
Beyond textbook derivatives, the derivative of an inverse function is a cornerstone of applied mathematics.As artificial intelligence, robotics, and sustainable engineering advance, demands for systems that learn, adapt, and optimize grow exponentially. This calculus concept—small in appearance, vast in reach—empowers such innovation. It enables engineers to build smarter algorithms, scientists to decode complex networks, and decision-makers to anticipate system behaviors with confidence.
In a world defined by speed, accuracy, and interconnectivity, the derivative of an inverse function stands as a vital lever. It is not merely a formula to memorize, but a lens through which change becomes clear, control becomes precise, and possibility becomes measurable.
To those navigating STEM disciplines, embracing this concept is to equip oneself with a silent but powerful tool—one that turns abstract inverse relationships into tangible, actionable insight.
In the evolving landscape of data and design, the derivative of an inverse function doesn’t just describe change; it accelerates progress.
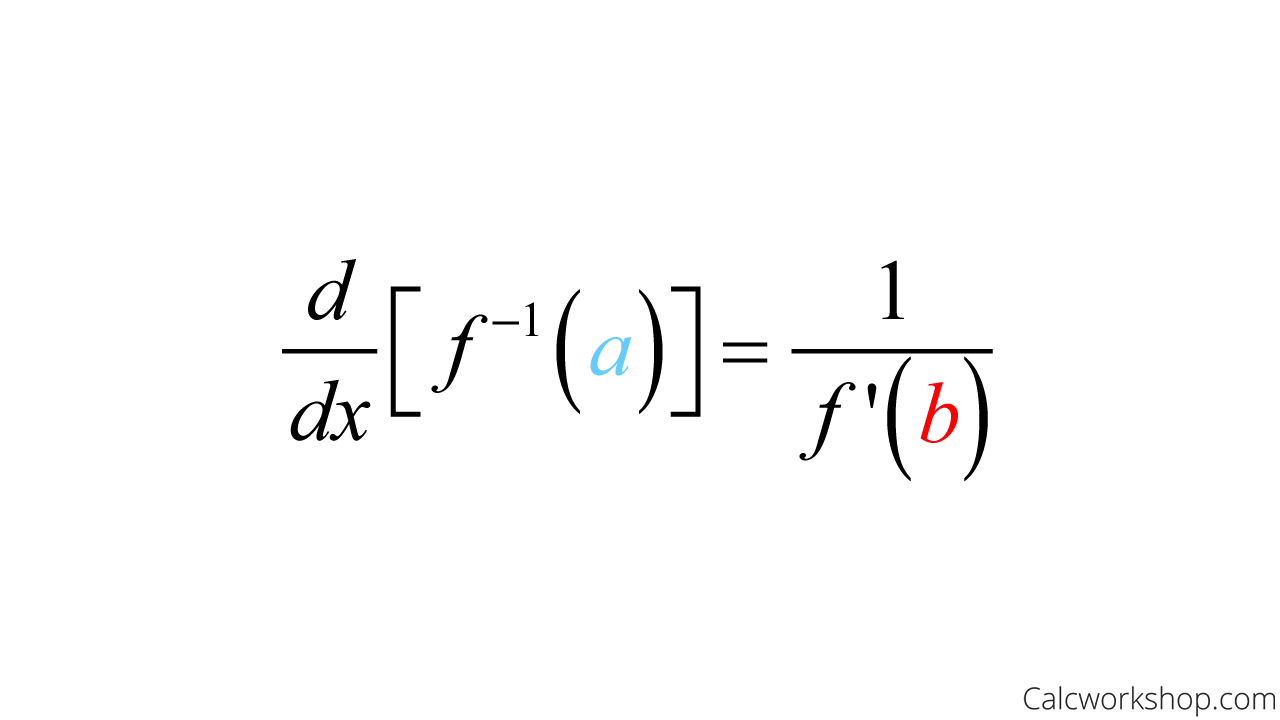
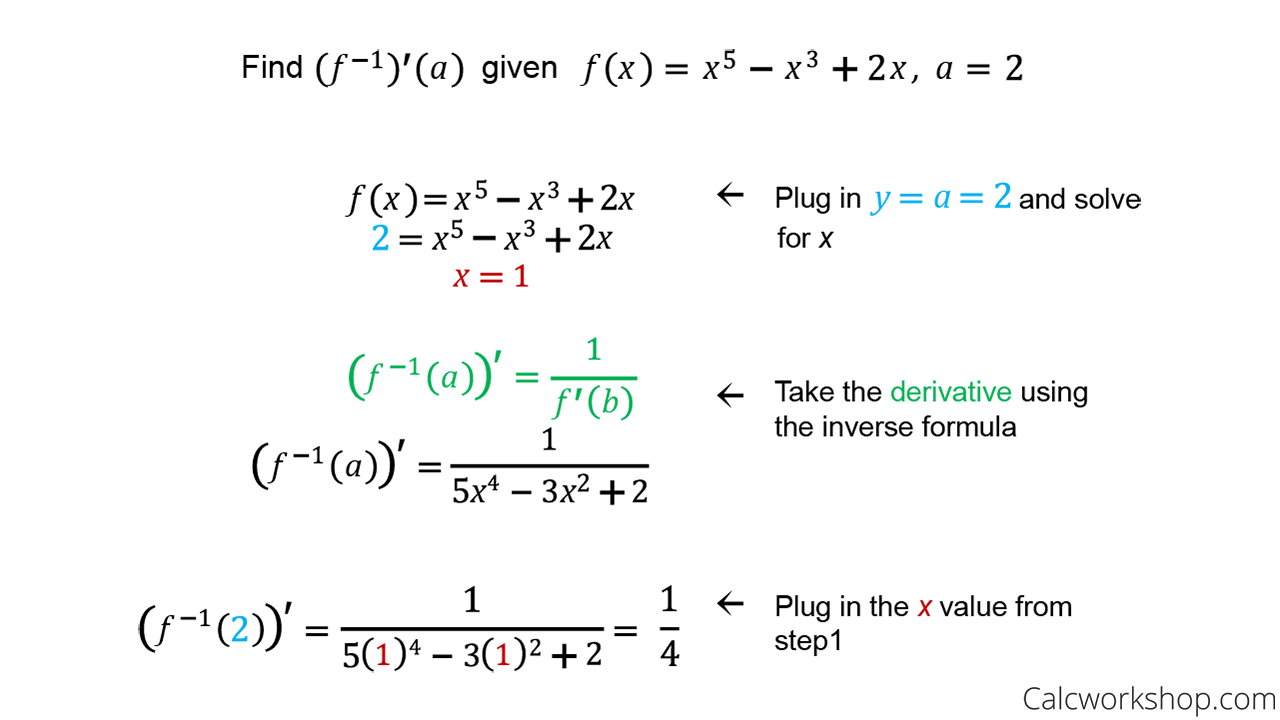
Related Post
Capital One Shopping What Is It and How Does It Transform Your Fall Mailpiece Experience

The Rise and Legacy of Abel Hernandez: From Wrestling Arena to Boxing Icon

From Power Ranger Stardom to Flourishing Resilience: How David Yost Turned Iconic Role Into a Lifelong Journey

WTF Games: Where Absurd Humor Collides with Gameplay Genius

