Unlocking Pressure’s Shape: How Boyle’s Law Graph Reveals the Pulse of Gas Behavior
Unlocking Pressure’s Shape: How Boyle’s Law Graph Reveals the Pulse of Gas Behavior
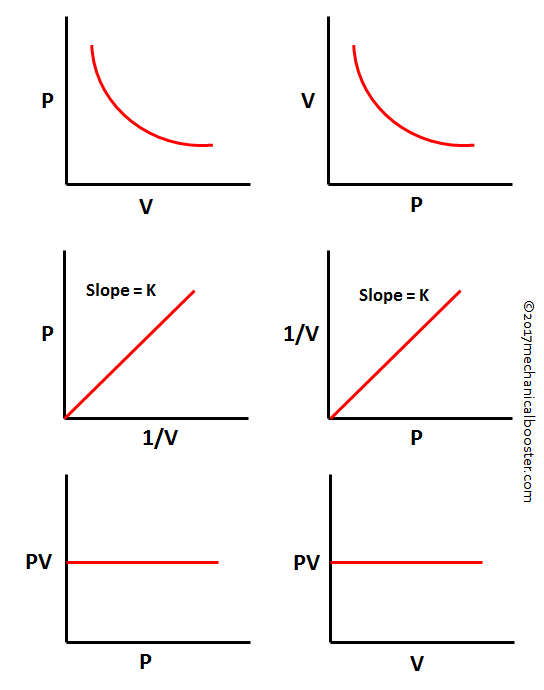
When gases bend under pressure like invisible springs under stress, their response traces a silent geometry—captured poignantly in the Boyle’s Law Graph. This foundational principle of thermodynamics, stating that at constant temperature, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure, unfolds not just in equations but in striking visual data. The graph reveals a hyperbola, a curve that not only debates tradition physics but also shapes modern engineering, medical devices, and climate science.
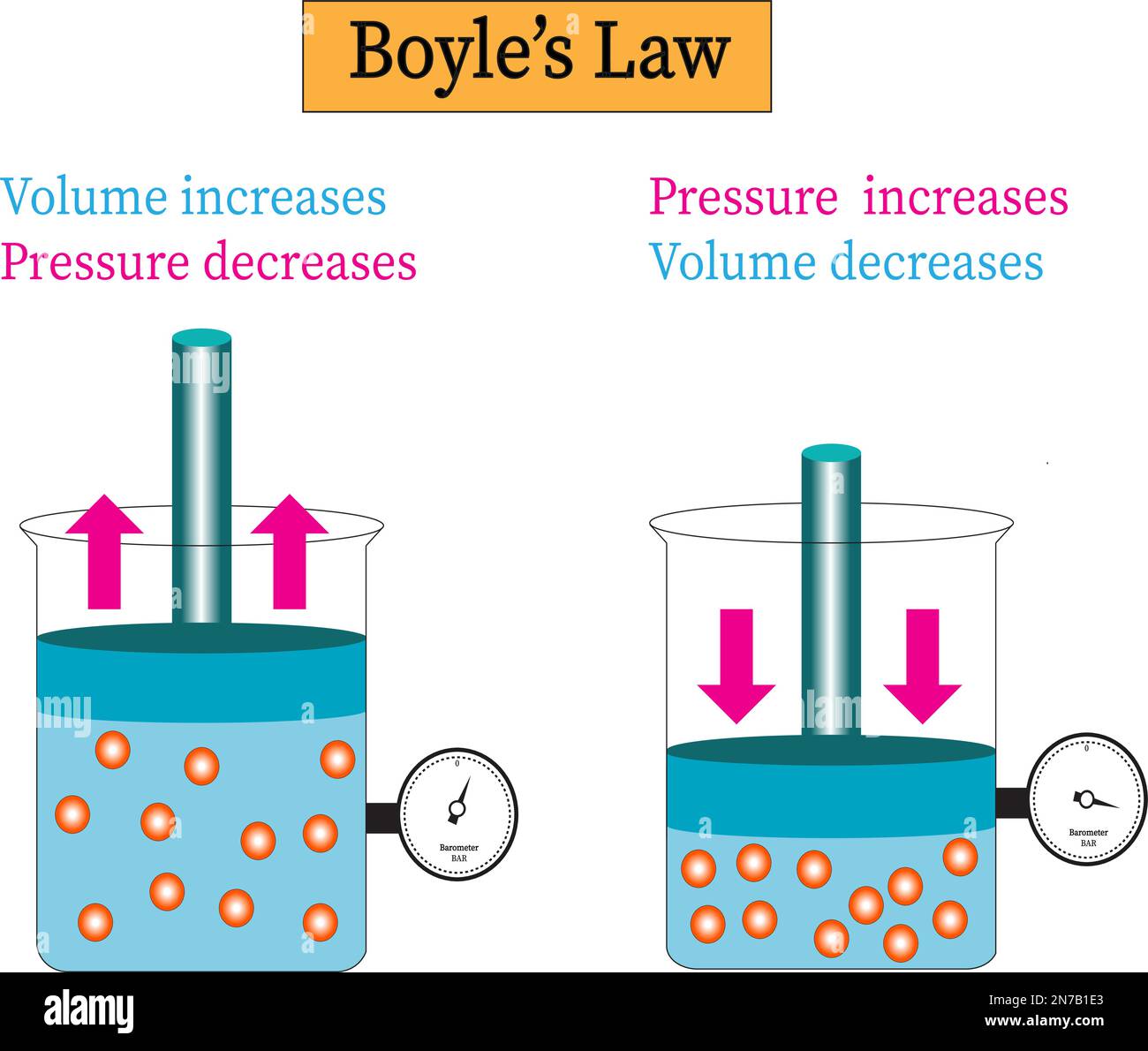
Understanding this relationship transforms abstract chemical laws into tangible, actionable insights. The Boyle’s Law Graph charts a precise inverse relationship: as pressure increases, volume decreases—and vice versa—without any change in temperature. Mathematically, it follows \( P \times V = k \), where \( k \) is a constant.
At first glance, the resulting curve resembles a symmetrical inversion, but its subtle arcs tell a deeper story about energy and molecular motion. “The graph reminds us that gas particles are not passive; they compress and expand in response to forces, weaving a physical narrative of balance and compromise,” observes Dr. Elena Marquez, a physicist specializing in gas dynamics.
Historically derived from experiments by Robert Boyle in the 17th century, the law was initially derived from observations using a J-shaped glass tube half-filled with mercury. By trapping a fixed quantity of air and measuring pressure and volume shifts, Boyle documented how pressure rose sharply as volume shrank—an early victory for empirical science. Today’s Boyle’s Law Graph retains that core truth but amplifies it with digital precision.
Modern iterations use calibrated sensors and real-time plotting, allowing researchers to visualize dynamic molecular interactions under controlled conditions.
At low pressures, gas molecules move freely, spacing far apart; increasing pressure forces them closer, reducing available volume. This compression illustrates constrained kinetic energy—molecules collide more frequently within a smaller space, elevating pressure.
Conversely, relaxing pressure permits expansion, lowering collision frequency and pressure. The hyperbolic curve reflects this extremity, bounded by asymptotic axes but never reaching infinite values—no gas occupies zero volume nor pressure vanishes without molecular motion ceasing. This mathematical elegance underpins countless applications.
The Boyle’s Law Graph is more than a textbook illustration—it is a functional blueprint.
In medical autoclaves, for instance, sterilization depends on steam at high pressure: compressing air in sealed chambers drives temperature rises essential for killing pathogens. Similarly, bicycle pumps manipulate the law daily; squeezing the handle compresses air (falling volume, rising pressure), which the tire resists—each pump cycle a practical dance with gas laws. In diving, the graph explains the danger of narcosis and decompression sickness: rapid deep descents compress inert gases in body tissues, altering solubility and risking bubble formation.
Beneath the graph’s smooth curve lies a critical assumption: constant temperature.
Real-world deviations occur when energy exchanges disrupt equilibrium, turning Boyle’s Law into part of a broader thermodynamic system. Yet within its ideal range, the inverse relationship holds with remarkable consistency. Engineers rely on Boyle’s Law to design pressure vessels, HVAC systems, and even spacewalk safety equipment.
Researchers use calibrated Boyle gas curves to predict behavior in chemical reactors, ensuring reactions proceed safely amid pressure shifts.
Interpreting the graph demands attention to units and scale. Plotting volume against pressure on a logarithmic scale, for example, transforms the hyperbola into a straight line—simplifying calculations while preserving accuracy. “This linear transformation reveals the elegant simplicity underlying the curve’s complexity,” explains Dr.
Marquez. It also enables quick validation of experimental data, confirming whether observed gas behavior conforms to theoretical predictions.
Industries harnessing this principle range from healthcare to aerospace. In portable oxygen concentrators, precise pressure control ensures therapeutic gas delivery.
Aircraft pressurization systems use Boyle’s principles to maintain cabin pressure, balancing passenger comfort against structural limits. Even weather balloons rely on predictable volume changes with altitude—a direct consequence of the gas law, where expanding altitude means falling pressure and expanding volume, risking explosion if not managed.
While Boyle’s Law explains ideal gases, real-world applications demand adjustments. Presence of moisture, non-ideal gas behavior at high pressures, and molecular speeds justify extensions beyond Boyle alone.
Yet the graph remains the cornerstone of gas law pedagogy and practice—a bridge between classical physics and modern innovation. “It’s not just a graph,” marries the physics community—it’s a lens through which we decode the invisible forces shaping the air we breathe, the machines we trust, and the environments we explore.
In the hands of scientists, engineers, and educators, the Boyle’s Law Graph evolves from a static curve into a dynamic tool of discovery. Its clean lines and precise mathematics offer more than clarity—they open doors to safer technologies, smarter designs, and deeper understanding of the elemental fabric of our atmosphere.As research advances and applications expand, this timeless relationship continues to illuminate the invisible dance of gas particles, one expansion and compression at a time. This silent, graphical story of pressure and volume is not just part of chemistry’s past—it defines the future of gas science.


Related Post
Natalie Espinoza Age Wiki Net worth Bio Height Boyfriend
Huge Savings Play in the Outdoors: How a Small, Budget-Friendly Extension Cord Drives the Best Results

Cristian Calderón: Architect of Judicial Integrity in a Turbulent Era
School Of Chaos: Unleash Functionality and Fun Through Interactive Mod Menus

