Unlocking Molecular Secrets: The HCN Lewis Structure and Its Pivotal Role in Chemistry
Unlocking Molecular Secrets: The HCN Lewis Structure and Its Pivotal Role in Chemistry
At the heart of covalent bonding lies a deceptively simple yet profoundly impactful molecule: hydrogen cyanide (HCN). With its linear structure and polar character, HCN serves as a cornerstone in organic synthesis, industrial chemistry, and even pharmaceuticals. Central to understanding its chemical behavior is the HCN Lewis structure, a graphical representation that reveals electron distribution and bonding patterns.
This structure not only explains HCN’s stability and reactivity but also underpins its role in synthesizing complex compounds, from amino acids to nylon. By decoding this molecular architecture, scientists gain insight into the forces shaping chemical interactions at the atomic level.
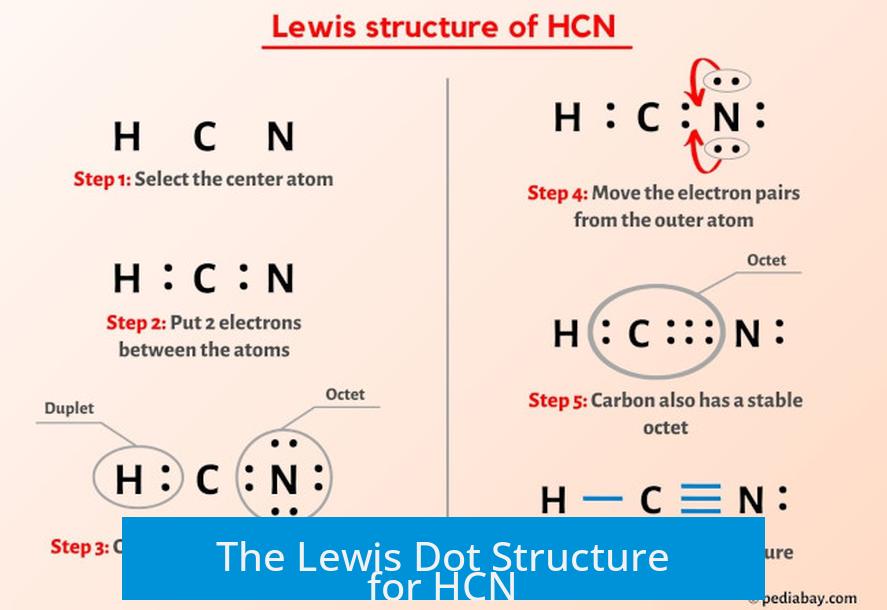
The Lewis structure of hydrogen cyanide—H–C≡N—epitomizes sp hybridization, where a carbon atom forms three high-energy σ bonds using one 2s and two 2p orbitals. This alternating triple bond between carbon and nitrogen gives HCN its remarkable stability despite the molecule’s toxicity.
The triple bond consists of one sigma and two pi bonds, forming a robust covalent linkage resistant to most common chemical reactions unless activated under specific conditions. "Understanding the Lewis structure provides the first rung on the ladder of reactivity," notes Dr. Elena Torres, a physical chemist specializing in nitrogen-containing compounds.
The Atomic Architecture: How HCN Bonds Are Built The hydrogen cyanide molecule features a central carbon atom forming a triple bond with nitrogen and a single bond with hydrogen.
This structure arises from sp hybridization, where one steeped orbital combines with two shallow orbitals to allow linear geometry—bond angles of 180 degrees. The triple bond’s composition—comprising one sigma and two pi bonds—confers both strength and reactivity. While sigma bonds ensure structural integrity, pi bonds create electron-rich regions prone to nucleophilic attack.
- **Oxidation State & Electronegativity Dynamics**: In HCN, carbon carries a +1 formal charge due to electron withdrawal, while nitrogen holds a -1, created by its higher electronegativity (3.04 vs. 2.20 for carbon). The dipole moment, pointing from C– toward N, enhances the molecule’s polarity—critical for solubility and intermolecular interactions.
This polarity facilitates HCN’s use as a protic solvent intermediate and supports its role in catalytic reactions. - **Resonance and Electron Delocalization**: Though the Lewis structure is best shown as H–C≡N, resonance effects subtly influence electron distribution. The triple bond’s fixed position limits delocalization, but adjacent lone pairs on nitrogen contribute to weak resonance stabilization, slightly lowering activation energies for reactions.
This balance of stability and reactivity defines HCN’s chemical versatility.
Bonds Beyond the Lewis Model: The Physical Reality While the Lewis structure captures the essence of electron sharing, HCN’s physical behavior demands deeper analysis. The triple bond, spanning just 1.09 Å, reflects bond strength intermediate between single (1.09 Å) and short triple bonds (~1.19 Å), yet with distinct resonance stabilization absent in pure alkynes.
This unique bond length results from sp hybridization’s orbital overlap efficiency, combining directional precision with partial back-donation. Infrared spectroscopy confirms the ACN triple bond’s signature at ~2250 cm⁻¹, indicative of strong C≡N stretching. Such spectral data align with Lewis structure predictions, reinforcing its predictive power.
Yet real-world conditions—temperature, solvent polarity, catalyst presence—can strained the model. For instance, strong acids protonate HCN to form the nitrilium ion (H₂C≡N⁺), altering reactivity pathways beyond standard Lewis assumptions. “The Lewis structure is a starting point, not an endpoint,” says Dr.
James Lin, a spectroscopy expert. “It sets the stage, but quantum mechanics and experimental data complete the picture.”
Reactivity: From Theory to Application HCN’s chemical significance stems from its reactive dinucleophilic profile. The electrophilic carbon in the triple bond attracts nucleophiles—critical in nucleophilic addition reactions.
For example, in amino nitrile synthesis, HCN reacts with amines to form intermediates like methyl cyanoacetate, precursors to amino acids. “The triple bond acts as a reactive playground,” explains Dr. Lin: “its pi electrons are poised to engage broad بشكل, opening doors to countless synthetic routes.” Industrial applications highlight HCN’s utility.
In polymer chemistry, acetonitrile—derived from HCN—serves as a solvent and monomer in high-performance polymers like polyacrylonitrile. In pharmaceuticals, nitriles derived from HCN appear in analgesics and antibiotics, showcasing the molecule’s medicinal relevance. Yet, caution is warranted: despite synthetic power, HCN is a potent cyanide toxin, underscoring the dual nature of chemical insight—enabling and endangering.
Why the HCN Lewis Structure Matters in Modern Chemistry
The HCN Lewis structure is more than a classroom drawing—it is a foundational tool enabling precise molecular design. From predicting reaction mechanisms to guiding catalyst development, this structure bridges atomic behavior and macroscopic function. Its hybridized carbon and polar covalent bond system reveal why HCN remains indispensable in labs and factories worldwide.
By mastering this simple yet profound blueprint, chemists harness the full spectrum of nitrogen and carbon reactivity, pushing the boundaries of material science, medicine, and sustainable chemistry. In a world driven by molecular engineering, understanding HCN through its Lewis framework ensures both innovation and responsibility.



Related Post
Legal Aid Danville VA: Your Gateway to Justice When Money Doesn’t Stop You

Sam Saboura: Unveiling the Life Story Behind Age, Height, Family, and Legacy
WWE Superstars Dont Want To Work With Charlotte Flair Now

Icelandic Vodka Cocktails: Refreshing Mixes That Ignite the Palate

