The Gravitational Constant G: The Cosmic Pacemaker That Binds The Universe
The Gravitational Constant G: The Cosmic Pacemaker That Binds The Universe
The gravitational constant, symbolized as G, is the universe’s quiet master architect—responsible for the invisible force that binds stars, planets, and galaxies together. With a measured value of approximately 6.674 × 10⁻¹¹ m³ kg⁻¹ s⁻², G lies at the heart of Newton’s law of universal gravitation, governing celestial motion with exquisite precision. Though imperceptible in everyday life, this tiny constant orchestrates cosmic choreography on an unimaginable scale.
This enigmatic number determines how two masses attract one another across the emptiness of space: the stronger G, the more powerful the gravitational pull. Yet despite decades of measurement efforts, G remains one of the most precisely scrutinized constants in physics—its exact value essential for modeling everything from satellite trajectories to the expansion of the universe.
The History and Discovery of G: From Theory to Measurement
The conceptual foundation of gravitational force was laid by Sir Isaac Newton in 1687 with his formulation of the law of universal gravitation.However, the actual determination of G as a measurable constant came over 150 years later, when British physicist Henry Cavendish performed his famous torsion balance experiment in 1798. By measuring the minute gravitational attraction between lead spheres, Cavendish yielded the first reliable estimate of G—approximately 6.74 × 10⁻¹¹, remarkably close to today’s accepted value. > “The value we now accept for G is the result of centuries of incremental precision,” says Dr.
Elena Varga, a physicist specializing in classical gravity at the Max Planck Institute. “Each experimental refinement sharpens our understanding of how matter interacts at large scales.” The Cavendish experiment remains a cornerstone: two Stevenson — or Cavendish-type — balances use fine metal rods suspended by thin wires, detecting minuscule forces as masses draw each other. Since then, technological advances—laser interferometry, vacuum environments, and ultra-stable clocks—have reduced measurement uncertainties, transforming G from a theoretical curiosity into a cornerstone of observational astrophysics.
G’s Role in Modern Physics and Space Technology
In contemporary science, G is indispensable for astrophysical calculations. It enables scientists to compute planetary orbits with precision, ensuring accurate satellite navigation, planetary mission planning, and gravitational wave detection. Without a precise G, predictions of celestial mechanics break down, endangering missions like the James Webb Space Telescope or interplanetary rovers.Despite its foundational importance, G stands apart: unlike Newton’s gravitational constant, G is neither dimensionless nor derived from first principles. Its measured value contains persistent, unexplained discrepancies across experiments—small but statistically significant variations reported in recent studies. These anomalies spark ongoing debate: “Why does G not remain perfectly consistent when measured by different methods?” wonders Dr.
Samuel Kline, a theoretical physicist at MIT. “Is it a limitation of our instruments—or does it hint at deeper physics beyond the standard model?” In practical terms, G is non-negotiable for space agencies. For instance, when designing the Mars Perseverance rover’s descent or aligning solar probe trajectories, engineers rely on G’s exact value to calculate gravitational influences across vast distances.
Every centimeter in mission planning hinges on its measured magnitude.
Unit of Gravitational Constant G: Definition and Conversion
The gravitational constant G operates in the SI system as a dimensionful unit: culminating in m³ kg⁻¹ s⁻², reflecting its role as a proportionality factor linking mass (kg), distance (m), and time (s) in Newton’s law. Its value translates physically as: one Newton per square meter per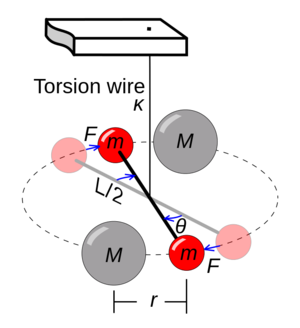



Related Post

HTTPS Security: Strengthening Public Safety with The 911 Security Org E-Bulletin

Unleashing Creativity: The Monumental Rise of Ficsh Roblox

Utah Jazz vs Timberwolves: A Clash Rooted in Rivalry, Resistance, and Relentless Back-and-Forth

