The Complete Blueprint of NHL Hockey: Rules, History, and Game Dynamics
The Complete Blueprint of NHL Hockey: Rules, History, and Game Dynamics
Absolute mastery of NHL hockey demands more than just watching frozen 토너먄 game—understanding its intricate structure, evolving traditions, and statistical heartbeat is essential for fans and analysts alike. The National Hockey League, founded in 1917, stands as the premier professional ice hockey league globally, blending centuries-old European hockey traditions with North America’s fast-paced, high-scoring modern style. Every aspect—from roster rules and scoring mechanics to iconic stadiums and legendary rivalries—shapes the league’s identity and ongoing transformation.
At the heart of the NHL’s appeal is its rich historical evolution. Originating as a merger of teams from Ottawa and Montreal to resolve disputes over player contracts, the league has grown from a regional Canadian circuit into a 32-team North American powerhouse. Over the decades, pivotal shifts include the 1979 expansion that welcomed new markets like Los Angeles and the 1990s introduction of European stars who redefined forward play and defensive schemes.
“The NHL’s transformation from a regional league to a global brand is one of the most dramatic sports evolutions of the 20th century,” notes a 2021 NHL commissioned history. “It reflects broader cultural and commercial trends far beyond hockey.”
Central to the game’s flow are its fundamental rules and scoring systems—mechanics that define both strategy and spectacle. A standard NHL game consists of three 20-minute periods, with overtime and shootouts determining winners in tie situations.
Unlike earlier formats, a goal counts as one point, awarded to the first player to deflect the puck past the goalie into the net. The awarding of penalties—minor, major, and short—regulates integrity, with accumulated time costing teams shorthanded and creating strategic opportunities for the opposition. “Penalties aren’t just disruptions—they’re turning points,” explains NHL rulebook historian David Rivett.
“They test coaching discipline and tactical flexibility under pressure.”
The Evolution of NHL Routes to the Zone
From Simple Passes to Strategic Power Plays
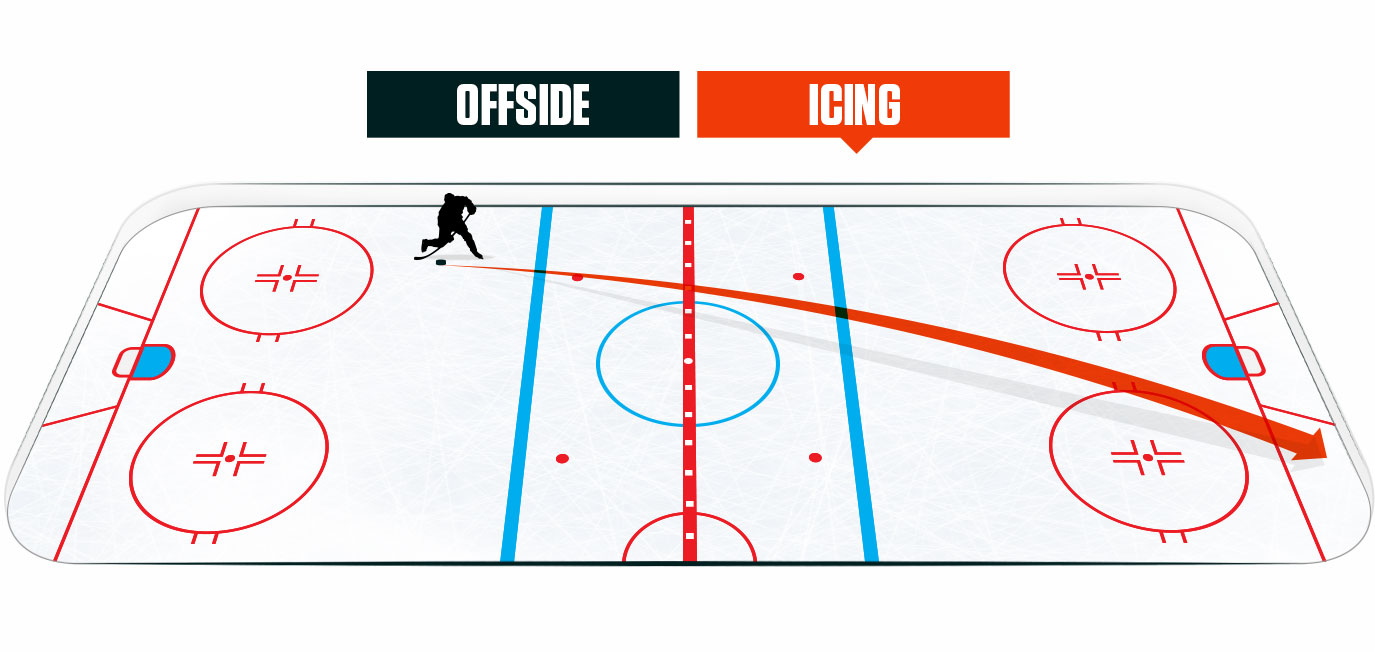
The offensive gameplay in the NHL has undergone dramatic changes, shaped by both rule adjustments and evolving strategies. The introduction of the faceoff circle as the primary stoppage point, combined with stricter enforcement of offside and icing rules, has refined puck possession and reduced stalling. However, the most transformative development has been the rise of the power play—now a cornerstone of modern tactical play.Since the 2006 Closer More Play approach, which standardized power play duration and enabled elite players to enhance speed and scoring in structured set-piece situations, penalty kills and offensive zone entries have become data-rich domains. Teams deploy complex zone defenses—such as the “2-1-2” trap and “stoppage zone” formations—to neutralize threats when their diffuser is shorthanded. “It’s not just about brute force anymore—success hinges on positioning, line combinations, and real-time adjustments,” states former coach Mike Babcock.
The NHL’s playful balance between physicality and precision continues to redefine offensive efficiency and defensive resilience.
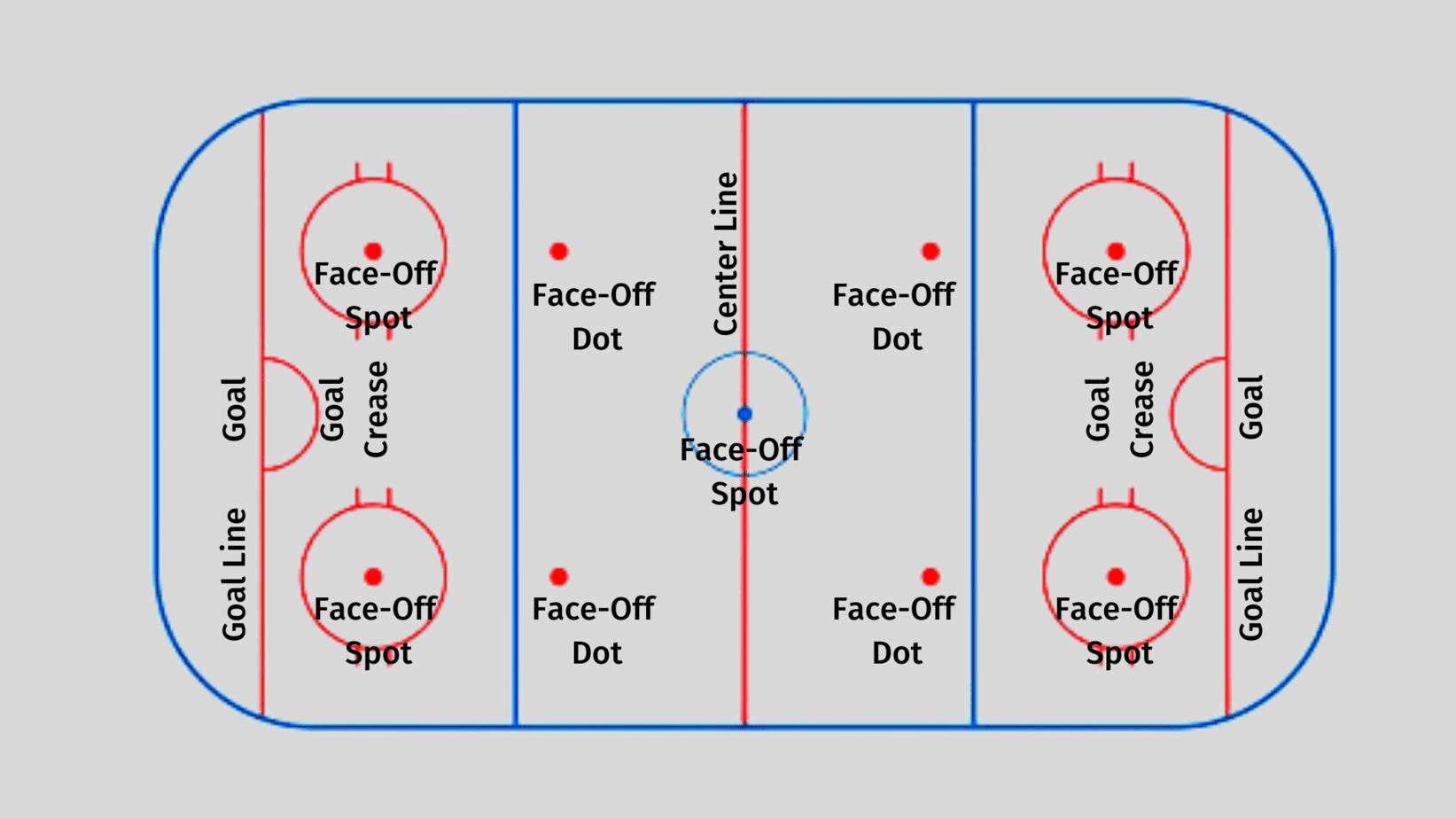
Specific zones within the ice carry distinct strategic value. The neutral zone serves as the pivot for transitions—teams that control it dictate ice space and pressure.
The forward 디프istor moves deep into the attacker’s zone to create scoring chances, while defensemen use the back toe to delay opposing rush plays and disrupt passing lanes. The crease—those critical dead-space areas around the net—remain the ultimate goal-scoring battleground, where saves become legends and momentum shifts in seconds.
Roster Dynamics and Player Classifications
Valid roster composition and strategic player deployment define team competitiveness.The NHL enforces strict norms: a team’s loaded roster must include at least 25 skaters and 3 goaltenders, with a maximum of 68 players on the ice per team during regulation. These rosters blend veteran leadership—often anchored by 35+ year-old capains with playoff experience—with emerging stars nurtured through drafts and development leagues.
Core Tiers and Player Categories
- **Core Roster**: The 20 skaters and 3 goalies actively competing during games, chosen primarily through the NHL Draft and free agency.Teams prioritize depth, often maintaining 3–4 prospect players on the extended roster to facilitate transitions and develop talent. - **Transferred/Rookies on Roster**: Limited trailers or developmental prospects, constrained by the 20-man limit. - **Developmental Pathways**: NHL hopefuls progress through junior leagues (e.g., NHL’s affiliation with NCAA and OHL/WHL), amateur farm systems (Colonial Affiliates), and European leagues—critical pipelines for skill refinement and tactical familiarity.
Every high-stakes playoff series demonstrates how roster depth and tactical acumen separate contenders from preseason curio. A balanced team leverages veteran savvy and youthful energy, ensuring stamina across grueling overtime and multiple shift changes. “Offense is about reading the game’s rhythm,” observes analytics specialist Craig Long.
“Defensively, resilience comes from composure—killing penalties cleanly and rotating smoothly under

Related Post

Apts Virginia Beach: The U.S. Defense Hub Transforming Coastal Maryland into a Military Epicenter
Kristen Connors Age Wiki Net worth Bio Height Husband
Melissa Roxburgh: The Rising Star Behind Emotional Depth and Versatile Artistry

