Planets in Order: The Solar System’s Cosmic Lineup That Defines Space Exploration
Planets in Order: The Solar System’s Cosmic Lineup That Defines Space Exploration
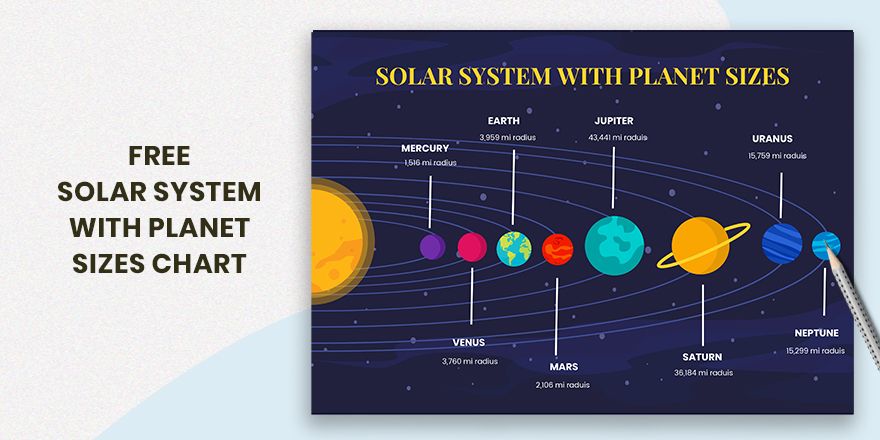
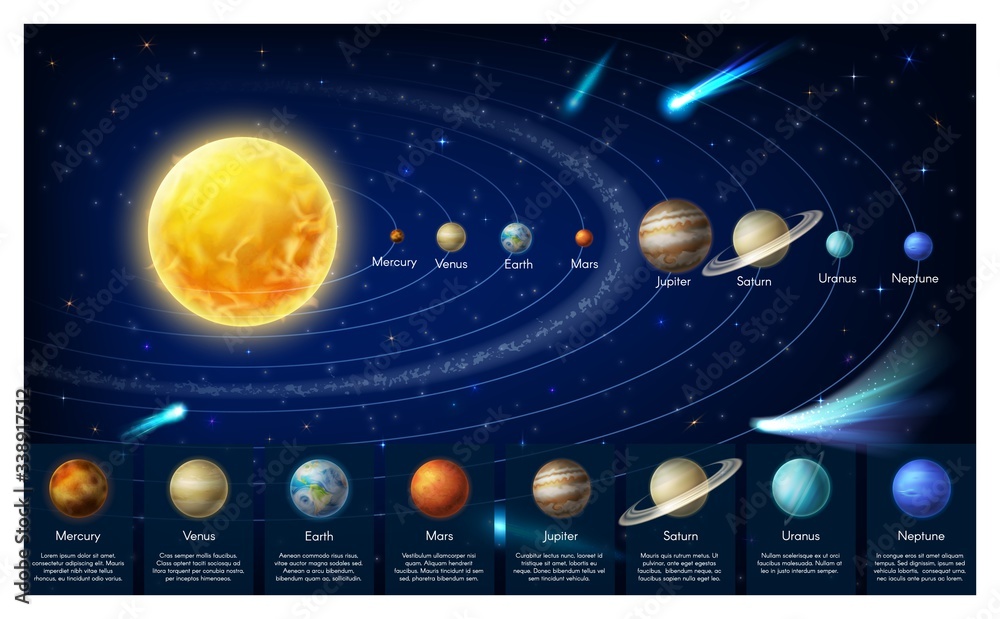
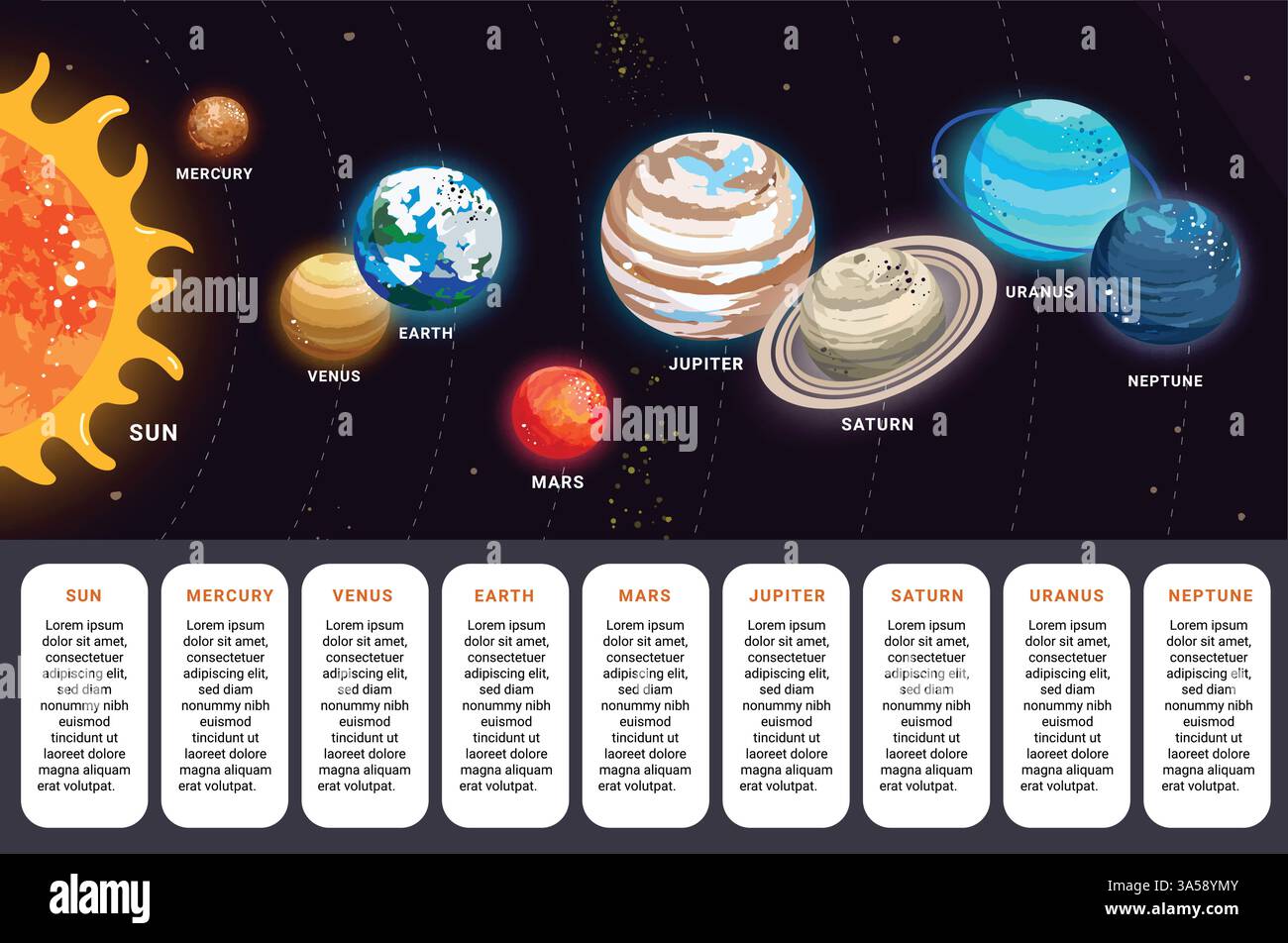
The order of the planets in our solar system is far more than a celestial catalog — it’s a detailed narrative of formation, composition, and orbital dynamics that reveals profound insights into planetary science and humanity’s quest to understand the cosmos. From Mercury’s scorching proximity to the Sun to Neptune’s icy frontier beyond the gas giants, each planet occupies a distinct niche in the planetary sequence shaped by gravity, temperature, and cosmic evolution. This structured alignment not only orders celestial bodies logically but also serves as a foundational framework from which scientists explore planetary diversity, climate systems, and the potential for life beyond Earth.
The immediate buildup from the Sun sets the stage for planetary classification. As the birthstone of the solar system, the Sun dominates with 99.86% of its total mass, dictating orbital mechanics through gravitational dominance. Nearest the Sun,
The Rocky Inner Planets: Mercury and Venus
spread a story of extremes: Mercury, the smallest and fastest-spinning world, experiences temperatures soanting to 800°F during daytime and plummeting below freezing at night, all within a single Earth day.Its surface bears ancient craters and tectonic scars, testimony to billions of years of bombardment and geological inactivity. Closer in, Venus blazes under thick carbon dioxide clouds that trap heat in a runaway greenhouse effect, making it Earth’s hottest planet with surface temperatures rivaling a volcanic furnace—reaching 900°F. “Venus is often called Earth’s sister planet due to our shared size and proximity,” notes planetary scientist Dr.
Elena Marquez, “but its hostile environment underscores how a delicate balance determines planetary fate.” Astronomers classify Mercury and Venus as terrestrial planets — small, dense, rocky worlds with solid surfaces. Mercury’s weak magnetic field and extreme day-night swings contrast with Venus’s dense atmosphere and retrograde rotation, a result of complex early solar system collisions. “Studying these inner planets offers a natural laboratory for planetary formation,” Marquez explains.
“They preserve clues about how Earth evolved under different conditions.” Moving beyond the inner zone,
The Fiery Gateway: Earth—The Special Case
stands apart not only in habitability but in the delicate equilibrium sustaining life. Earth occupies the “Goldilocks zone,” where temperatures allow liquid water to persist—a rare condition among planets. With a nitrogen-oxygen atmosphere, dynamic weather systems, and tectonic activity recycling minerals, Earth supports biodiversity unmatched elsewhere.Its singular biosphere makes it the only known planetary home, a fact that fuels both scientific curiosity and philosophical reflection on humanity’s place in space. Beyond Earth, the solar system transitions into a vast expanse dominated by the giants — gas and ice worlds whose sheer scale redefines planetary diversity.
The Gas Giants and Icy Titans: Gas and Ice Planets of the Outer Realm
pivot from rocky surfaces to colossal atmospheres composed largely of hydrogen and helium, with deeper layers of exotic ices — water, ammonia, and methane — beneath.Jupiter, the largest planet, eclipses Earth in mass by more than double and governs the asteroid belt with gravitational muscle. It spins rapidly, forging a distinctive oval shape, and hosts the Great Red Spot — a centuries-old storm larger than Earth. Jupiter’s powerful magnetosphere, ten times stronger than Earth’s, traps energetic particles in intense radiation belts, posing challenges for orbital missions.
Astronomers emphasize Jupiter as a cornerstone: “As the most massive planet, Jupiter shaped the architecture of the solar system, possibly deflecting comets that might otherwise strike inner worlds,” argues NASA astrophysicist Tom Reynolds. Saturn, the jewel of the outer system, captivates with its breathtaking ring system — a disk of ice and rock particles stretching over 175,000 miles wide, yet remarkably thin. Its low density makes Saturn less massive than Earth’s moon despite a larger volume.
Saturn’s moons, including Titan and Enceladus, reveal subsurface oceans and organic chemistry, redefining where life’s prerequisites might lie. “Saturn is starring in a new chapter of planetary science,” says Reynolds. “Its moons are not just neighbors but potential portals to understanding habitable environments beyond Earth.” Beyond Saturn lies
The Icy Frontier: Uranus and Neptune
, planets of frozen extremes shaped by distance and slow orbits.Uranus orbits tilted nearly 98 degrees, spinning on its side in a strange dance that creates extreme seasonal variations. Neptune, despite being farther and less massive than Uranus, glows with intense blues from methane absorbing red light, its winds reaching 1,500 mph — the fastest in the solar system. “Uranus and Neptune represent the outer edge of classical planetary formation,” notes planetary geochemist Dr.
Lin Chen. “Their volatile compositions challenge models of how planets assemble beyond the frost line, offering critical data for studying distant exoplanets.” Despite their remoteness, these ice giants are pivotal to understanding planet formation, climate dynamics, and the chemical evolution of the solar system. Their ghastly blue hues mask inner complexity — dense mantles of superionic ice, intense gravitational fields warping space-time locally.
Each visit, whether via flybys or future missions, deepens our grasp of planetary physics under conditions impossible to replicate on Earth. The sequence from Mercury to Neptune is not arbitrary but a story laced with physical laws: distance from the Sun regulating temperature, mass determining gravity and atmosphere, and angle of axial tilt influencing seasons. This celestial order reflects billions of years of orbital mechanics and cosmic evolution.
From Mercury’s scorched plains to Neptune’s tempestuous winds, each planet contributes a vital piece to the puzzle of planetary science. Understanding planets in order advances more than classification — it guides exploration, informs climate models, inspires engineering marvels for space travel, and humbles humanity beneath a cosmos grounded in precise, observable patterns. As humanity eyes Mars and beyond, the ordered lineup of planets remains both a science foundation and a mirror of our deepest questions: how did we form, where are we going, and what else might lurk in the dark beyond?
The sequence is complete — and rich with discovery.

Related Post
The Definitive Guide to Planets In Order: Mapping Our Solar System
From Mercury to Neptune: The Planets in Order as Astronomers See Them

Unveiling The Extraordinary World Of Johnny Flynn: Discoveries And Insights
This Simple Trick Will Make You Irresistible—Science-Backed and Universally Effective

