Pap Smear Cost In The Philippines: What You Need To Know
The cost of a Pap smear in the Philippines remains a critical concern for women’s health, shaping access to cervical cancer screening and preventive care. With rising rates of HPV-related cervical cancer and persistent disparities in healthcare affordability, understanding Pap smear pricing, funding options, and where to access services is essential. This guide unpacks everything you need to know—from average costs and government support programs to variations by region and healthcare provider—to empower informed decisions about preventive screenings.
Understanding the Average Pap Smear Cost in the Philippines
Publicly, a Pap smear (also known as a Pap test or cervical cytology screening) typically ranges between PHP 800 and PHP 2,000 in the Philippines, depending on location, facility type, and inclusion of ancillary services like HPV co-testing.Private clinics often fall toward the higher end, averaging PHP 1,500 to PHP 2,500, while public health centers—particularly in urban hospitals—may offer the test for as low as PHP 500 to PHP 1,200, especially under government health initiatives. “Despite its proven life-saving potential, many women remain unaware of cost-efficient options for cervical screening,” notes Dr. Maria Santos, a reproductive health specialist at Manila General Hospital.
Her insight reflects a broader need: affordability directly influences screening adherence, particularly among low-income and rural populations.
Factors influencing cost include:
- Type of healthcare provider (public hospital vs. private clinic)
- Whether HPV testing is included
- Location—urban areas generally charge more than rural clinics
- Whether cost-reduction programs or government subsidies apply
Public vs.
Private: Cost Disparities and Accessible Alternatives The public healthcare system plays a vital role in making Pap smears accessible. Under the government’s Nacional Inteligencia ng mga Sanallow sa Populasyon (NISPOP) and expanding Universal Health Care (UHC) programs, cervical cancer screening is prioritized, especially for women aged 30–60. Many facilities integrate Pap tests into broader women’s health packages, reducing out-of-pocket expenses significantly.
“In our women’s clinics, we often cover Pap tests entirely for uninsured patients, especially when bundled with lipid profile or diabetes screening,” explains Clinic Director Reynaldo Santos of a public health center in Quezon City. “This model encourages early detection where cost once acted as a barrier.” Private providers, while generally more expensive, offer streamlined services with short wait times and often additional diagnostic support like rapid HPV testing. Some offer subsidized packages for members or via health insurance plans, making access feasible even for middle-income women seeking prompt care.
For those navigating affordability, two key government-backed programs reduce costs substantially:
- PhilHealth: Expanded Coverage for Cervical Cancer Screening – Enhanced idec 23 (PhilHealth Code 40530) now includes Pap tests and co-tests for chronic disease patients at 0% co-payment for eligible participants across public hospitals.
- Department of Health (DOH) Screening Campaigns – Annual nationwide screenings are promoted through free mobile units and community outreach, with minimal or zero direct cost to patients.
City-dwelling women benefit from centralized health bureaus and specialized women’s health centers, though metropolitan centers still tend to charge higher due to operational costs. Conversely, rural women face significant logistical and financial hurdles, including travel expenses and limited clinic availability. Yet, the DOH’s “Screen for Life” mobile units have bridged gaps by delivering Pap smear services directly to remote barangays, sometimes even offering transportation vouchers to reduce indirect costs.
Private sectors respond with flexible payment plans, some clinics waiving fees for patients below the poverty line or enrolled in micro-insurance schemes. Popular urban centers like Makati and Cebu offer specialized women’s health chains with transparent pricing and patient loyalty programs, reinforcing competition that gently pushes costs lower.
For women unsure of insurance status, exploring referral networks—such as the Philippine College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (PCOG) referral directories—helps locate low-cost screenings without compromising quality.
These verified referrals afford access to accredited labs and trained cytologists, ensuring reliable results regardless of price point.
Top Tips for Affordable and Seamless Pap Smear Access
- Check PhilHealth idec codes: Confirm coverage using 23 for Pap testing (30630) or 40530 for HPV co-testing to avoid unexpected expenses. - Leverage free/subsidized campaigns: Annually, the DOH launches targeted campaigns with free screening; local government units often sponsor such efforts in rural barangays.- Use mobile health units: These reach underserved communities; wait times are shorter and costs are minimal or nil. - Compare clinic offerings: Ask for breakdowns of fees—some clinics bundle services at discounted rates and offer payment flexibility. - Carry proof of enrollment: If on PhilHealth or a micro-insurance plan, having documentation accelerates processing and coverage verification.
Understanding Pap smear costs in the Philippines is not just about price tags—it’s about ensuring every woman can prioritize preventive health without financial strain. Through public programs, mobile outreach, and informed consumer choices, access to cervical screening is within reach across socioeconomic strata. Empowerment begins with knowledge, and in the Philippines, affordable Pap smears are increasingly not just a possibility, but a tangible reality for those who know how and where to access them.


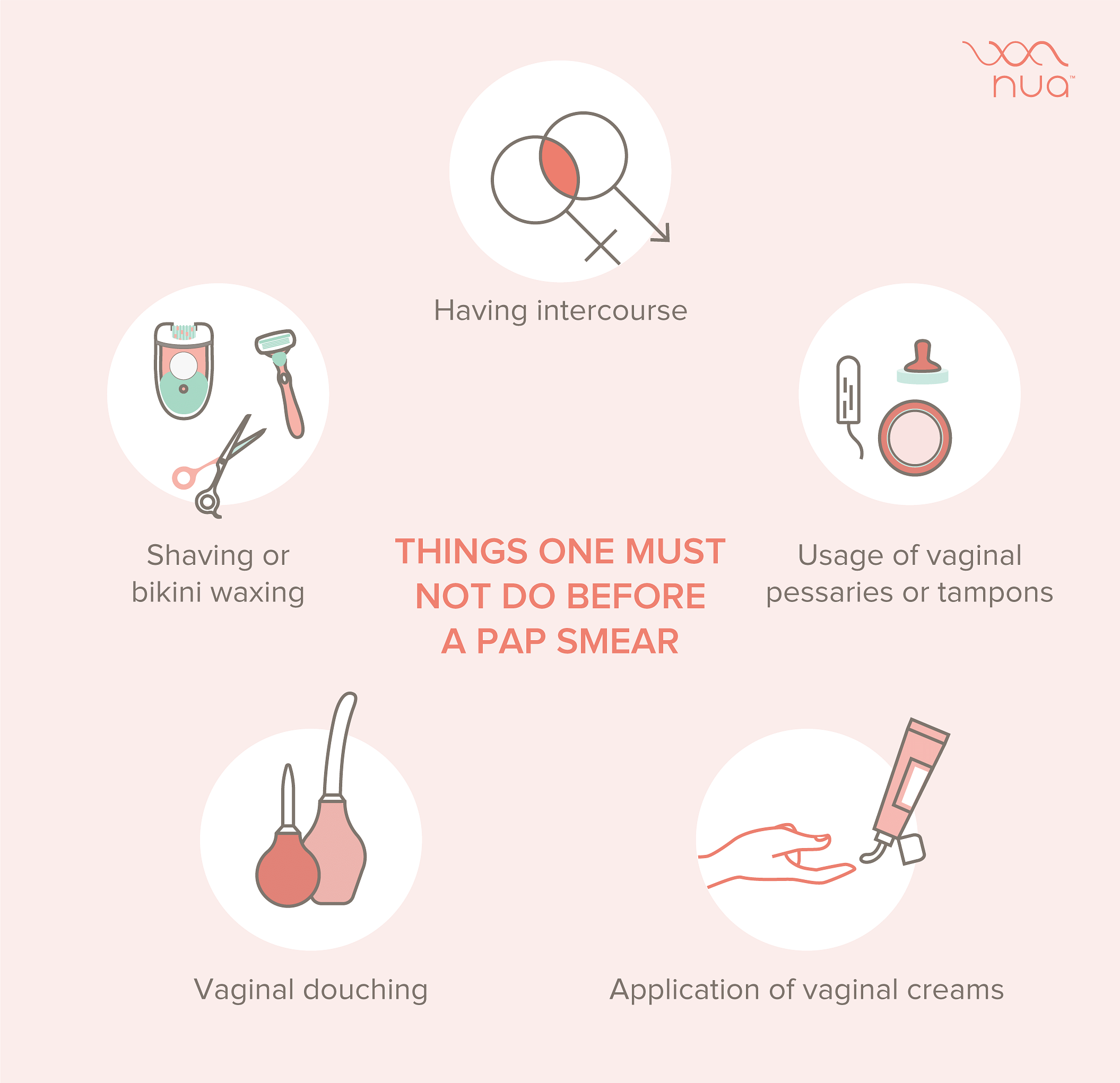
Related Post
The Unseen Fallout: Analyzing The Mexican Government's Response to 'No Mercy in Mexico Gore' and the 2015 Mission Critical Flight Incidents
Stephen Collinson CNN Bio Wiki Age Wife Politics Salary and Net Worth

Geminitay Irl: Where Next-Gen Technology Meets Real-World Impact

“Somebody That I Used To Know”: Decoding the Emotional Weight in Lyrics and Translation

