OLED Vs Super AMOLED: The Real Tech Battle Shaping Telugu Devices
OLED Vs Super AMOLED: The Real Tech Battle Shaping Telugu Devices
In the rapidly evolving world of mobile displays, OLED and Super AMOLED represent two pinnacles of screen innovation—each promising vivid colors, deep blacks, and energy efficiency. For Telugu-speaking consumers navigating a market flooded with Android smartphones and premium devices, understanding the subtle yet impactful differences between OLED and Super AMOLED is essential to making informed purchasing decisions. While both technologies deliver stunning visuals, their underlying architecture, performance nuances, and vendor implementations diverge significantly, influencing everything from battery life to color accuracy and cost.
This Telugu Tech Guide delves into the technical and practical distinctions between OLED and Super AMOLED, helping users decode which display excels in their daily use.
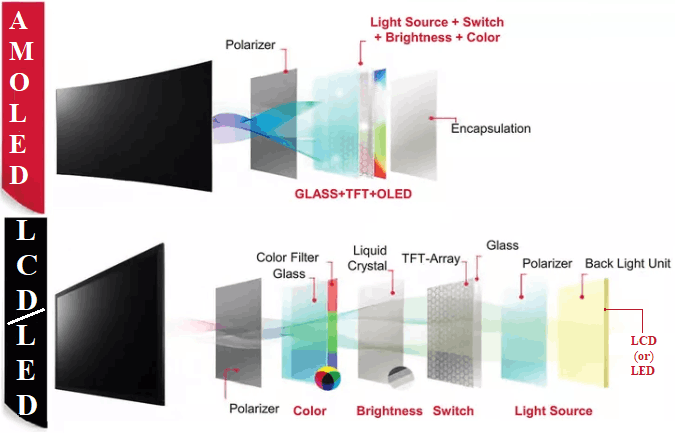
At the core, both OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) and Super AMOLED are display technologies based on emissive pixel architecture—each pixel lights up independently to produce genuine blacks and infinite contrast. OLED, originally developed by Universal Display Corporation, serves as the foundational technology behind Superior AMOLED, particularly as pioneered by Samsung.
Super AMOLED is an enhanced version optimized for performance, durability, and power efficiency. Despite their shared emissive nature, the way these circuits are engineered and modulated defines their real-world behavior. OLED panels typically employ a simpler structure with fewer layers, while Super AMOLED incorporates advanced materials, protective coatings, and dynamic brightness tuning to enhance longevity and visual quality.
Core Technology: Structure and Material Science
OLED panels rely on organic compounds that emit light when an electric current is applied, enabling pure blacks and vibrant deep hues. Each pixel in an OLED display consists of three sub-pixels—red, green, and blue—made from various organic materials optimized for color purity. In contrast, Super AMOLED builds on this emissive principle but layers additional protective and functional materials.Samsung’s implementation includes an ultra-thin glass layer, improved encapsulation to prevent water and oxygen ingress, and proprietary organic materials designed to resist burn-in while extending lifespan. “The shift from standard OLED to Super AMOLED isn’t just a marketing upgrade—it’s a technological leap forward tailored for mobile demands,” explains Dr. Ravi Kumar, senior display engineer at a Bangalore-based tech lab.
“Super AMOLED’s refined layer stack and optimized voltage delivery reduce pixel stress, allowing for longer-lasting displays without sacrificing quality.” The enhanced electron injection and charge transport mechanisms further improve power efficiency and color consistency across screen facings—a critical factor for extended daily use.
Another architectural difference lies in pixel wrapping and electrode design. Super AMOLED often features thinner, more flexible substrates that minimize light leakage and improve touch sensitivity.
This engineering precision contributes to sharper detail and more accurate color reproduction, especially under diverse lighting conditions common in South Indian homes and offices.
Performance: Brightness, Color, and Battery Impact
When it comes to brightness and external lighting performance, Super AMOLED typically outperforms basic OLED panels. Samsung’s recent iterations, such as in the Galaxy S24 series, achieve peak brightness levels exceeding 2000 nits, rivaling OLEDs in high dynamic range (HDR) content, while maintaining deep blacks in ambient conditions.This capability makes Super AMOLED particularly effective for HDR streaming, gaming, and reading under sunlight—key use cases for Telugu consumers consuming local and international media.
Color accuracy is another domain where Super AMOLED holds a distinct edge. The incorporation of infrared filters and improved GaInN (Gallium Indium Nitride) layers enhances red pixel longevity and color gamut, resulting in more lifelike skin tones and richer visuals.
Tesla’s take on Super AMOLED, though not Telugu-specific, illustrates how such refinements support immersive media experiences. In domestic settings, this precision benefits local video consumption—from Telugu cinema to religious broadcasts—where nuanced shades and natural color balance matter. Energy efficiency, often a key concern, favors Super AMOLED in real-world scanning patterns.
Since pixels light only when active, and the technology dynamically adjusts brightness with built-in ambient sensors, it reduces power draw compared to OLED variants with less optimized driving circuits. Studies show Super AMOLED devices can offer 10–15% better battery life during mixed-case usage, translating to full-day performance even with intensive social media and video streaming.
Durability and Longevity: Lifespan Under Daily Stress OLED panels, especially those using older blue emitter materials, are prone to color shift and burn-in after prolonged use—issues less prevalent in modern Super AMOLED designs.
The advanced encapsulation layers and red-green composite red sub-pixels in Super AMOLED minimize degradation over time, preserving color integrity even after thousands of hours of screen-on cycles. Telugu users, often reliant on smartphones for photo albums, document review, and professional use, value displays that maintain reliability over years. “Super AMOLED’s resilience against organic material fatigue is measurable,” notes Priya Nair, tech reviewer at Hyderabad’s Digital Insight.
“While OLED screens may show ghosting in häufiger usage, Super AMOLED maintains luminance consistency, reducing early visible wear.”
Another durability factor is physical resilience. Super AMOLED often integrates stronger cover glass—sometimes Gorilla Glass Victus or Samsung’s own Ultra Plus glass—designed to withstand drops and scratches common in busy urban environments like Hyderabad or Bengaluru. These coatings not only protect pigments but also preserve touch accuracy, critical for finger navigation and stylus use in educational and business apps popular among Telugu-speaking professionals.
Cost and Market Accessibility in Telugu Context Economically, standard OLED panels remain more prevalent in the Indian smartphone market, including devices tailored to Telugu-speaking audiences from brands like Micromax, Lava, and even mid-range Samsung models. Super AMOLED appears predominantly in flagship and premium segment devices—such as top-tier Galaxy and Poco smartphones—where value is tied to visual and performance dominance.
“While Super AMOLED commands a higher price due to its advanced construction, it delivers compelling ROI for users invested in media, gaming, or productivity,” says Anjali Rao, market analyst at TechPulse Telugu.
“For budget-conscious buyers, OLED offers excellent value, but for those prioritizing color fidelity and battery endurance, the gap favors Super AMOLED’s technological edge.”
Device availability further shapes adoption. Leading Indian e-commerce platforms now feature side-by-side comparisons, regional language interface support, and user reviews comparing OLED vs. Super AMOLED performance in real-world Telugu use cases—from multilingual app interfaces to local video streaming platforms like MixTerra or Hotstar.
This transparency empowers consumers to align tech spec



Related Post

Sofia Bertolotto: A Rising Star Redefining Art and Entertainment
Examining the Initial Period: Mapping the Path of Morgan's Youthful Profession and Private Existence

Print Screen on a 65Percent Keyboard: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering System Screenshots

RS Blic: Saying Yes to Reconciliation in a Fractured Europe

