Mole Fraction: The Hidden Language That Governs Mixtures and Determines Chemical Behavior
Mole Fraction: The Hidden Language That Governs Mixtures and Determines Chemical Behavior
In the quiet world of chemistry, where gaze-tingling reactions unfold at the molecular scale, a fundamental insight shapes our understanding: not the mass or volume of components alone, but their relative proportions—expressed through mole fractions—dictate the behavior of chemical mixtures. Mole fraction, a dimensionless ratio describing the fraction of moles of one component relative to all components in a mixture, is far more than a mathematical curiosity. It is the cornerstone of expression in thermodynamics, solution chemistry, and industrial processes, offering a precise language to quantify composition without being mired in unit dependencies.
This article explores mole fraction’s scientific foundation, its pivotal role across disciplines, and why it remains indispensable in both research and application.
At its core, mole fraction (denoted as _x_i_) is defined mathematically as the number of moles of component _i_ divided by the total number of moles in the mixture. For a system with three components—A, B, and C—with moles n_A, n_B, and n_C respectively, the mole fraction is calculated as x_A = n_A / (n_A + n_B + n_C), and similarly for B and C.
“Mole fraction transforms disparate substances into a single, universal metric,” notes Dr. Elena Marquez, a chemical engineer specializing in multiphase systems. “Whether analyzing steam in turbines or electrolyte solutions, this ratio strips away distraction, focusing pure on composition.”
One of mole fraction’s most powerful attributes lies in its unitless nature, making it universally applicable across contexts where mass or volume measurements would falter under varying conditions.
Unlike concentration expressed as grams per liter or molality, mole fraction remains invariant as long as component amounts are known—precisely why it is preferred in vapor-liquid equilibrium studies and phase equilibrium calculations. “In vapor-liquid equilibria, mole fraction determines partial pressures and fugacities directly,” explains Dr. Marquez.
“It allows engineers to predict how a mixture will vaporize or condense under pressure without reconstructing the entire molecular balance.”
Applications Spanning Multiple Disciplines Mole fraction is not confined to academic papers; it drives innovation across industries. In environmental science, mole fractions of atmospheric gases determine pollution impact and climate modeling. Carbon dioxide’s mole fraction in the air—now exceeding 420 parts per million—serves as a key metric for tracking emissions and understanding greenhouse dynamics.
In pharmaceuticals, the mole fraction of active ingredients versus solvents ensures drug efficacy and reproducibility. For precise dosage, “small deviations in mole fraction can drastically alter pharmacokinetics,” explains Dr. Liam Chen, a formulation chemist.
“A 2% difference in component mole ratios might change how a drug is absorbed, metabolized, or excreted.”
In materials science, mole fraction is central to alloy design and polymer blending. Steel, for example, is defined by the mole fraction of iron and carbon, influencing hardness, ductility, and corrosion resistance. Similarly, plastic blends rely on mole fractions to achieve desired mechanical and optical properties.
“Mole fraction reveals the synergy—or incompatibility—of components at the atomic level,” says Dr. Marquez. “It’s this insight that accelerates development of stronger, lighter, and more resilient materials.”
Critical to mastering mole fraction is understanding its relationship with other concentration metrics.
Unlike molarity (moles per liter), mole fraction is independent of volume, sidestepping distortions caused by temperature or pressure changes. Ammonia solution, for instance, can be described equivalently using mole fraction or molality, but the former avoids assumptions about solution density. Vapor-liquid equilibria particularly depend on mole fraction, as Raoult’s Law and Dalton’s Law use these ratios to predict how pressure independent phases will interact.
When water and ethanol form a mixture, the mole fraction of each dictates vapor pressure, guiding distillation efficiency and separation processes in refineries and biorefineries. “Vapor-liquid systems thrive on mole fraction because they depend on component identity, not bulk density,” Dr. Chen emphasizes.
Despite its foundational role, mole fraction is often overshadowed by more familiar metrics—yet dismissing it is a missed opportunity.
“Mole fraction is the unsung hero” observes Dr. Marquez. “It’s how scientists decode the microscopic rules of macroscopic behavior, from breathable air to bioengineered tissues.” Whether in lab synthesis, industrial scaling, or environmental monitoring, mole fraction bridges theory and application.
It enables reproducibility, supports accurate modeling, and empowers engineers to manipulate mixtures with intention and precision. Each time scientists refer to mole fraction, they are accessing a shared scientific language—one built on clarity, dimensional consistency, and universal truth.
As research advances into nanomaterials, responsive gels, and next-generation energy storage, the importance of mole fraction only grows. It isn’t just a tool or a formula; it’s a lens through which the invisible becomes quantifiable.
In the intricate dance of chemicals and processes shaping modern technology and daily life, mole fraction stands as a silent architect—guiding reactions, ensuring stability, and unlocking innovation. Understanding and applying this simple yet profound ratio is not just for chemists—it’s essential for anyone navigating the science that underpins our modern world.




Related Post
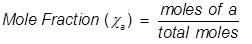
Unlocking Mixture Mysteries: How Mole Fraction Formula Powers Chemistry Design

The Molecular Compass: Decoding Mixtures Through Mole Fraction

Revolutionize Your Memory Collection: How iCloud Photos Transforms Digital Photo Management

