Master the Physics Regents Formula Sheet: Your As-Monoment Guide to Success
Master the Physics Regents Formula Sheet: Your As-Monoment Guide to Success
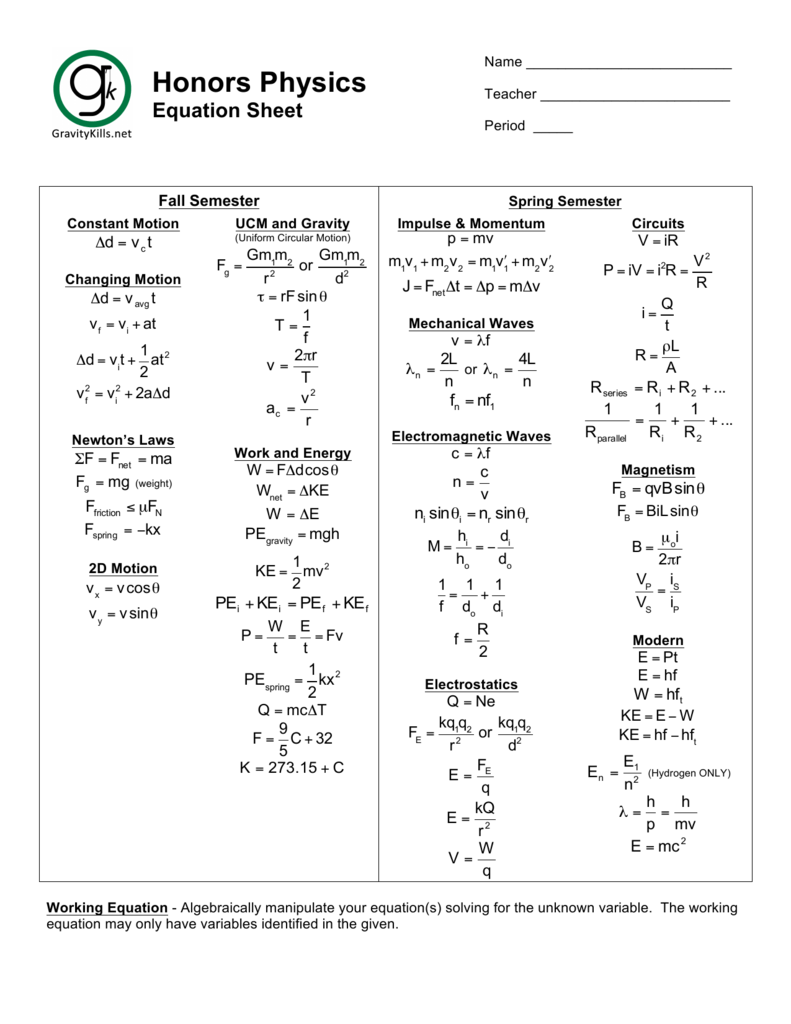
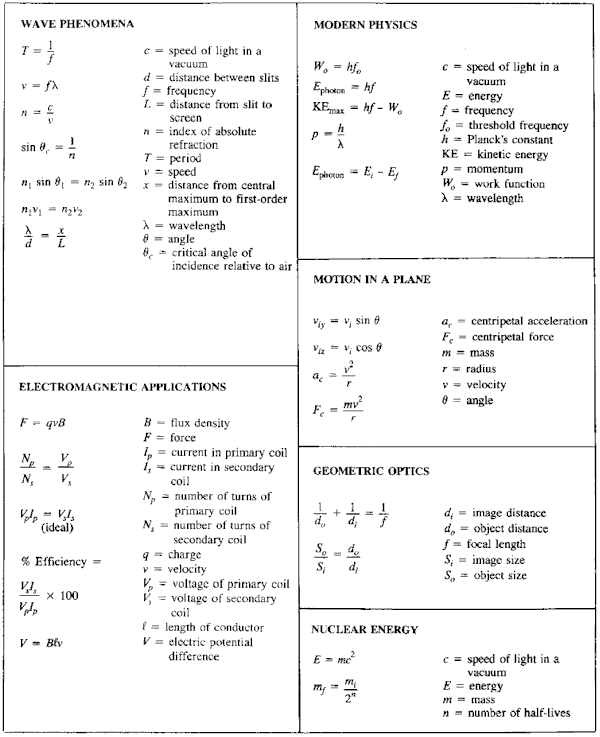
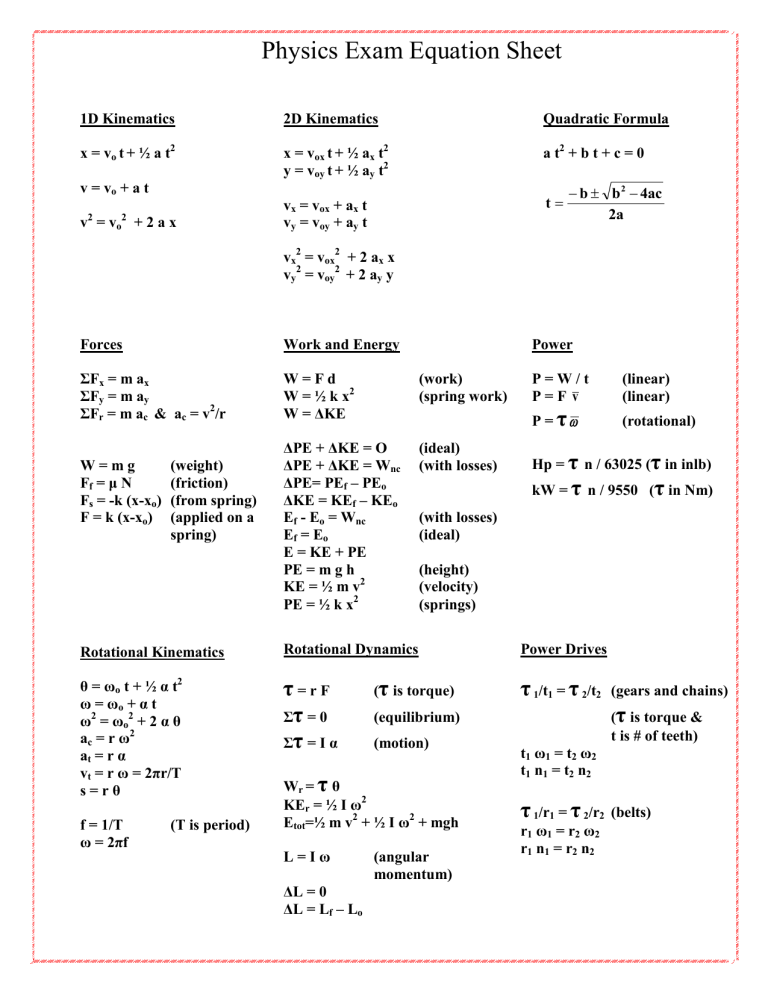
At the heart of every successful Physics Regents exam performance lies not just deep conceptual understanding—but a sharp, accessible grasp of the essential formulas distilled into a trusted formula sheet. This concentrated tool is far more than a summary: it is a strategic roadmap guiding students through complex problems with speed, accuracy, and precision. In the high-stakes environment of Physics Regents exams, where fractions of a point separate distinction from mediocrity, knowing every formula by heart—and understanding when and how to apply it—is non-negotiable.
Embodying clarity amid complexity, the Physics Regents Formula Sheet serves as both memory anchor and problem-solving catalyst, transforming abstract equations into actionable steps. The formula sheet compiles the most fundamental laws and expressions critical across mechanics, algebra, geometry, calculus, and trigonometry—disciplines that collectively form the Regents’ core physics domains. From Newton’s foundational second law to kinematic relations, energy conservation principles, and vector operations, each entry reflects the standards-specific knowledge examiners expect students to deploy.
Far from a passive list, this curated collection embodies intentional sequencing—prioritizing formulas that optimally support multi-step reasoning and vector-based problem solving.
Mechanics Arrays: The Core Building Blocks
At the center of the formula sheet are Newtonian mechanics—arguably the most frequently tested domain. Newton’s Second Law,F = ma, remains indispensable: force equals mass times acceleration.
Used in problems involving Newton’s third law pairs, action-reaction systems, and equilibria, this equation fuels calculations of dynamics and motion in one, two, or three dimensions. Complementing F = ma, the net force resolution formula—Fnet = ΣF—empowers students to break complex force systems into components along chosen axes, ensuring vector summation aligns with coordinate geometry.
Equally critical is the work-energy theorem,W = ΔKE = F·d along constant forces, which links force and energy without requiring direct acceleration data. Pairing this with equations for gravitational work—mgh and momentum conservation—enables seamless transitions between force-based and energy-based reasoning.
For systems involving springs, Hooke’s Law (F = -kx) introduces elastic behavior, while gravitational force—F = G(m₁m₂)/r²—ties mass interactions to universal gravitation, essential for both planetary and everyday contexts.
Kinematics and Projectile Motion dominate motion under constant acceleration. The fundamental displacement equation,s

Related Post

The Ilken Throne of Glass: Where Dorian, Manon, and Fernanda Forge a Kingdom of Shattered Light

Time in Virginia: From Colonial Sundials to Smart Clocks, How Measurement Shapes Daily Life Across the Old Dominion
Unlocking the Johnson Family Secret: A Deep Dive into the Foundations of Life, Love, and Learning in Bryan Johnson’s Children’s World

Kordell Beckham: The Life Journey of a Philanthropist, Century-Built Athlete, and Generational Icon

