Lisinopril Class: The Cornerstone of Modern Hypertension and Heart Failure Treatment
Lisinopril Class: The Cornerstone of Modern Hypertension and Heart Failure Treatment
A widely prescribed ACE inhibitor, Lisinopril stands as a frontline weapon against hypertension, heart failure, and cardiovascular complications. Belonging to the Lisinopril Class of drugs, it functions by relaxing blood vessels and reducing the heart’s workload, offering patients significant improvements in both quality of life and survival rates. Its proven efficacy, safety profile, and affordability make it a mainstay in guidelines issued by leading medical organizations worldwide.
Under the umbrella of the ACE inhibitors, Lisinopril distinguishes itself as one of the most extensively studied and trusted medications in cardiovascular pharmacology.
This angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor works by blocking the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II—a key hormone that triggers vasoconstriction and sodium retention. By dampening these effects, Lisinopril promotes vasodilation, reduces blood volume, and eases pressure on weakened hearts. As Dr.
Emma Carter, a cardiologist at the Mayo Clinic, notes: “Lisinopril doesn’t just lower blood pressure; it reshapes the disease itself by slowing progression in heart failure patients.”
Mechanism of Action: How Lisinopril Works at the Molecular Level
Lisinopril inhibits the enzyme ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme), primarily found in the lungs and vascular system. This inhibition prevents angiotensin I from being converted into angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor and key driver of aldosterone release. Aldosterone encourages sodium and water retention, further elevating blood pressure.By curbing angiotensin II, Lisinopril achieves multiple benefits: - Vasodilation reduces peripheral resistance - Reduced aldosterone levels decrease fluid overload - Lowered systemic pressure protects renal and myocardial tissue Moreover, plaque stabilization and reduced cardiac remodeling distinguish ACE inhibitors like Lisinopril from other antihypertensives, offering long-term organ protection.
Indication: Beyond Hypertension—Heart Failure and Post-Myocardial Infarction
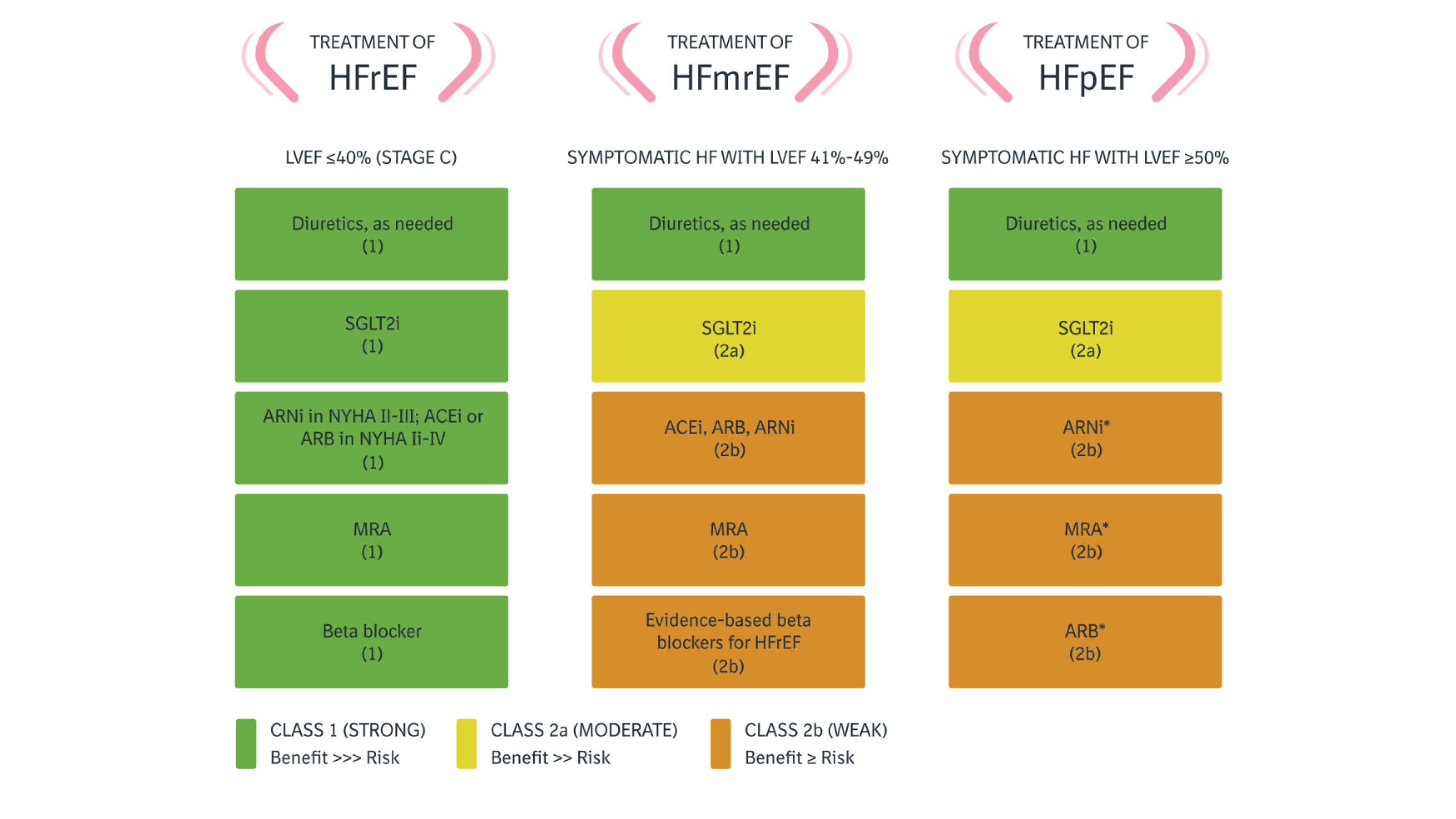
While initially developed for hypertension, Lisinopril’s clinical footprint extends far beyond blood pressure control. Its benefits are well-established in managing systolic heart failure, where it significantly reduces mortality and hospital admissions. In the
-on-the-management-of-HFpEF-infographic.png)

Related Post

Vei Face Reveal Bae: The Revolutionary Tech That Redefines Self-Expression
The Unsung Architect of Reno Wards: Uncovering the Vision Behind a Modern Urban Revival
Who Is Garcelle Beauvais Eldest Son Oliver Saunders
Who Is Dee Jay Mathis James Caans Exwife

