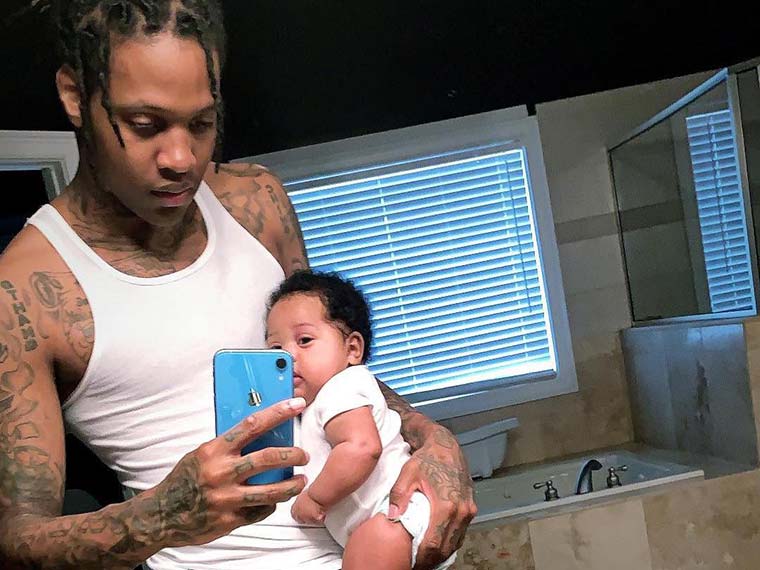
Judicial Branch In A Flash Icivics Answer Key
How power shapes justice: The Judicial Branch In A Flash, from iCivics, explains the Supreme Court’s critical role in interpreting laws and balancing government power—where constitutionality meets real-world impact, all distilled into the answer key’s clear, actionable framework. This authoritative guide reveals how judicial review, landmark rulings, and institutional design empower the courts to shape American life.
The Judicial Branch: America’s Guardian of the Constitution
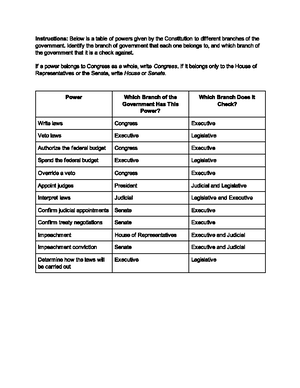
The U.S. Judicial Branch stands as a cornerstone of democratic governance, uniquely empowered to interpret the Constitution and safeguard civil liberties.As outlined in the iCivics Judicial Branch In A Flash answer key, courts do more than resolve disputes—they ensure that laws and government actions align with constitutional principles. This function, rooted in judicial review, was formally established by Marbury v. Madison (1803), where the Supreme Court declared it the duty of the judiciary “to say what the law is.” Today, this authority enables courts to check legislative and executive overreach, protecting individual rights and maintaining the balance of federal power.
Judicial Review: The Court’s Constitutional Superpower
At the heart of the judicial branch’s influence is the power of judicial review—the ability to invalidate laws and government actions conflicting with the Constitution. The iCivics module explains this as the court’s “check on illegality,” centered in Article III, Section 2 of the Constitution. Through landmark cases like Marbury v.Madison
and United States v. Nixon (1974), the Supreme Court has affirmed its role as the ultimate interpreter of constitutional meaning. Judicial review transforms abstract legal principles into enforceable safeguards, ensuring no branch operates above the law.The Supreme Court’s Role in National Decision-Making
Beyond reviewing laws, the Supreme Court shapes national identity through landmark rulings. The iCivics answer key highlights how cases such as Brown v. Board of Education (1954) (ending school segregation) and Obergefell v.Hodges (2015)
(legalizing same-sex marriage) reflect evolving societal values interpreted through constitutional lenses. These decisions demonstrate the court’s dual function: upholding foundational legal frameworks while adapting to contemporary justice. Each ruling carries the weight of precedent and carries life-altering consequences for millions.Structure and Independence: How Courts Maintain Authority
The independence of the judicial branch relies on structural safeguards. Justices serve lifetime terms, insulating them from political pressure and enabling impartial decision-making—a key theme in the iCivics answer key. This stability, however, is balanced by accountability mechanisms: judicial nominations involve congressional scrutiny, and impeachment remains a constitutional fallback.The system’s design reflects a deliberate balance—ensuring both independence and public trust in the courts’ integrity.
Judicial Rulemaking: Influencing Policy Beyond Justices’ Benches
Courts exert influence not only through rulings but also through judicial rulemaking—issuing interpretive guidelines that guide lower courts, agencies, and even Congress. The answer key emphasizes how decisions in areas like voting rights, environmental law, and criminal procedure often shift policy landscapes.For example, Shelby County v. Holder (2013) reshaped federal oversight of state voting laws, showing how judicial pronouncements extend far beyond individual cases into the nation’s governance fabric.
Student Focus: Navigating the Judicial Branch In A Flash Answer Key
Civics learners using iCivics’ Judicial Branch In A Flash module gain strategic tools to decode complex judicial concepts.The answer key distills essential knowledge into clear, accessible explanations: - Understanding judicial review as the courts’ interpretive authority under Article III - Recognizing landmark cases and their transformative societal impacts - Analyzing the Supreme Court’s role in shaping constitutional meaning over time - Evaluating how structural independence protects judicial legitimacy - Identifying how judicial rulings influence public policy and daily life Each question is framed to test comprehension of these core ideas, with real-world examples grounding theoretical knowledge. Students learn not just *what* courts do, but *how* and *why* their decisions matter.
The Judicial Branch In Action: Principle Meets Practice
The Judicial Branch In A Flash answer key reveals a branch fundamentally committed to constitutional fidelity and democratic resilience.Through judicial review, landmark rulings, and insulated independence, the courts serve as both arbiters of law and guardians of liberty. In a nation where power is divided and often contested, the judicial branch ensures that no branch becomes unaccountable—upholding the Constitution as a living, enforceable framework. As the iCivics guide makes unequivocally clear, the courts’ authority is not just legal—it is essential to justice, stability, and the ongoing project of American democracy.



Related Post

The Fantastic Four Pose: A Powerful Symbol of Unity, Strength, and Balance
Unveiling the Mark-Recapture Method: How Scientists Track Populations with Precision and Persistence

Unlocking Indonesia: How a Simple Map Transforms National Navigation and Identity
SK P5: All You Need To Know - Unpacking the Latest Regulatory Framework

