Iran vs Saudi Arabia: Who Would Emerge Winner in a Hypothetical Full-Scale War?
Iran vs Saudi Arabia: Who Would Emerge Winner in a Hypothetical Full-Scale War?
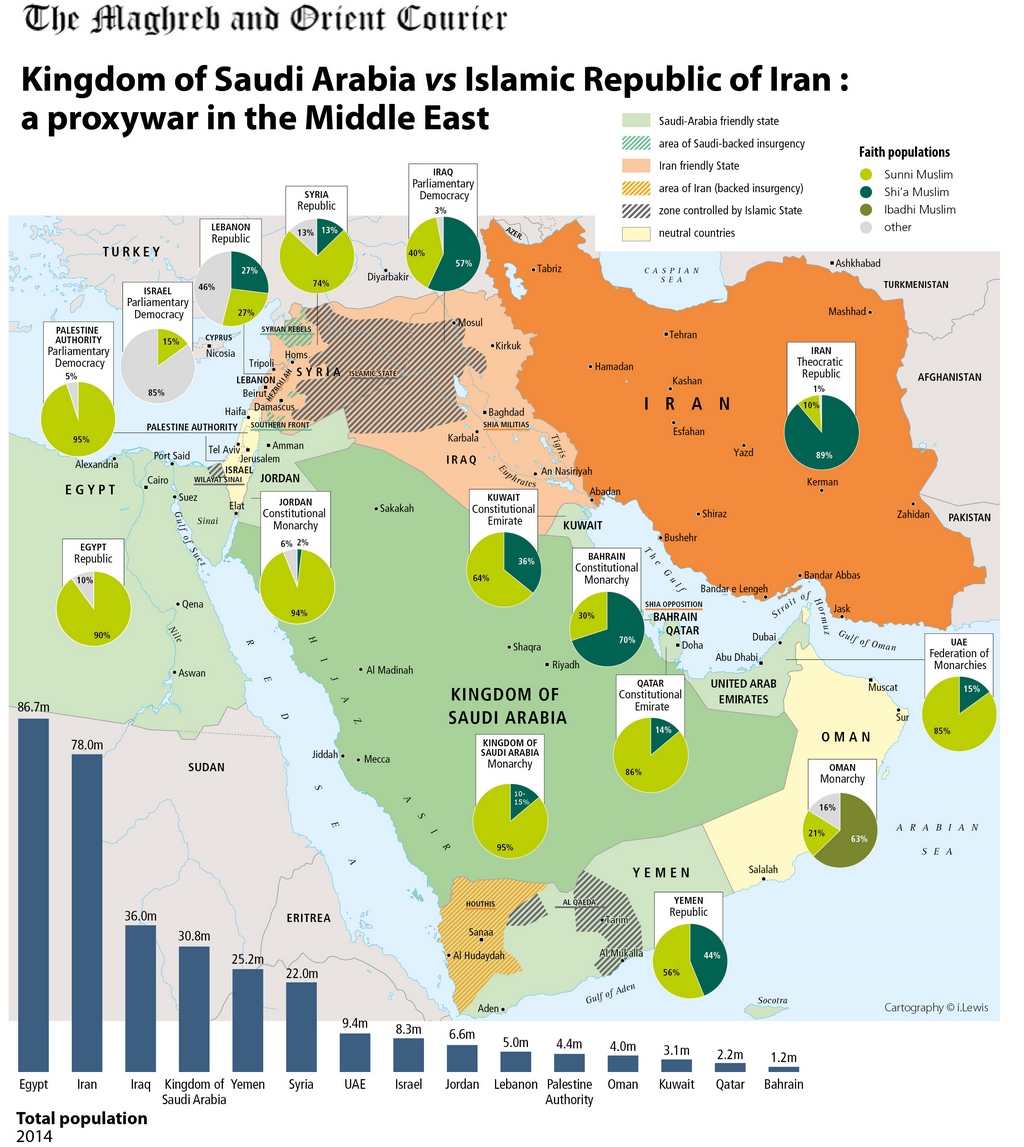
In a region steeped in historical rivalry, deep sectarian divides, and competing geopolitical ambitions, a direct military confrontation between Iran and Saudi Arabia would ignite one of the most consequential conflicts of the 21st century. While no open war currently exists between the two regional powers, the potential for direct conflict—fueled by proxy battles, proxy weapons, and ideological warfare—remains a sobering reality. Their rivalry spans decades, underpinned by Sunni-Shia tensions, competing visions for Middle Eastern leadership, and strategic struggles over dominance in Iraq, Syria, Yemen, Lebanon, and beyond.
Analyzing how each nation would fare in a full-scale war requires a detailed examination of their military capabilities, strategic depth, economic resilience, and the geographic and logistical realities of regional warfare.
The Military Strengths: Might and Preparedness
Both Iran and Saudi Arabia maintain substantial armed forces, but their military structures, doctrines, and readiness levels differ fundamentally. Iran’s military relies on a hybrid model blending conscription, a large reserve force, and a sophisticated network of revolutionary guards and proxy militias.Its ground forces are configured around rapid maneuver warfare, missile batteries, and asymmetric tactics honed through years of asymmetric engagements in Syria and Iraq. Iran fields an estimated 500,000 active personnel with over 400,000 paramilitary forces under the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), which functions as both a military and political engine. The IRGC’s Quds Force orchestrates regional destabilization through proxy networks, giving Iran leverage far beyond its borders.
In contrast, Saudi Arabia’s military is larger in nominal numbers—boasting over 120,000 active soldiers supported by a substantial defense budget—and benefits from advanced Western-supplied technology, including Apache helicopters, precision-guided munitions, and U.S.-made air defense systems. Its royal armed forces emphasize conventional deterrence, rapid intervention capabilities, and air superiority. However, Saudi reliance on foreign arms and coalition support introduces vulnerabilities in prolonged confrontations, particularly given logistical challenges in sustaining operations across wide fronts.
Iran’s emphasis on asymmetrical warfare and missile arsenal offers significant deterrence against conventional invasions. It operates over 2,000 ballistic missiles of varying ranges, capable of hitting key Saudi infrastructure, particularly its oil facilities and airbases. In 2021, Iran conducted a historic missile salvo into Iraqi bases—striking targets linked to opposition groups—demonstrating operational speed and coordination with allied militias.
Saudi Arabia’s conventional force, while formidable, lacks Iran’s integrated militia networks. Its army is smaller in size, with roughly 80,000 professional soldiers and auxiliary reserves, raising questions about sustainability in a drawn-out conflict. Yet Saudi strength lies in its ability to mobilize advanced airpower and maintain coalition coherence through U.S.
and NATO partnerships. Military analysts note that while Saudi Arabia possesses superior air and naval capabilities on paper, Iran’s doctrine prioritizes defense-in-depth and endurance—qualities honed during its long-standing support for allied forces in proxy wars.
Geographic and Logistical Challenges Salt the Battlefield
Terrain plays a decisive role in shaping military outcomes.Saudi Arabia’s vast desert landscape favors rapid armored thrusts but complicates deep interior operations, especially in mountainous or urban zones. Its major population centers—Riyadh, Jeddah, Dhahran—are heavily defended, while its primary oil infrastructure lies along a narrow eastern coast. Control of this coastline enables dominance over regional energy exports but exposes critical economic targets to Iranian missile and drone strikes.
Iran’s geography offers distinct advantages: rugged terrain, high-altitude plateaus, and proximity to multiple conflict zones give it strategic depth and improved survivability. Iranian forces could leverage mountain redoubts to launch ambushes, retreat into secure areas, and sustain operations despite high-intensity airstrikes. Moreover, Iran’s longer supply lines into Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, and Yemen provide basing leverage and forward operating zones for its regional allies.
Access to maritime chokepoints—especially the Strait of Hormuz—defines naval competition. Iran has repeatedly threatened to disrupt



Related Post

Is Chris Brown’s Mother in Jail? Unraveling the Family Shadow Behind the Celebrity

Unveiling Roblox Surprise Com: The Game That Redefines In-Game Reveals

Unpacking Taylor Swift’s Conceptual Boyfriends: The Timeless Enigma Behind Her Boyfriends Revealed

The Life And Love Of Cynthia Erivo An Insight Into Her Personal Journey With Her Husband Gotceleb

