IIS Certificate Auto Renewal: Stop Expiring Digital Identities Before They Break Your Web Services
IIS Certificate Auto Renewal: Stop Expiring Digital Identities Before They Break Your Web Services
In the fast-paced world of web infrastructure, Automatic Certificate Authority (CA) renewal for IIS websites is not just a technical nicety—it’s a mission-critical operational necessity. Digital certificates power secure HTTPS connections, safeguarding user data and maintaining trust; yet, without proper auto-renewal, even the strongest SSL/TLS implementations can collapse when a certificate expires, triggering widespread outages and security warnings. Among the most powerful tools available to developers and sysadmins, Microsoft’s Internet Information Services (IIS) offers elegant, automated certificate renewal workflows—particularly when integrated with modern CA platforms.
This comprehensive guide explores IIS Certificate Auto Renewal in depth, detailing how to implement, manage, and optimize this essential safeguard, ensuring continuous, secure access for users and services alike.
Certificate expiration is one of the silent catastrophe vectors in enterprise environments. A single expired SSL certificate can trigger browser warnings, disrupt API integrations, and erode customer confidence.
Studies show that over 60% of HTTPS errors stem from certificate failures, many preventable with proactive management. When integrated with IIS, automated renewal eliminates manual oversight, reduces human error, and aligns security practices with DevOps efficiency. The core principle is simple: certs must renew before expiration—ideally days in advance—without service interruption.
Why Auto-Renewal Matters for IIS and HTTPS Security
Modern web applications depend on seamless, continuous encryption. IIS, Microsoft’s flagship web server platform, supports widespread certificate management via integrations with Windows Certificate Store (StoreCert), Microsoft Total Validation (MTV), and third-party public CAs like DigiCert or Sectigo. Without automation, administrators must manually track expiration dates, issue new certificates, and deploy updates—processes prone to delays, miscommunication, and downtime.Auto-renewal transforms this fragmented, reactive workflow into a system-wide, proactive safeguard. When properly configured, certificate renewals occur silently in the background: the new certificate is issued, trusted, and deployed before the old one expires. This prevents unexpected outages and maintains uninterrupted HTTPS connectivity.
Beyond reliability, this practice strengthens security posture by ensuring only valid, CA-signed certificates are active—critical in environments governed by compliance standards like PCI DSS, HIPAA, or GDPR that mandate trusted, valid encryption. Automation as a Cornerstone of Secure DevOps Pipelines In today’s continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) era, integrating certificate renewal into automated deployment pipelines is no longer optional—it’s foundational. Manual intervention introduces delays and inconsistencies; automation brings consistency, speed, and traceability.
With IIS certificate auto-renewal, organizations can embed certificate management directly into release workflows, ensuring every deployed build uses up-to-date credentials. Tools such as Windows Server Automation Scripting, PowerShell modules for PVH månaden (Password Hashing), and hybrid CI platforms like Azure DevOps or Jenkins support scripting certificate renewal with time-based triggers. For example, a nightly PowerShell script could query expiring certificates, validate renewal eligibility, request new certificates via API from a CA, import them into IIS StoreCert, and confirm successful renewal—all without human input.
Setup and Configuration: Step-by-Step Implementation Implementing IIS certificate auto-renewal begins with foundational setup: ensuring trust, enabling background renewal, and validating the process.
Step 1: Configure Trust and Enable Background Renewal in IIS
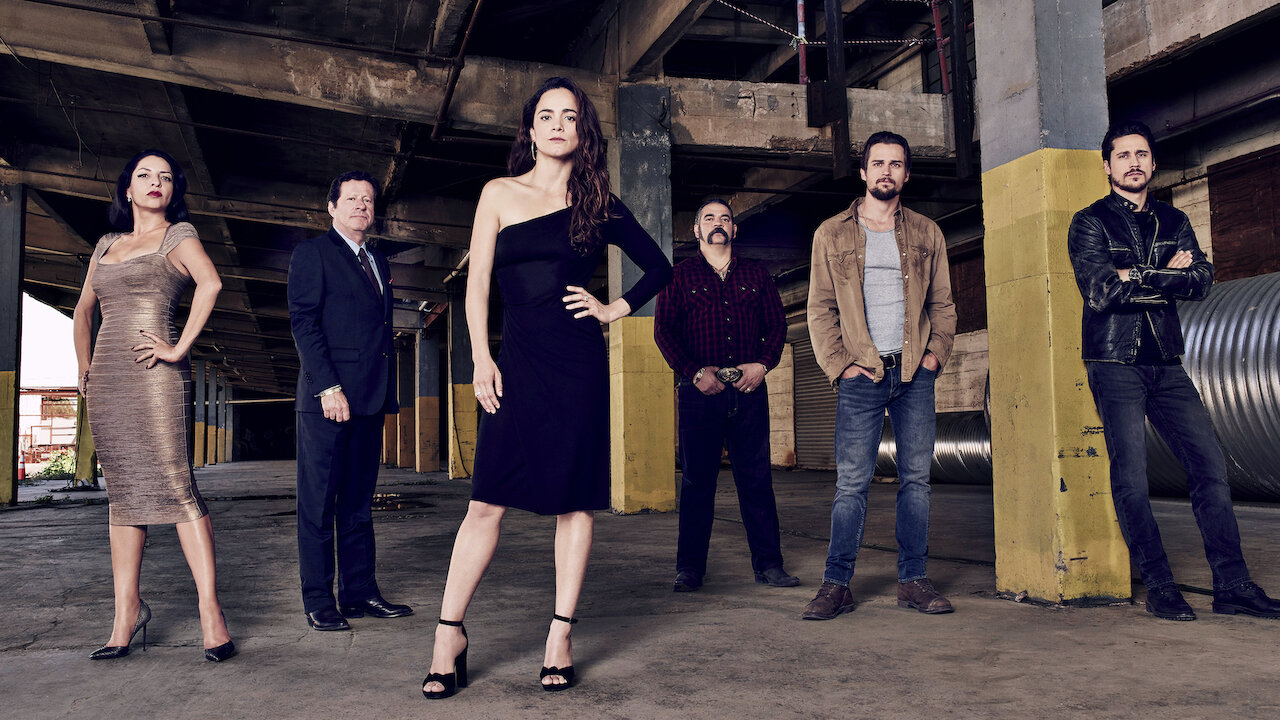
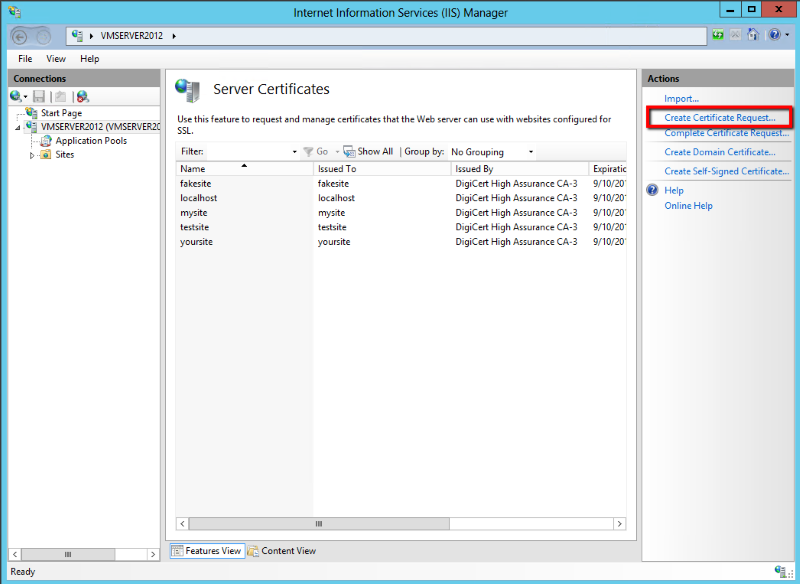
Start by enrolling your server and certificates in a trusted Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). In IIS, navigate to *IIS Manager* → *Server Certificates* → select the server certificate, and configure enrollment settings—either via Windows Certificate Store (for self-signed or internal CA codes) or through Microsoft Total Validation for extended validation (EV) certificates.Ensure the certificate is properly imported into the StoreCert pool: 1. Open IIS Manager. 2.
Navigate to *Server Certificates*. 3. Right-click the server certificate and select *Enroll in Microsoft Total Validation* or *Enroll in StoreCert*.
4. Confirm enrollment and specify a renewal interval (recommended: 30–60 days before expiry). Critical: Enable background renewal by setting the renewal policy to “Automatically renew before expiration.” In the StoreCert counseling window or web.config config, ensure renewal triggers occur at least 14 days prior—this window avoids last-minute bottlenecks.
Step 2: Script-Based Renewal with PowerShell
While IIS supports event-driven renewal, predictable, scalable automation demands scripting. PowerShell, tightly integrated with Windows infrastructure, offers robust control over certificate lifecycle management. Example PowerShell snippet to trigger renewal and deployment: ```powershell $certName = "MyWebAppSSL" $validFrom = (Get-EventId -Filter NAME -Property Subject -Match "$certName").IssueDate $validTo = $validFrom.AddDays(365) $daysBeforeExpiry = 45 # Check current status $cert = Get-Exception -Property PublicKey -FilterSubjectName $certName if (-not $cert) { Write-Error "Certificate not found: $certName" exit } $daysRemaining = [Math]::Round($validTo - $validFrom).Divide(1, 365) if ($daysRemaining -lt $daysBeforeExpiry) { Write-Host "Renewing SSL certificate: $certName ($daysRemaining days left)" # Request new certificate via certificate request (example using CN Guru) $requestFigure = New-CertificateRequestSubject -Identity $certName -Subject "Common Name=*.mywebapp.com;OU=Servers;OU=Production" -SelfSigned $false $requestPartner = Add-CertificateRequestPartner -EntityId $requestFigure.Id -CAExamples @{"Microsoft Total Validation"="https://tpm2-v2.microsoft.com/tls"} # Submit request (replace with actual CA API call if not using Microsoft Total Validation) Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "https://certs.microsoft.com/va/CreateCertificateRequest" -Method Post -Body ($requestFigure | ConvertTo-Json -Depth 10) -ContentType "application/json" $newCert = Get-EventId -Filter SubjectName -Matches $certName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Select-Object -First 1 if ($newCert) { # Import and install newly issued certificate Import-Certificate -FilePath "$env:WindowsDir\Certificates\StoreCert\$($certName).cer" -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My -Destination Certificate Install-WebServerCertificate - certificateThumbprint $newCert.Thumbprint -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My # Update IIS certificate pool and trigger deployment Register-WebSite - Name "MyWebApp" - Type HTTP - PhysicalPath "C:\inetpub\wwwroot\mywebapp" - SSLProblemFile "$env:ProgramData\WebSSS\Certificates\$certName.cer" Restart-IIS - Force -Wait Write-Output "Certificate $certName auto-renewed and deployed to IIS successfully." } else { Write-Warning "Failed to obtain renewed certificate for $certName" } } ``` This script monitors expiration, triggers renewal requests via trusted CA endpoints, updates IIS certificate stores, and restarts services—all automatically.When embedded in a scheduled task (cron or Task Scheduler), it ensures daily compliance.
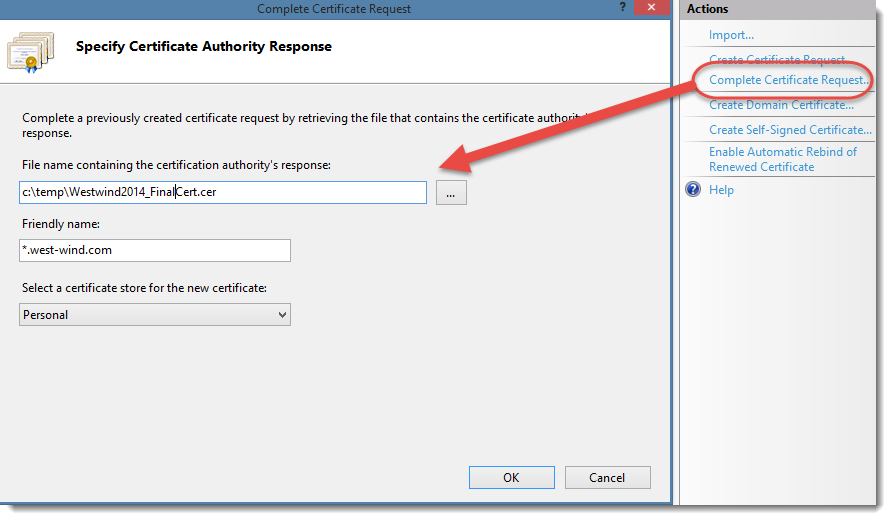
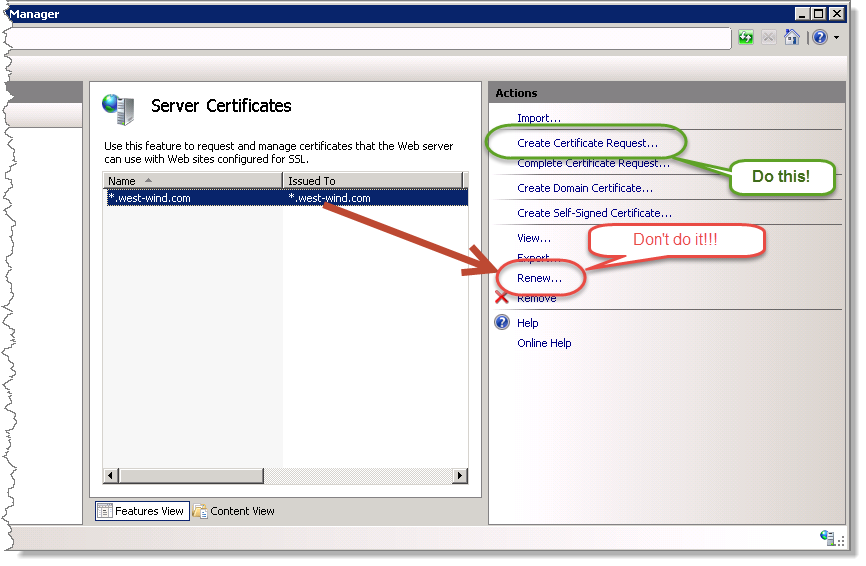
Step 3: Monitor, Audit, and Optimize Renewal Workflows
Auto-renewal reduces manual burden but does not eliminate oversight. Continuous monitoring is essential to verify certificate validity, renewal success, and deployment integrity.- Use IIS logs and Windows Event Viewer to track renewal attempts, errors, and certificate status changes. - Implement alerting via System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) or custom dashboards for failed renewals or pending triggers. - Maintain audit trails by logging renewal execution details—timestamp, issuer, validity window, and outcome—supported via Windows Event Forwarding or third
Related Post

Harry Enten: A Portrait of a Public Figure — Age, Height, Wife, and Career in Focus

How Did Al Capone Die? The Lethal Blow Behind the Legend of the Gangster Kingpin

The Indispensable Lais Deleon: Shaping Modern Latin American Thought Through Faith, Culture, and Intellectual Rigor

Yippee Meaning: Unlocking the Hidden Joy in Wordplay That Transforms Everyday Language

