Identify Motherboard Components Part 1: Unlock the Brain of Your PC
Identify Motherboard Components Part 1: Unlock the Brain of Your PC
Beneath every powerful desktop or precise laptop lies the unspoken champion of performance: the motherboard. Often overlooked by casual users, this intricate circuit board serves as the central nervous system of a computer, orchestrating the flow of data, power, and signals between every component. From the CPU and memory to storage and peripherals, each motherboard component plays a decisive role in determining system stability, speed, and expandability.
Understanding these core parts is essential for users, technicians, and enthusiasts seeking to optimize or repair their systems with confidence. This first in a series of deep dives into motherboard anatomy reveals the essential Building Blocks, decoding their functions and significance. Each motherboard is a meticulously designed platform composed of several key elements, each engineered to fulfill specific roles in a functional computing ecosystem.
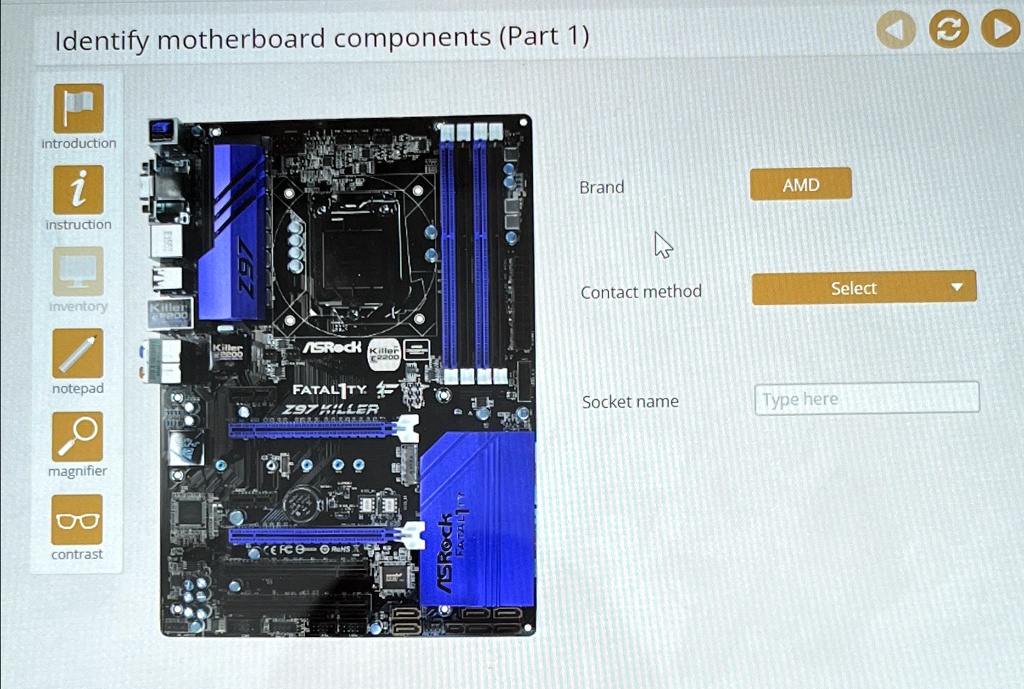
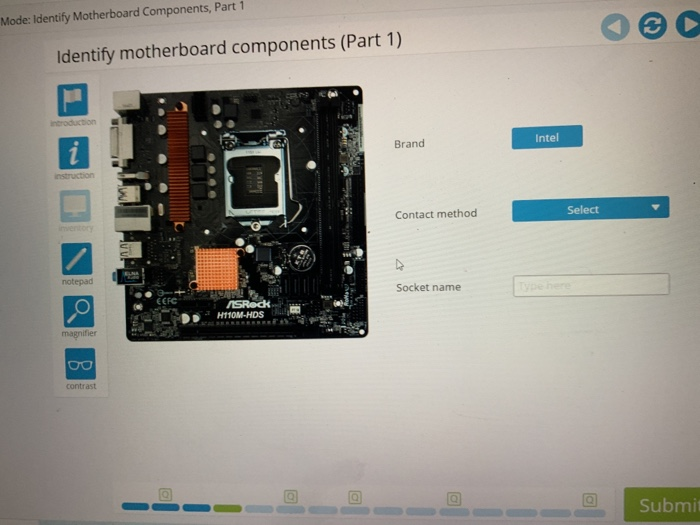
At the heart of this architecture is the **CPU socket**, a specialized connector where the processor resides. This socket not only secures the CPU but also manages critical thermal and electrical interfaces, ensuring optimal heat dissipation through heat spreaders and integrated cooling solutions. Without a secure and thermally efficient CPU placement, even the most advanced processor risks throttling or damage.
<.h2>Core Components: Where Computation Takes Place CPU Socket and Supporting Heat Management The CPU socket is the centerpiece where silicon intelligence meets physical engineering. Designed to accommodate a range of processor packages—such as LGA (Land Grid Array) or PGA (Pin Grid Array)—it ensures precise alignment and efficient power delivery via dedicated electrical contacts. Modern sockets, like the Z690 or X670 platforms, also integrate support for advanced cooling features, including standoff-height balancing and built-in thermal pads, reflecting the growing importance of maintaining processor stability under load.
As one PC engineer notes, “The socket is not just a connector—it’s the foundation of computational performance, influencing thermal efficiency, clock stability, and long-term reliability.” Memory Slots: The Speed Gateway to RAM Adjacent to the CPU socket lie the memory slots, designed for hosting RAM modules. These slots follow strict ECC (Error-Correcting Code) and CL (CAS Latency) standards, governing both data accuracy and speed. Contemporary motherboards typically feature dual or quad-channel configurations, enabling data throughput of 6400+ MHz and supporting SO-DIMM or DIMM formats depending on device form factor.
Proper installation—aligning notches and ensuring full contact—is critical, as missed slots or incorrect installation can cause system failure or reduced performance, highlighting the need for meticulous handling.
Expansion Slots: Bridging Three Decades of Technological Evolution At the upper half of the motherboard, expansion slots serve as portals for external devices and enhance functionality through compatible components. The **PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express)** standard dominates modern boards, offering four successive generations (PCIe 3.0, 4.0, 5.0) with dramatically increased bandwidth.
PCIe x16 slots, designed primarily for GPUs, now deliver over 4 GB/s per lane on 5.0 slots, supporting real-time ray tracing and ultra-high-definition rendering. Complementing this, **PCIe Gen 4 and Gen 5** interfaces extend performance deep into legacy expansion zones, enabling seamless integration of upgraded graphics cards, NVMe RAID controllers, and high-speed capture cards. For developers, engineers, and power users, mastery of these slots unlocks full system scalability.
Power Delivery Network: The Lifeline of Stability Beneath the visible circuits lies a complex power delivery (PD) network essential for converting and distributing power from the PSU to each component. Key elements include: - The **VRM (Voltage Regulator Module)**, typically comprising MOSFETs, inductors, capacitors, and heat sinks, step down 12V or 5V from the PSU to low voltages (3.3V, 1.35V) required by the CPU, chipset, and memory. High-quality VRMs—especially those with 1+1 or 2+2 cooling strategies—minimize voltage droop during intensive workloads, directly affecting overclocking potential and system endurance.
- The **power connectors**, such as the 8-pin EPS 12V and 6/8-pin CPU power, deliver massive current, often 200+ watts, demanding precise manufacturing and connection integrity. - Attention to **grounding and noise filtering**, often via dedicated capacitors and star grounding layouts, prevents voltage interference that can cripple diagnostics or memory stability. “A robust PD network is the sole conduit of reliable power,” emphasizes electrical systems analyst Jordan Reyes.
“Even the fastest CPU cannot operate without precise, loss-minimized power routing.”
Integrated Chipsets: The Brain Within the Board Embedded within the motherboard’s silicon fabric is the chipset—BIOS-level hardware that
![[GET ANSWER] Practice Mode: Identify Motherboard Components, Part 1 ...](https://cdn.numerade.com/ask_images/6c06848cfce8481d84101c72a4849cf2.jpg)
Related Post
Uncut Ullu: The Untamed Webseries That Defies Expectations—What You Need to Know Before Bingeing

Transformers The Last Knight: A Comprehensive Guide to Cast, Characters, and Cinematic Legacy
RVD Katie Forbes Celebrate Their Wedding Day

