How To Reopen a Closed Tab: Master the Secrets Behind Restoring Lost Web Sessions
How To Reopen a Closed Tab: Master the Secrets Behind Restoring Lost Web Sessions
Every website user has experienced the frustration: you’re mid-scroll, a critical download finishes, or a session expires — and suddenly, that open tab vanishes like smoke. Reopening a closed tab isn’t just about restarting a browser window; it’s about understanding the subtle mechanics that govern tab persistence, tracking mechanism behavior, and platform-specific workarounds. Whether due to automated session timeouts, security safeguards, or browser design choices, knowing how to reopen a closed tab empowers users to save time, retain workflow, and navigate digital spaces with confidence.
In this comprehensive guide, we break down the technical realities behind tab closure, explore why tabs close in the first place, and present proven methods—from native browser recovery tools to developer-level insights—on how to handle each scenario effectively.
Tabs don’t just close accidentally. Modern browsers and web platforms close tabs proactively to manage memory, secure user data, and prepare for dynamic browsing patterns.
Automated closures often trigger when a tab becomes idle for several minutes, a security policy enforcement, or when a page finishes loading resources that lock out new interactive content. Understanding these triggers reveals that tab closure is not always permanent—it’s often configurable and reversible.
The Technical Mechanics of Tab Lifecycle Management
At the core of tab behavior lies a combination of memory management strategies and security protocols. Browsers assign each tab a lightweight process to handle JavaScript events, render content, and synchronize with streaming or real-time data.When idle time exceeds threshold limits—typically 5 to 15 minutes—engines such as Chromium’s Blink or Gecko in Firefox initiate closure to free system resources. In parallel, HTTPS security standards and cross-site scripting (XSS) protections require browsers to limit long-running tab processes that could compromise session integrity. Additionally, some platforms use tab-specific checksums or cryptographic tokens to detect stale sessions, flagging them for termination.
This layered defense ensures responsiveness without sacrificing security, though it leaves users navigating unexpected disconnections. Why Your Tab Might Be Gone (and What Actually Happened: Before restoring a tab, identifying the cause is essential. Common triggers include: - **Idle Timeout:** Most browsers close inactive tabs after 10–15 minutes to optimize performance.
- **Session Expiry:** Automatic logout due to inactivity enhances account security. - **Resource Blocking:** Long-heavy pages (with video, ads, or scripts) trigger closure to conserve RAM. - **User-Action Required:** Autoplay audios or embedded content often pause or close tabs until manually resumed.
- **System Interventions:** Some mobile browsers or enterprise gateways forcibly close tabs under strict data policies. Understanding these patterns helps anticipate closure and plan recovery—such as saving progress before navigating to a time-intensive page.
If a tab vanished silently, survive the next steps with targeted recovery tactics tailored to the context.
Restoring a Tab: Proven Methods for Different Scenarios
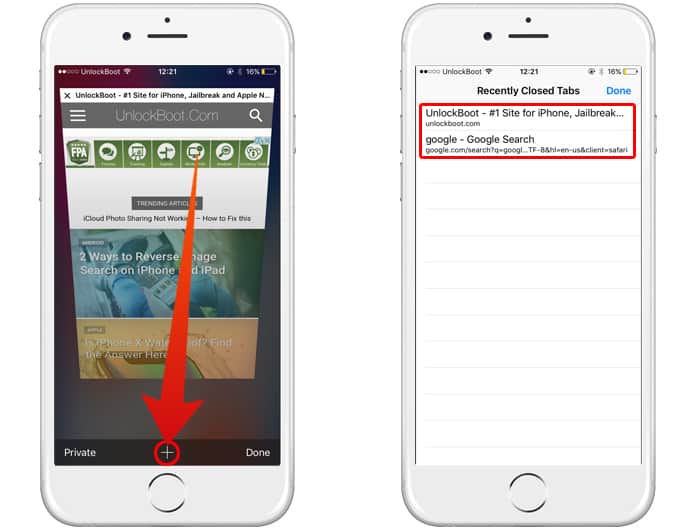
Check Browser Auto-Recovery Tools Modern browsers embed recovery features designed to automatically reopen recently closed tabs within minutes.In Microsoft Edge and Chrome, for example, tab restoration works through the “Open tabs” snapshot—usually retained for 12 hours. To access this: - On desktop: Use keyboard shortcut Ctrl+Shift+T (Windows/Linux) or Command+Shift+T (Mac). - On mobile (Chrome): Long-tap the tab area or swipe up; some versions restore recently closed tabs instantly via internal caching.
- In Firefox: Reopen from the menu or via shortcuts; the browser remembers active sessions closely. These tools rely on persistent user activity logs and do not typically restore fully interactive tabs instantly but offer immediate re-entry within recovery windows. Manually Refresh or Reopen via Shortcuts When auto-tools don’t act, manual intervention proves reliable.
For Chromium-based browsers: - Press `Ctrl + Shift + R` (hard refresh) to reload the current page and reopen associated tabs. - In Chrome, use `Ctrl + Shift + O` to reset all tab views, refreshing page state and opening all pending tabs. Firefox users benefit from simply refreshing via menu or restarting the session—reopening links and restoring context.
On macOS, restoring from Spotlight or Activity Monitor histories may reignite dormant tabs if browser cookies were preserved. Backup Workflow Proactively to Catch Closures Early Rather than reacting, build habits to prevent loss. Always: - Save progress in editable documents or spreadsheets before



Related Post

Next Genshin Banner: What’s Driving the Next Wave of the Original’s Dominance

Columbus Ohio Zip Codes Your Ultimate Guide: Decoding the Numbered Heartbeats of America’s Midwestern Hub

Where Is Benfica From? Tracing the Roots of a Football Dynasty

