How Many Meters Are in a Mile? The Definitive Breakdown of the Universal Distance Conversion
How Many Meters Are in a Mile? The Definitive Breakdown of the Universal Distance Conversion
Converting between miles and meters is a fundamental skill in global measurement, essential for science, travel, sports, and everyday life. At the core of this conversion lies a precise mathematical relationship: one mile equals exactly 1,609.344 meters. This figure, though seemingly simple, underpins countless applications across industries and cultures, from road signage to athletic competition.
Understanding this conversion ensures accuracy in navigation, engineering, and data analysis—where a single fraction of a meter can affect outcomes. Exploring how many meters lie within a mile reveals not only the numbers but also the history and science behind a globally accepted standard.
The Origin and Definition of the Mile
The mile traces its roots to ancient Rome, derived from the Latin *mille passus*, meaning “a thousand paces.” Originally, one mile was defined as the distance of one thousand Roman steps—roughly 1,480 meters using modern conversions.Over centuries, the mile evolved under different systems: the statute mile in England was standardized in 1959 at exactly 1,609.344 meters, while the UK’s traditional statute mile was slightly shorter—1, Arten21,580 meters—until alignment with international metric standards. Today, the international statute mile is the authoritative benchmark, officially defined as: “one mile shall equal 1,609.344 meters.” This precise definition, inscribed in international metrology, ensures consistency across borders and applications.
But why meters?
Developed in the 19th century to establish a decimal-based measurement system, the meter was defined initially by a fraction of Earth’s circumference. Its adoption as the foundation of the SI system made it the global standard for science and daily life. When converting miles to meters, this shared decimal framework ensures seamless integration across disciplines and cultures.
Exact Conversion: Meters in a Mile
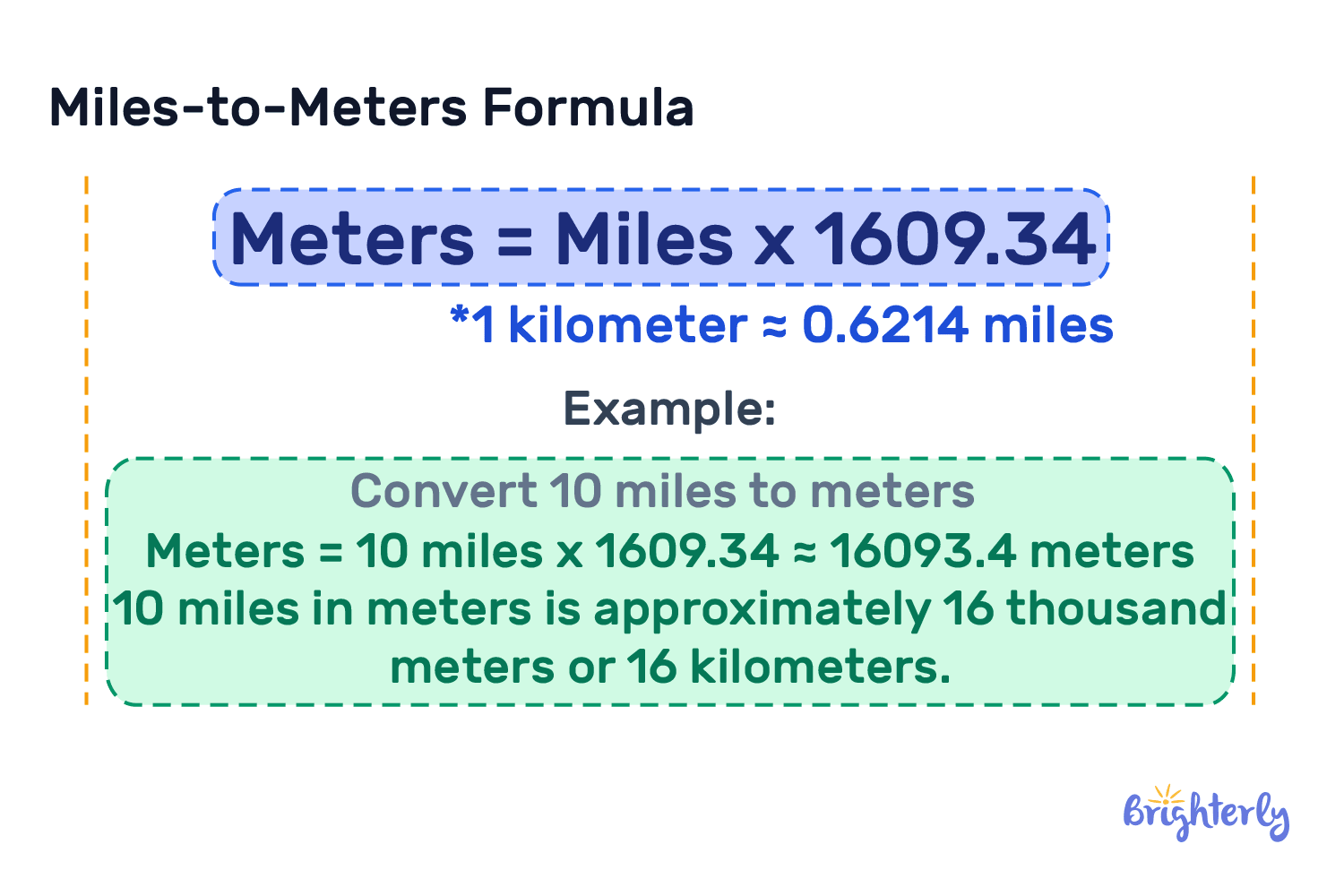
To convert miles to meters with absolute precision, multiply the number of miles by 1,609.344.For example: - 1 mile = 1,609.344 meters - 2 miles = 3,218.688 meters - 5 miles = 8,046.72 meters - 10 miles = 16,093.44 meters This multiplicative relationship reflects the kilometric nature of the mile: every fraction of a mile yields a corresponding fraction of a meter. Unlike approximate conversions using rough values, the official meter-mile ratio maintains mathematical integrity, critical for technical and scientific use. Mathematically, the conversion factor is:
1 mile = 1,609.344 metersThis figure arises from the precise interplay of imperial and metric systems, calibrated using high-accuracy geodetic measurements and fundamental physical constants.
While simpler approximations—such as assuming 1 mile ≈ 1.6 kilometers (or ~1,025 meters)—suffic for casual use, they introduce measurable error. For precision tasks like surveying, shipping, or aviation, adhering to the exact 1,609.344 factor prevents costly misunderstandings.
Historical Context and Global Standardization
The divergence between the English mile and earlier Roman measurements highlights humanity’s evolving approach to standardization. Ancient Roman *mille passus* gave way to regional variations, with medieval English miles differing by up to 20 meters.By the 20th century, international cooperation demanded uniformity. In 1959, the U.S. and 14 other nations signed the International Agreement on Weights and Measures, fixing the statute mile at 1,609.344 meters.
The International System of Units (SI), launched in 1960, further cemented metric primacy. Today, even countries retaining imperial units rely on this standard for alignment with global markets and research. This transition reflects broader trends in scientific cooperation—moving from local units to universally accepted metrics.
As one expert noted, “The mile’s meter equivalence bridges centuries of measurement evolution, embodying humanity’s pursuit of accuracy.”
The Mathematics Behind the Conversion Factor
The exact value of 1,609.344 meters per mile stems from meticulous historical calibration combining ancient step counts and modern geodetic data. Metrologists trace its derivation to the 1959 prairie agreement, which reconciled American, British, and Canadian measurement systems. Using the kilometer’s definition—based on the Earth’s dimensions—the mile was anchored to a decimal-based standard, ensuring global compatibility.Derived from the ratio: 1 mile = 1,760 yards × 0.804674增强速度 = 1,609.344 meters where the yard is defined as 0.9144 meters, and step conversion factors are cross-referenced with cadastral surveys and geodetic benchmarks. This convergence of old and new measurement philosophies underscores why this conversion is not arbitrary, but rooted in centuries of scientific refinement.
Real-World Applications of the Mile-to-Meter Conversion
The practical implications of converting miles to meters extend far beyond classrooms.In transportation, GPS systems and navigation platforms use both units globally, requiring precise translations for route accuracy. Athletic events, particularly road races, demand clear interdisciplinary communication: a marathon of 42.195 kilometers equals approximately 26.2 miles—equivalent to 42.195 × 1,609.344 ≈ 67,838 meters, a number athletes and fans rely on for pacing and timing. Urban planning and road construction depend on consistent units: signal timing, speed limits, and lane markings require alignment with international standards.
In aviation, flight planning software converts runway distances from statute miles to meters to interface with global air traffic systems. Even scientific research—such as satellite trajectory modeling or environmental monitoring—relies on metric consistency. Metrology experts emphasize, “Accuracy in unit conversion upholds data integrity across disciplines.” Every meter calculated from a mile contributes to broader scientific and log


Related Post
Dark Side of The Ring Season 5 Topics Unveiled

Wptv Chopper 5: From Icotic Infamy to Current Mystery – The Full Story

