How Does Air Tag Work? Inside the Tiny Tracker That Tracks Your World
How Does Air Tag Work? Inside the Tiny Tracker That Tracks Your World
At its core, Apple’s Air Tag is a revolutionary Bluetooth-enabled personal tracking device designed to help users locate lost or misplaced belongings—Keys, bags, wallets, or small gifts—within a MetroRadius of a paired iPhone. More than a simple Bluetooth beacon, the Air Tag leverages a sophisticated blend of wireless technology, sensor fusion, and cloud integration to deliver accurate, real-time tracking with minimal effort. Its operation hinges on a seamless partnership between hardware innovation and Apple’s global Network service, transforming a pocket-sized gadget into a powerful visibility tool.
The Air Tag itself measures just 1.7 inches in diameter, weighs less than 5 grams, and fits quietly on everyday items thanks to its minimalist, weather-resistant clamshell design. Its primary function is enabled by a Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) module, calibrated to operate on the 2.4 GHz ISM band—a frequency standardized worldwide for short-range device communication. By continuously broadcasting a low-power signal, the Air Tag becomes detectable within up to 30 to 50 meters (approximately 100–165 feet), depending on environmental conditions and obstructions.
Unlike older Bluetooth trackers, however, the Air Tag incorporates ultra-wideband (UWB) technology in recent models, allowing for centimeter-level accuracy in close proximity—enabling users to pinpoint an item’s last known location with precision when paired with compatible iPhones running iOS 17 or later.
But detecting a signal is only half the battle; interpreting and conveying location data requires deeper technology. When a user’s iPhone comes within range, the Air Tag’s broadcast triggers a response through Apple’s Network service—a dedicated cloud-based platform dedicated exclusively to Bluetooth Low Energy object tracking. This system employs direction-finding algorithms and signal triangulation by anchoring the Air Tag’s BLE broadcast to its physical location within the user’s Apple Network.
“The Network uses multiple iOS devices in the vicinity to calculate the tag’s exact position based on signal strength and timing,” explains Apple’s technical documentation. “This process is passive and occurs within milliseconds—no extra user action is needed.” The result is a real-time map update on the paired iPhone’s Find My network interface, visually marking the item’s trajectory across space and time.
The tracking capability is enhanced by a suite of passive sensors embedded within the Air Tag. A triaxial accelerometer detects movement patterns, distinguishing between drops, swings, or idle placement, while a magnetometer stabilizes orientation and orientation data helps assess whether the tag is upright or displaced.
These inputs feed contextual awareness into the tracking logic, reducing false alerts and improving accuracy in crowded urban environments where signal interference is common. “We designed the Air Tag to understand not just its own location, but the dynamics of its placement,” said one Apple hardware engineer in internal documentation. “It doesn’t just track—it learns.”
To set up, users simply activate the Air Tag via the Find My app, pair it with their iPhone via Bluetooth, and the system begins transmitting.
Once active, the tag enters a 10-second wake cycle every 10 minutes to conserve battery, ensuring continuous promise without rapid depletion. When an item is misplaced, location history is viewable in the Find My app—displaying routes or geofences—that helps users reconstruct how and where their belongings last moved. In rare cases where an Air Tag is verloren, the Network service supports re-location tracking through overlapping iOS devices, though responsiveness depends on local Apple infrastructure density.
“Apple’s Network is built for privacy and reliability,” notes a cybersecurity analyst. “Each tag’s data remains encrypted and user-controlled—no personal tracking occurs beyond what AirTags are designed to provide.”
Powering the Air Tag is a lithium-polymer battery rated for up to one year with typical use. Designed for minimal maintenance, the battery requires replacement only after significant depletion—typically every year—or manually via a small removal nub.
The compact form factor and low power demands make this long lifespan feasible, with manufacturers emphasizing durability through shatter-resistant materials and sealed electronics. “We optimized every layer to keep the practicality barrier nearly invisible,” said a product designer involved in the Air Tag’s development. “The device should feel like a normal keychain—not a battery warning on your back.”
The ecosystem integration defines the Air Tag’s true strength.
It works natively with Apple’s Find My network, a global infrastructure spanning millions of iOS devices, enabling rapid pickups even if the tag stays out of direct iPhone range. It also syncs across devices when matched to a user account, supporting multiple owners and shared family items. For non-Apple users, however, functionality is limited—the AirTag is intentionally optimized for iOS devices, with Android compatibility restrictive due to privacy and spectrum regulations.
Still, third-party trackers and GPS-enabled alternatives exist, though they lack the seamless Apple ecosystem synergy and real-time precision of the native Air Tag experience.
Resilience to interference remains a key engineering focus. The BLE signal operates independently of Wi-Fi or cellular networks, minimizing congestion risks. Direction-finding through the Network service employs beamforming-like techniques across multiple iOS devices, effectively filtering obstacles like walls or metal.
“Even

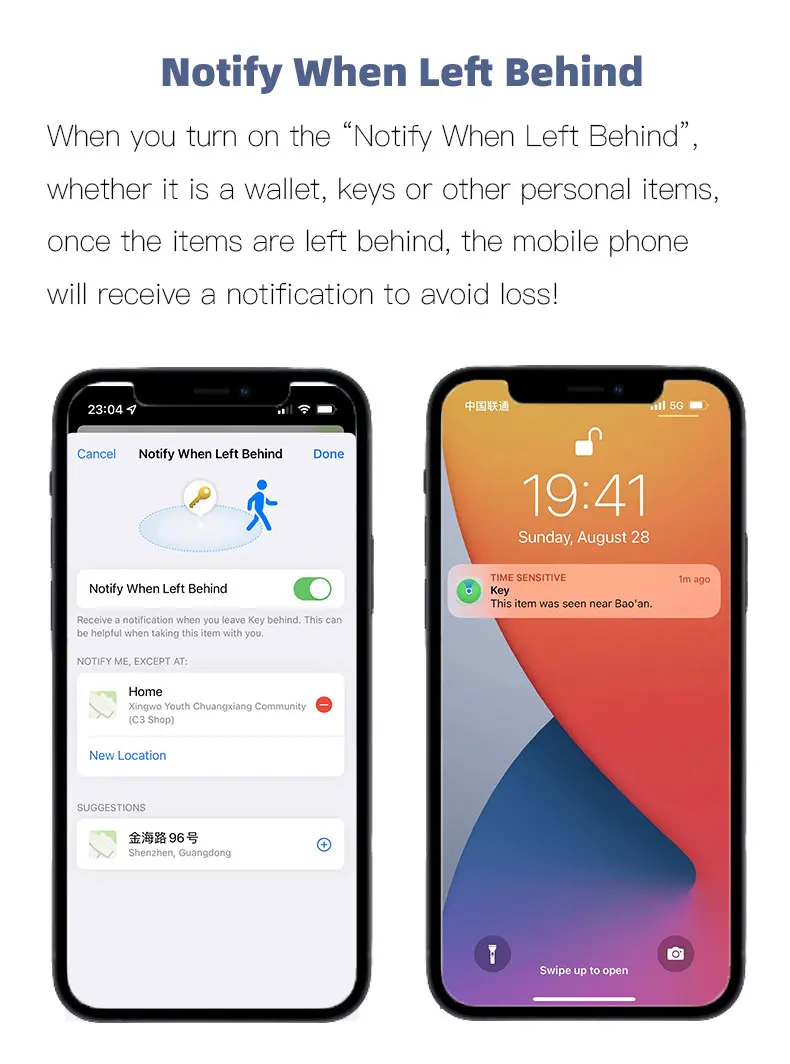

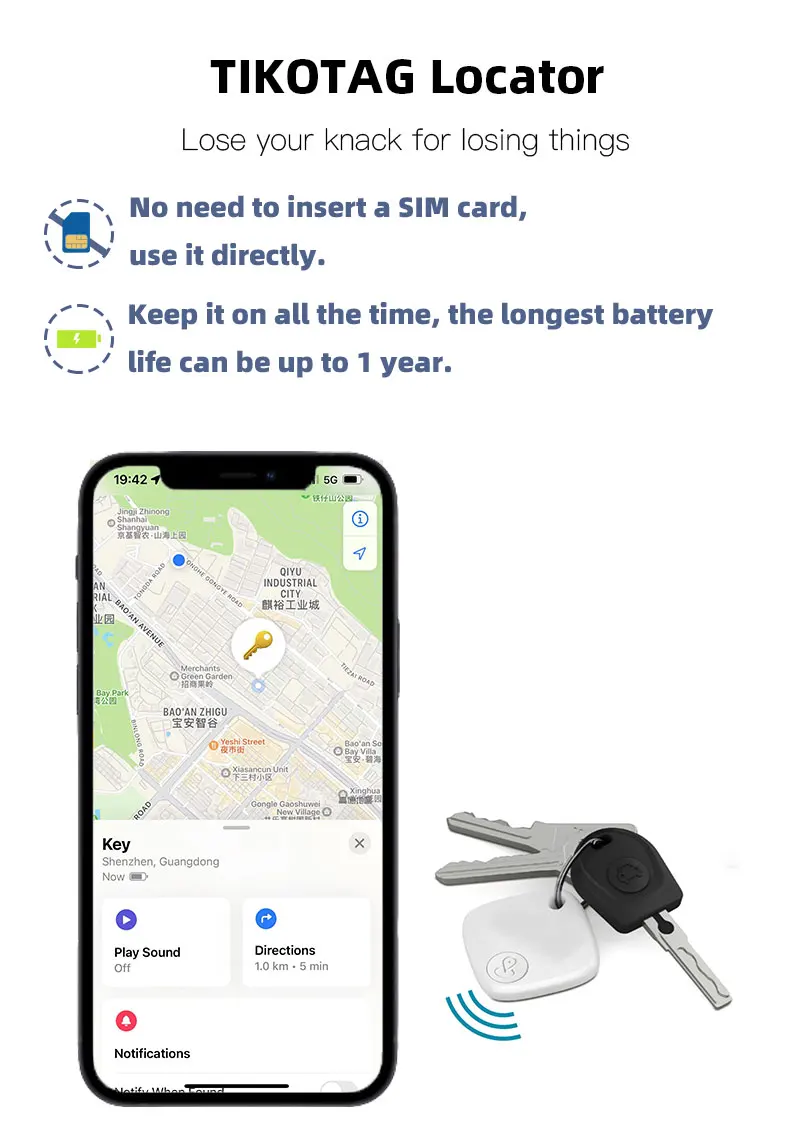
Related Post
How Does AirTag Work: The Smart Tracker Revolutionizing Everyday Location.

The Power of Authentic Voice: How Mythr Org Employees Shine on Their Official YouTube Channel

Is Camryn Grimes Pregnant? What the Public Wants to Know About Her Current Status

Columbus Zoo Breaks Barriers: Latest News & Live Updates Redefining Modern Zoological Excellence

