Houston’s Energy Edge: How the Spindle City Powers America’s Future
Houston’s Energy Edge: How the Spindle City Powers America’s Future
At the heart of Texas’ most dynamic metropolis, Houston stands not just as a sprawling urban center, but as the operational nerve center for the global energy industry—specifically oil, gas, and emerging clean energy transitions. From its towering skyline intertwined with energy firm headquarters to its deepwater ports and research institutions, Houston commands a strategic influence that reverberates far beyond its Gulf Coast borders. With over 4,000 energy companies headquartered or maintaining major operations in the city, Houston doesn’t merely participate in energy markets—it shapes them.
This article explores the city’s evolving role in energy innovation, infrastructure, and sustainability, revealing how its historical strengths are aligning with tomorrow’s demands.
Conventions of industrial might and innovation, Houston’s energy landscape is a study in transformation. Once synonymous solely with drilling rigs and petrochemical refines, the city now leads in technological adaptation and strategic diversification.
According to the Greater Houston Partnership, the energy sector contributes over $300 billion annually to the local economy, supporting more than 220,000 direct jobs and countless indirect roles across logistics, engineering, and research. Yet beyond economic scale, Houston’s real power lies in its unique ecosystem: a convergence of Fortune 500 giants like ExxonMobil and Chevron, elite research hubs such as Rice University and the University of Houston, and regulatory and trading centers that make real-time energy decisions possible.
The Infrastructure That Fuels a Global Energy Hub
Houston’s dominance is not accidental—it is built on world-class infrastructure engineered to support high-volume energy production, processing, and export. The city’s port complex, the Houston Ship Channel, ranks as one of the busiest in North America, handling more than 240 million tons of cargo each year and serving as a critical corridor for crude oil exports and refined product distribution.The channel stretches 190 miles and supports over 5,000 oil and gas-related terminals, making Houston the top U.S. port for energy exports.
Beyond maritime access, Houston’s intricate pipeline network—grubbed with over 1,300 miles of pipelines—feeds domestic refineries and feeds into offshore platforms in the Gulf of Mexico.
Coupled with Hess Energy Terminal and the proposed Gulf Coast Express pipeline, this system ensures rapid, secure energy conveyance from wellhead to market. According to a 2023 report by the Energy Infrastructure Center, Houston’s infrastructure enables up to 15% of U.S. crude oil exports, a figure expected to grow with new LNG export facilities underway.
Innovation at the Crossroads: From Fossil Fuels to Clean Energy While legacy fossil fuel operations remain foundational, Houston is pioneering the transition toward a lower-carbon energy future.
The city’s shift reflects both market pressures and deliberate local policy, driving investments in carbon capture, hydrogen, and renewable integration. The Clean Energy Hub at Rice University, launched in 2022, exemplifies this forward-looking approach—blending academic research with industry partnerships to develop scalable clean tech solutions tailored to Houston’s industrial footprint.
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) has emerged as a cornerstone of this transition.
Projects like those spearheaded by Occidental Petroleum’s 45Q Initiative—aimed at sequestering millions of tons of CO₂ annually—leverage Houston’s deep technical expertise to reduce emissions from both existing plants and new energy ventures. Meanwhile, hydrogen hubs are gaining traction: the Houston Hydrogen Cluster, backed by industry leaders and the U.S. Department of Energy, aims to position the city as a national leader in green and blue hydrogen production.
The cluster’s planned infrastructure—including pipelines, storage facilities, and refueling nodes—will serve industrial clusters across Texas, turning Houston into a regional clean energy nexus.
Workforce, Talent, and the Human Engine of Energy Change A city’s energy future depends equally on its people. Houston’s energy sector thrives on a diverse, skilled workforce cultivated through robust educational pipelines and workforce development initiatives.
Rice University’s Rice Energy Initiative trains engineers and scientists in energy systems, while the University of Houston’s Cullen College of Engineering offers specialized programs in offshore operations, reservoir modeling, and sustainable infrastructure.
Community colleges such as Houston Community College (HCC) deliver targeted technical training in pipeline maintenance, automation, and digital monitoring—fields crucial to modernizing energy operations. These institutions, partnered with energy firms through




Related Post
Decoding 'Do A Barrel Roll Do': A Deep Dive into Gaming History and Internet Culture

Bluewaffles: The Hidden Powerhouse Transforming Modern Food Innovation
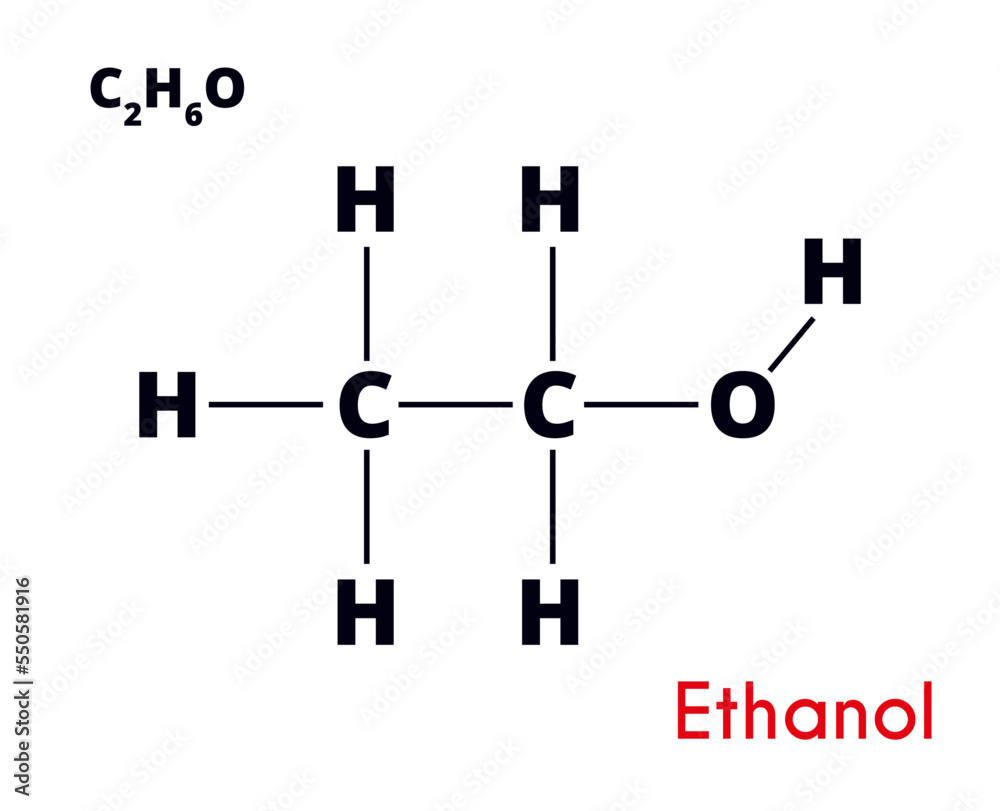
Ethanol’s Chemical Formula: The Simple Molecule Driving Global Impact

