Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling: The Proven Performance Edge — or Hidden Bottleneck?
Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling: The Proven Performance Edge — or Hidden Bottleneck?
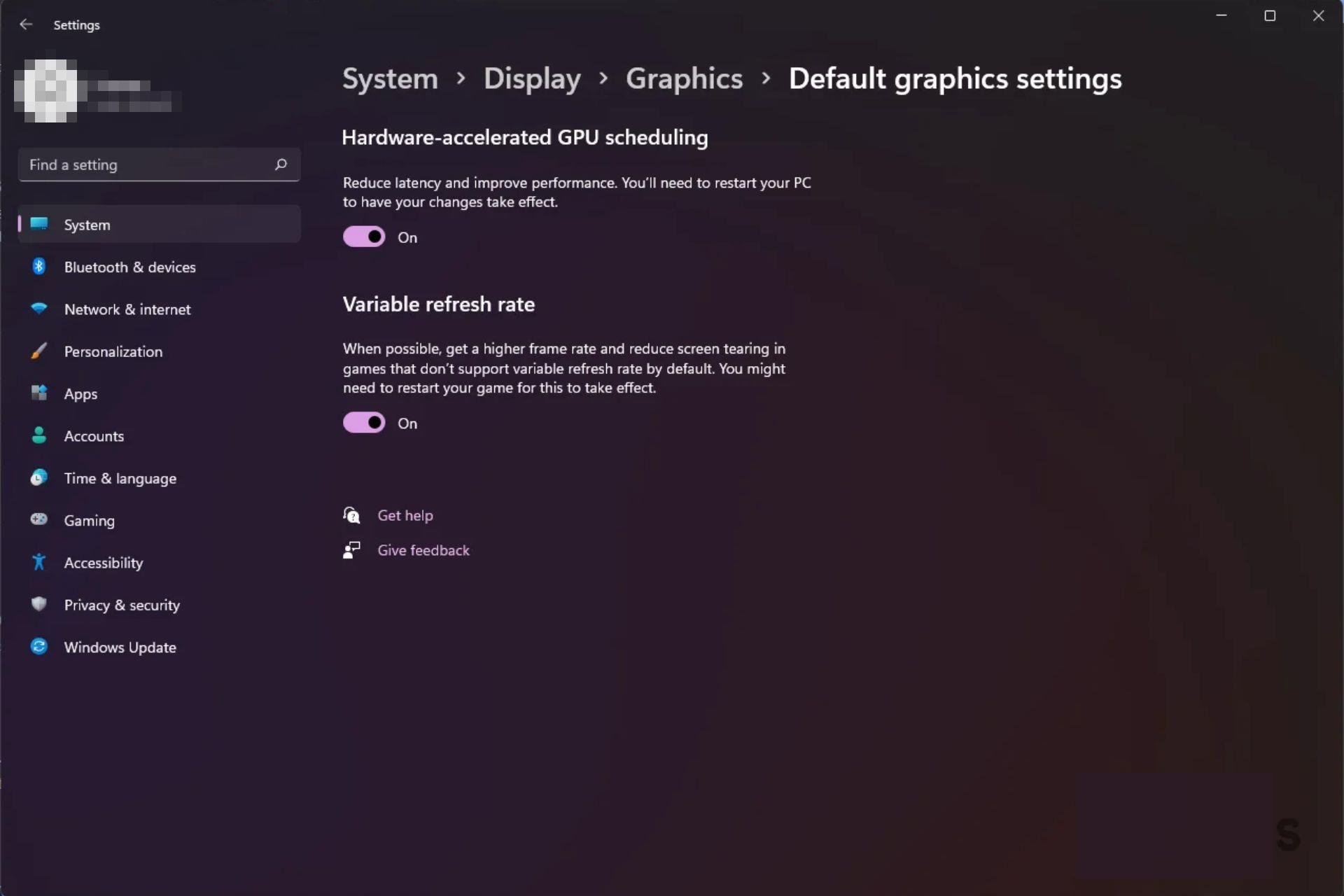
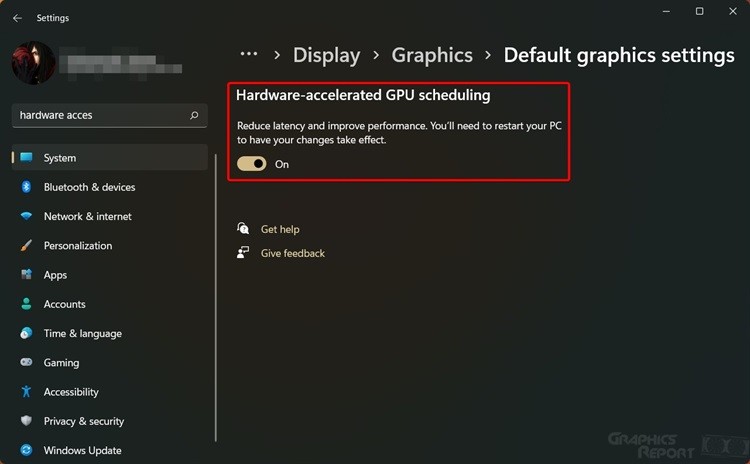
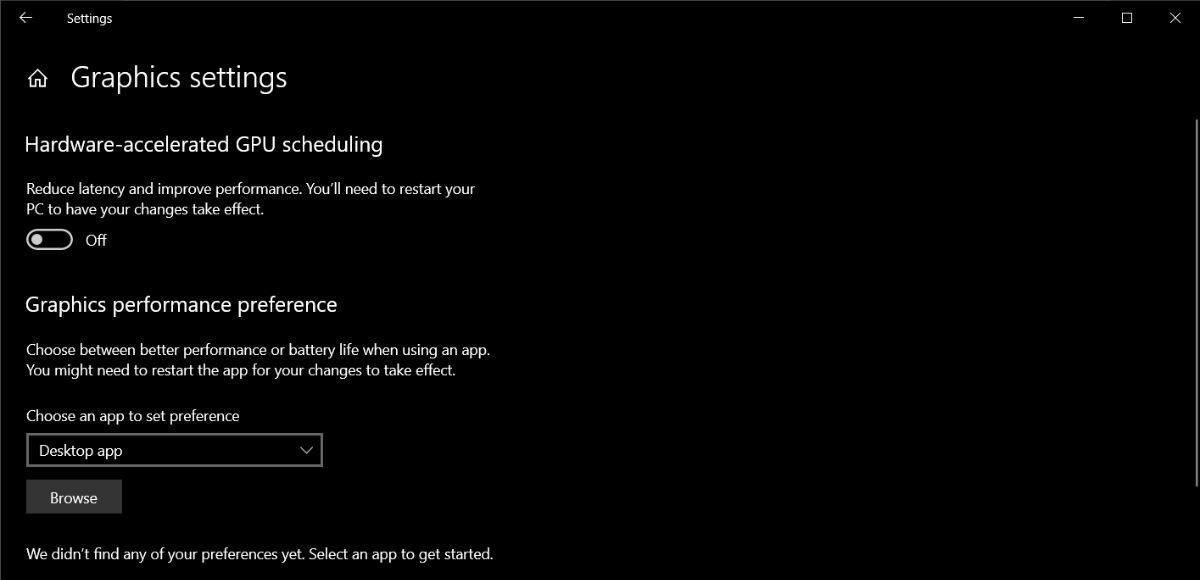
In an era dominated by demanding graphics workloads, from real-time ray tracing in AAA gaming to AI inferencing in edge computing, hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling has emerged as a cornerstone of efficient computing. This technology assigns and prioritizes GPU tasks across cores and memory, aiming to maximize throughput while minimizing latency. But is it truly a breakthrough or just a false promise wrapped in hardware glow?
The true effectiveness of GPU scheduling lies in its execution — and its impact is far from uniform across applications and platforms. What is hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling? At its core, it’s the intelligent orchestration of GPU tasks by the system’s scheduler, leveraging dedicated hardware or firmware to allocate resources dynamically, often in real time.
This contrasts with older, static scheduling that treated all workloads equally, leading to wasted cycles and underutilized cores. Modern GPUs are highly parallel, soon even multi-core with dozens or hundreds of streaming multiprocessors — yet raw raw power remains useless without efficient scheduling. Hardware-accelerated scheduling seeks to bridge this gap by dynamically adjusting task priorities based on workload type, memory access patterns, and even thermal or power constraints.
“The scheduler acts as the CPU’s silent conductor,” explains Dr. Elena Marquez, a GPU architecture researcher at Stanford. “It decides which threads run when, how much memory each gets, and whether to offload work to dedicated tensor or ray tracing units — all in microseconds, with minimal overhead.” The benefits of this precision scheduling are compelling.
In high-fidelity gaming, for example, hardware-accelerated scheduling ensures frame pacing stays smooth by quickly shifting focus between rendering, physics, and AI logic. In machine learning, it enables rapid batch processing of tensor operations, crucial for training deep neural networks. “Without smart GPU load balancing, even the most powerful card wastes cycles killing less aggressive processes,” notes Mark Reynolds, senior engineer at a leading GPU vendor.
Performance benchmarks consistently show up to 30-45% gains in rendering throughput and 20-35% lower latency in compute-heavy tasks when scheduling is optimized. Yet, the technique is not without drawbacks. When misconfigured or overloaded, GPU scheduling can introduce bottlenecks that tribalize performance.
Legacy drivers or mismatched workload characteristics — such as highly irregular GPU threads — may confuse the scheduler, turning theoretical efficiency into deadlock or thrashing. “The scheduler’s effectiveness hinges on accurate workload profiling,” says Dr. Marquez.
“If a task disguises itself as GPU-bound but leaks memory or blocks unnecessarily, the scheduler confirms that blockage — amplifying frustration rather than solving it.” This repression of diagnostic transparency further complicates troubleshooting, leaving developers to chase elusive optimization leaks. From an operational standpoint, hardware-accelerated scheduling often demands close alignment between software and hardware. APIs like Vulkan and DirectX 12 Native expose explicit control over scheduling behavior, empowering developers but increasing complexity.
Meanwhile, desktops and servers with early-generation GPUs may lack robust, hardware-backed scheduler APIs, leaving scheduling to volatile, driver-dependent algorithms. Energy efficiency is another critical layer: shadows of excessive scheduling overhead can spike power draw, undermining battery life in mobile devices and cooling demands in data centers. Real-world usage illustrates the stark contrasts.
A 2023 study comparing GPU workloads across gaming, video editing, and AI training revealed: - Gaming: Scheduling reduced dropping frames by 32% on high-end RTX 50 series GPUs. - Video Rendering: Selectively scheduling decompression and encoding threads improved throughput by up to 40%. - Machine Learning: Exclusive use of tensor cores with intelligent prefetching cut average batch latency from 1.8s to 1.1s.
But for legacy 3D modeling software on half-frozen drivers, the same scheduling mechanisms failed to stabilize performance, instead triggering erratic thread preemption. The roadmap to optimal GPU scheduling favors adaptability. Future directions include AI-driven pre-scheduling, where predictive models anticipate workload patterns before execution, and enhanced cross-layer integration between CPU orchestrators and GPU schedulers.
Standardization of DPUS (DirectComponents of the GPU Scheduler Interface) aims to unify scheduling behavior across platforms, reducing optimization silos. Emerging technologies like programmable shader pipeline stages and real-time scheduling hooks in GPU register files promise finer-grained control. Despite its technical promise, hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling remains a double-edged sword.
When properly tuned and supported by robust drivers, it elevates performance to near-ideal efficiency. When mismanaged or forced onto unsuitable workloads, it introduces invisible costs that erode gains. It is not inherently good or bad — but profoundly pivotal.
As computational demands grow more intense, the scheduler’s role evolves from background helper to frontline enabler. Understanding its mechanics, limitations, and proper application is no longer optional for developers, platform vendors, or enthusiasts. In the race for computing supremacy, mastering GPU scheduling is not just advantageous — it is essential.
The verdict: hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling is a transformative technology, but its efficacy depends on context, execution, and alignment with workload needs. When wielded with precision, it delivers remarkable performance wins. When neglected, it becomes a hidden bottleneck.
Its future hinges on smarter design, clearer diagnostics, and deeper integration—ensuring that every frame rendered, every tensor processed, runs as efficiently as possible.

Related Post

Val Warner Husband: The Unseen Architect Behind a Life of Purpose and Partnership

Unlocking Your Potential: Pittsburgh Neurosurgery Fellowship
Paying Tribute to Michael Galeotti: This Life Terminated

