Exergonic Energy: Harnessing the Power of Spontaneous Energy Release
Exergonic Energy: Harnessing the Power of Spontaneous Energy Release
Exergonic energy—released spontaneously through self-sustaining chemical, nuclear, or biochemical reactions—forms the invisible backbone of countless natural and engineered systems that drive modern civilization. Unlike endergonic processes, which absorb energy, exergonic transformations liberate usable energy, enabling everything from cellular respiration to power plants and industrial processes. Understanding exergonic energy not only unveils the elegance of energy flow in nature but also opens pathways for cleaner, more efficient technologies.
With global demand for sustainable energy on the rise, exergonic systems are increasingly pivotal in solving energy challenges of the 21st century.
Defining Exergonic Energy: The Science Behind Spontaneous Power
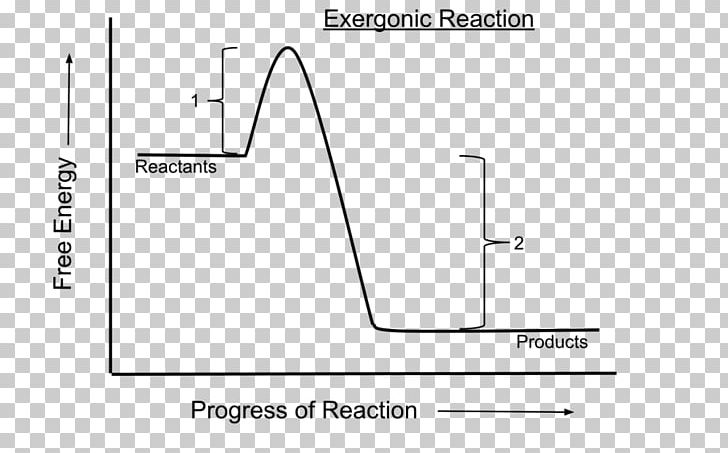
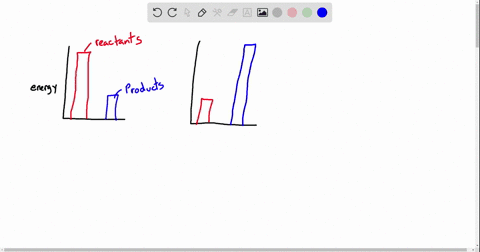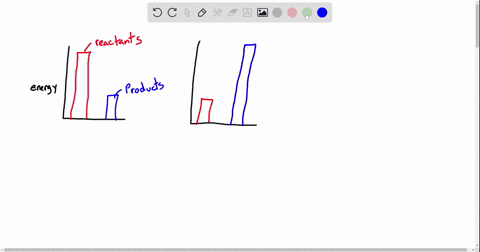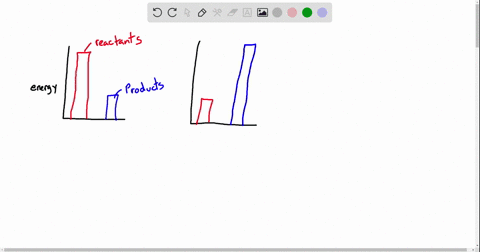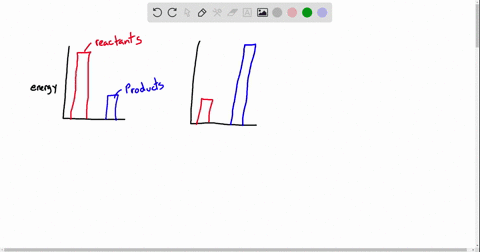
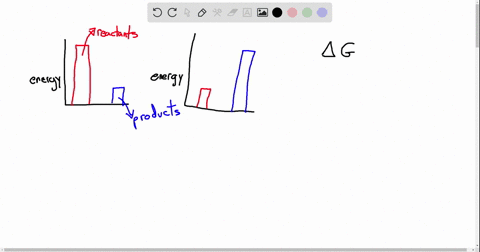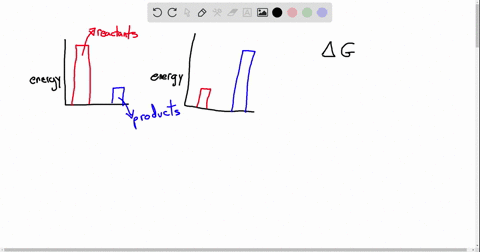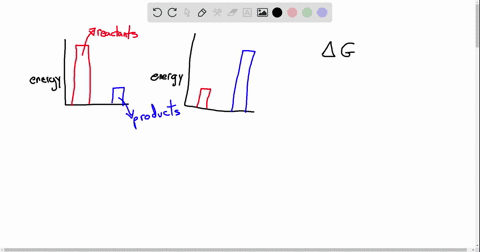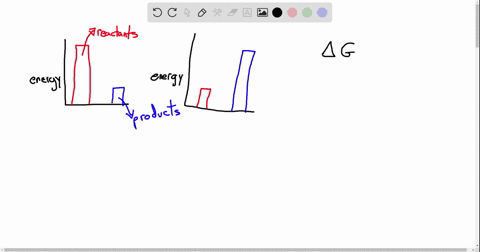
Exergonic energy arises when a reaction proceeds in a direction that decreases total free energy, releasing energy that can be harnessed as heat, electricity, or mechanical work. At its core, the concept is rooted in thermodynamics: if the Gibbs free energy change (ΔG) of a process is negative (ΔG < 0), the reaction is exergonic by definition. This releases usable energy without external input, distinguishing it from non-spontaneous endergonic reactions that require continuous energy supply.
Common exergonic processes include: - Cellular respiration, where glucose oxidation generates ATP—the cellular energy currency.
- Combustion of hydrocarbons, a principle behind gasoline engines and power generation. - Nuclear fission, which powers reactors by splitting heavy atoms to release massive energy. - Redox reactions in microbial fuel cells, converting organic waste into electricity.
“Exergonic reactions are nature’s efficient engines—extraordinary in their ability to transform stored energy into usable forms effortlessly,” notes Dr. Elena Martinez, a biophysicist specializing in energy metabolism.
Biological Foundations: How Life Relies on Exergonic Transformations
Life itself is powered by a cascade of exergonic reactions.
In biological systems, energy is extracted through redox processes in mitochondria, where glucose and oxygen undergo oxidation, releasing energy captured as ATP. This biochemical machinery turns food into usable energy with remarkable efficiency—up to 40% of energy yield in aerobic respiration, far surpassing many industrial counterparts.
The principles extend beyond human metabolism: from photosynthetic bacteria generating biomass to deep-sea vent microbes thriving on sulfur compounds, biological exergonic pathways illustrate evolution’s mastery of energy extraction.
As research shows, even extremophiles in hostile environments exploit low-energy gradients through finely tuned exergonic reactions, offering clues for synthetic energy systems.
“In every breath we take and every cell that functions, exergonic energy is silently resolving biochemical equations—delivering sustainability at microscopic scales,” says Dr. Rajiv Nor, a leading expert in bioenergetics.
From Cells to Industries: Applications of Exergonic Energy in Technology
The technological exploitation of exergonic energy spans generations.
In biological contexts, engineered systems like microbial fuel cells generate electricity by mimicking natural metabolisms, treating wastewater while producing power.
In engineered systems: - Batteries and fuel cells exploit exergonic redox chemistry—lithium-ion batteries, hydrogen fuel cells—providing compact, high-density energy storage. - Combustion turbines and internal combustion engines rely on engineered exergonic reactions to convert fuel energy into motion and electricity, underpinning transportation and grid power. - Radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs) use nuclear decay’s exergonic heat to supply long-duration power for space missions and remote installations.
Emerging innovations, such as enzymatic bio-batteries and plasma-assisted combustion, aim to harness exergonic processes with higher efficiency and lower environmental impact, positioning exergonic energy at the heart of future energy transitions.
Advantages and Challenges of Exergonic Systems
Exergonic energy offers compelling advantages: it delivers concentrated, reliable power with high energy density and minimal external input when properly managed.
Its spontaneous nature enhances efficiency and reduces entropy buildup compared to systems dependent on constant energy supply.
Yet it presents critical challenges: uncontrolled exergonic reactions—like unmanaged combustion—risk thermal runaway and hazards. Additionally, managing byproduct formation, especially in nuclear or chemical processes, demands strict containment and waste protocols. Environmental considerations also arise: fossil fuel combustion, while exergonic, emits greenhouse gases, reinforcing the need for clean exergonic alternatives.
Balancing efficiency with safety and sustainability remains paramount.
According to Dr. Lin Wei, a thermodynamic strategist, “The true potential of exergonic energy lies in intelligent design—systems that release power predictably, safely, and with minimal ecological footprint.”
The Future of Energy: Exergonic Processes as Catalysts for Sustainability
As global energy demands surge and climate imperatives intensify, exergonic energy emerges not just as a scientific phenomenon but as a cornerstone of future innovation. Advances in nanotechnology, synthetic biology, and materials science are unlocking new ways to capture, store, and deploy exergonic reactions with unprecedented precision and efficiency.
Researchers are engineering biohybrid systems that merge living cells with electronic circuits, harnessing metabolic exergonic flows for sustainable electricity.
Meanwhile, catalytic processes inspired by enzymatic pathways are streamlining industrial chemical production, slashing energy waste. In nuclear fusion—still emerging—the controlled harnessing of exergonic plasma reactions promises a near-limitless, low-carbon energy source.
Exergonic energy’s potential extends beyond raw power: it redefines how societies generate, store, and distribute energy. “The future energy landscape will be shaped by our ability to wield spontaneous energy flows wisely,” reflects Dr.
Womeneng Chen, a frontier energy researcher. “Exergonic systems offer the blueprint—efficient, transformative, and essential for a resilient, low-carbon world.”
In essence, exergonic energy stands as the silent force behind life’s vitality and technological progress. Its mastery unlocks deeper efficiency, cleaner power, and sustainable growth, making it not just a scientific concept but a vital pillar of global energy evolution.
Related Post

Unveiling The Life And Career Of Carolina Ramirez: From Humble Beginnings to Global Recognition

Kent Ehrhardt’s Current Wife: Insights into the Life of a Private Life Amid Public Recognition

Nīn: Unveiling the Timeless Wisdom of a Tradition That Shapes Identity and Community

Posiciones De Copa Centroamericana De Concacaf: Where Inside Lines Define Triumph

