Ethyl Acetate’s Molecular Weight: The Silent Star Behind Smooth Finishes and Flavor Innovation
Ethyl Acetate’s Molecular Weight: The Silent Star Behind Smooth Finishes and Flavor Innovation
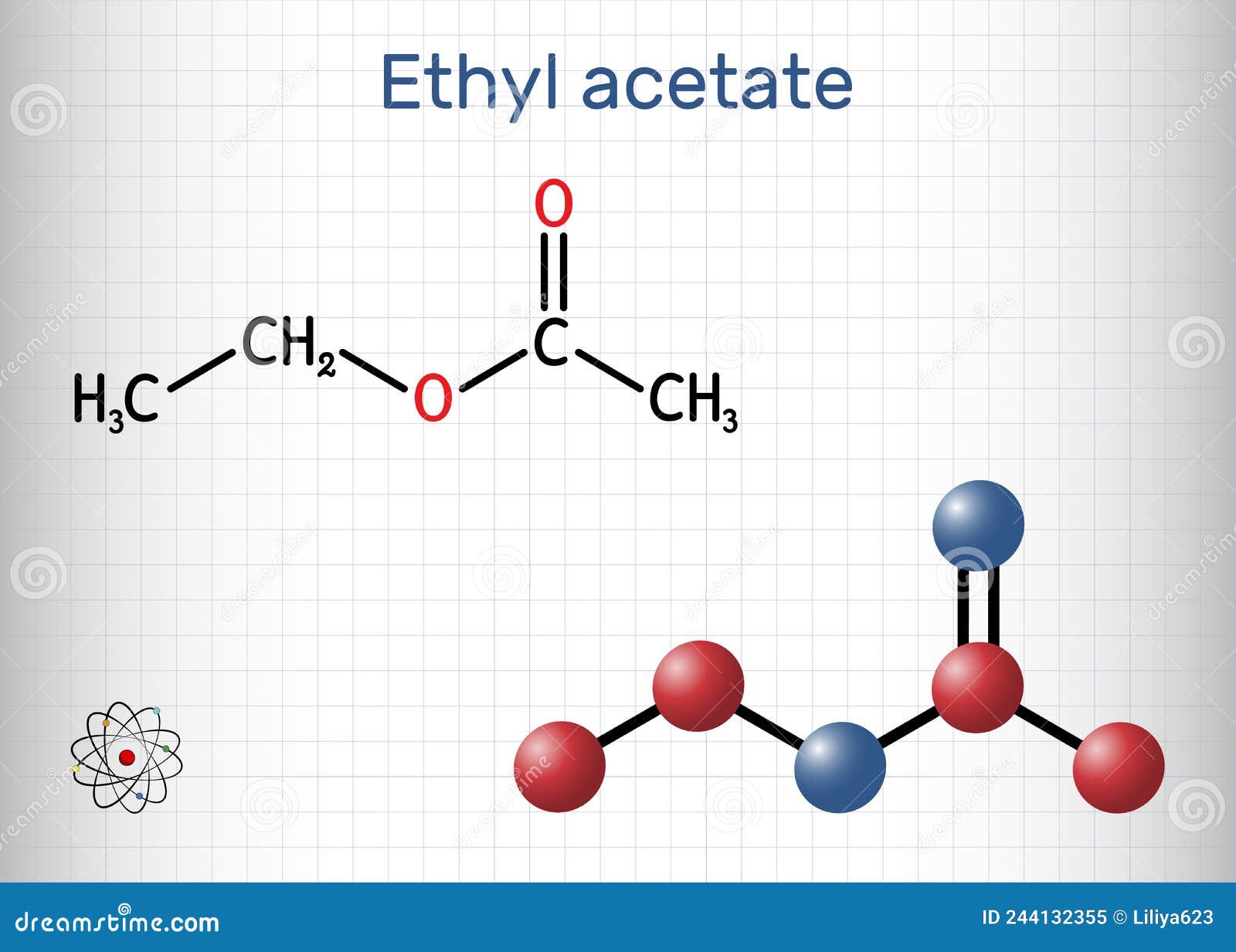
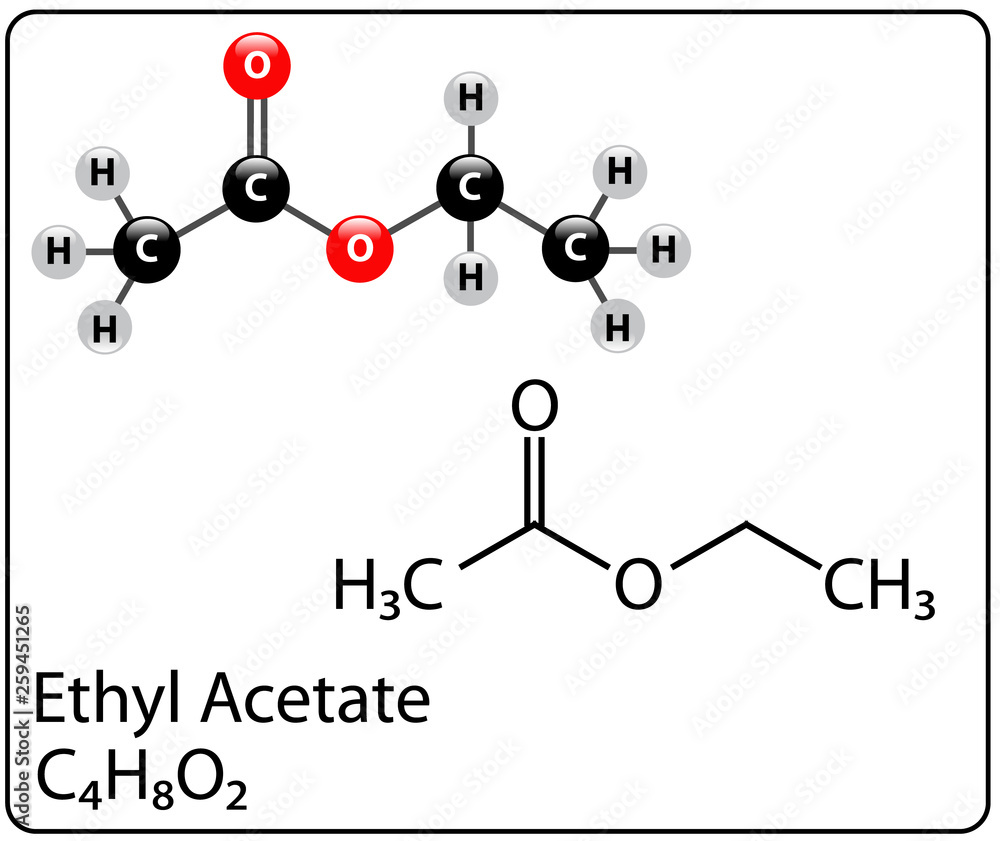
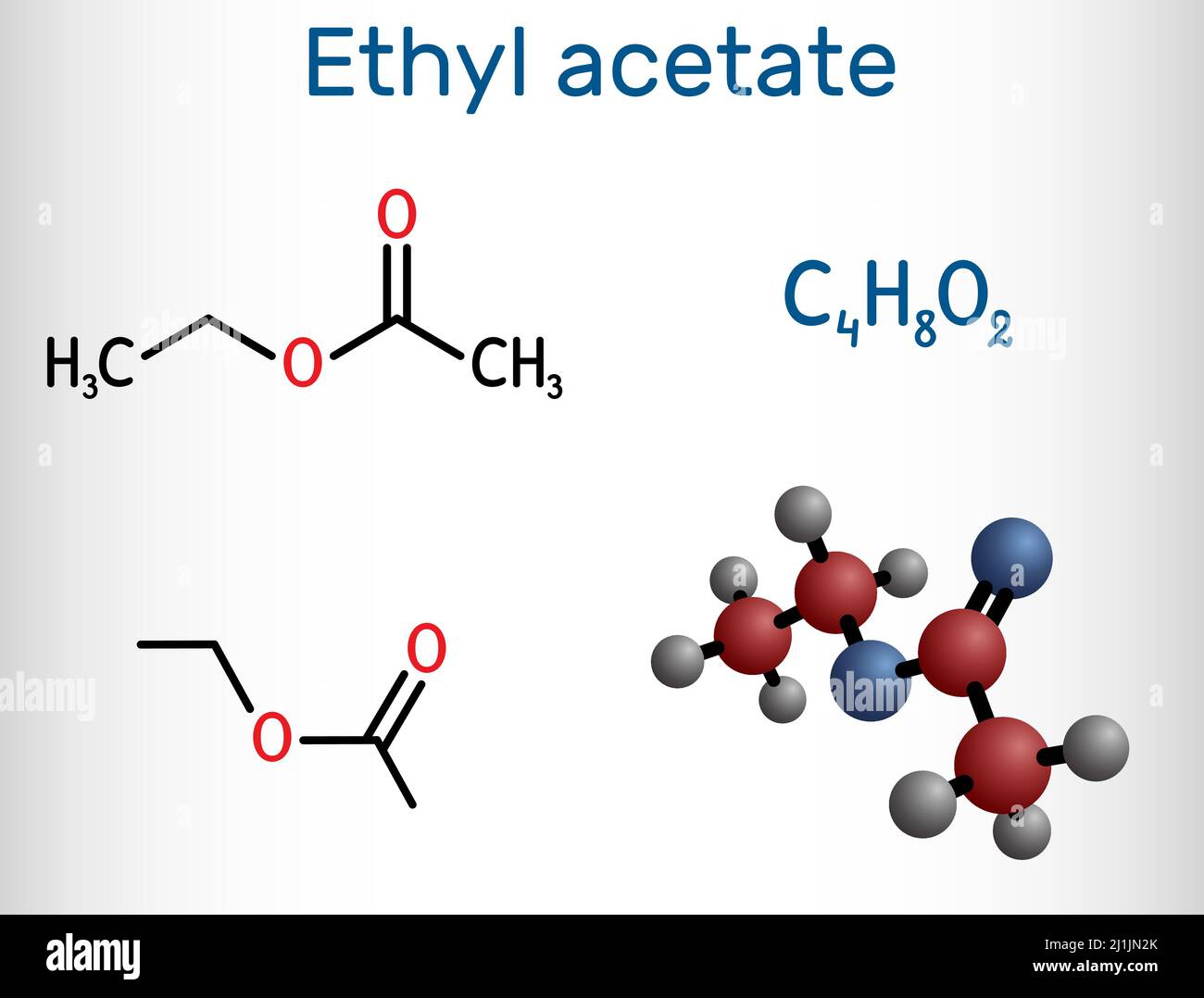
Molecular weight, though invisible to the naked eye, governs the behavior, application, and impact of chemical compounds—nowhere is this more evident than in ethyl acetate. With a well-defined molecular weight of 88.11 g/mol, ethyl acetate stands out as a cornerstone solvent in industries ranging from coatings and pharmaceuticals to flavor chemistry and electronics manufacturing. Understanding this value is key to unlocking the molecule’s versatility and safety profile.
Though the number itself may seem simple, it underpins a wide range of practical and ecological considerations, making ethyl acetate far more than just a synthetic byproduct. The precise molecular weight of ethyl acetate—88.11 g/mol—stems from its two primary components: ethanol and acetic acid, combined through esterification. This precise balance influences not only its volatility and solvency power but also its regulatory classification and handling requirements.
Unlike larger or more complex organic molecules, ethyl acetate’s moderate molecular weight supports controlled evaporation rates, ideal for drying coatings without leaving residue. Industrially, this weight directly affects its vapor pressure and thermal stability, ensuring consistent performance across diverse applications.
What makes ethyl acetate uniquely valuable is more than its molecular weight—it’s how that value translates into real-world function.
With a boiling point of approximately 77°C (170.6°F) and low toxicity, it serves as a safe, effective solvent for both industrial and consumer products. In nail polish removers, paint thinners, and flavoring agents, its ability to dissolve oils and resins while maintaining moderate evaporation ensures smooth application and rapid drying. The molecular weight plays a central role here: intermediate enough to sustain controlled evaporation, yet light enough for efficient dispersion.
As the compound rises in popularity within green chemistry initiatives, understanding its molecular weight aids scientists in optimizing formulations with reduced environmental impact.
The story of ethyl acetate begins with its synthesis: a reaction between ethanol (C₂H₅OH, molecular weight 46.07 g/mol) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH, molecular weight 60.05 g/mol), forming the ester with a total molecular weight of 88.11 g/mol. This precise stoichiometry shapes its physical properties—solubility in both water and organic solvents, controlled volatility, and compatibility with a broad range of materials. Unlike heavier esters, ethyl acetate evaporates quickly but doesn’t escape into the atmosphere in harmful quantities, making it a preferred choice in regulated industries.
Industry experts note its “ideal middle ground” in solvent performance, a balance directly tied to its molecular weight. At 88.11 g/mol, ethyl acetate ranks among the lighter organic solvents, a factor crucial for applications requiring fast drying and minimal residue. In coating formulations, for example, its molecular weight supports thinner film formation without compromising durability.
In food science, where purity and safety are non-negotiable, its well-defined molecular weight assists regulatory compliance and risk assessment. Toxicological data consistently show low acute toxicity—largely attributable to its moderate molecular weight, which limits cellular penetration and systemic exposure. Developed in the 19th century as a byproduct of early industrial chemistry, ethyl acetate has evolved into a ubiquitous solvent.
Its molecular weight remains central to modern applications, from pharmaceutical drug delivery, where it helps dissolve active ingredients, to fragrance industries, where it stabilizes volatile aroma compounds. Advances in green chemistry have deepened scrutiny of such metrics: understanding ethyl acetate’s molecular weight aids in designing lower-emission alternatives, pairing performance with sustainability.
Environmental and health impact assessments consistently highlight ethyl acetate’s favorable profile, with its molecular weight playing a subtle but decisive role.
At 88.11 g/mol, the compound exhibits controlled vapor pressure—evaporating sufficiently for fast drying but avoiding rapid dispersion into air. This balance supports worker safety and regulatory approval across continents, including under REACH, EPA, and Codex Alimentarius guidelines. While its flammability and solvency demand handling precautions, the molecular weight underscores its relative safety compared to heavier, more persistent solvents.
Moreover, ethyl acetate’s moderate molecular weight enables efficient recovery and recycling in industrial processes. Unlike higher-weight compounds, it can be distilled and purified with relative ease, reducing waste and resource consumption. This efficiency aligns with emerging circular economy principles, where chemistry’s molecular design directly influences sustainability outcomes.
As industries shift toward greener, healthier formulations, ethyl acetate’s molecular weight emerges as a silent yet pivotal parameter. Its 88.11 g/mol value is more than a number—it defines stability, solubility, safety, and environmental compatibility. In coatings that dry to a flawless sheen, in perfumes that linger just right, in pharmaceuticals that deliver actives with precision—ethyl acetate performs with precise intent, governed by the science of its molecular weight.
Understanding this value deepens appreciation for a compound that quietly shapes modern life, balancing power and prudence with every molecule.

Related Post
The Unseen Engine: Deep Dive into the Actors For Cars 3 Voice Cast

From Home Run Swings to Crown Leadership: The Multifaceted Legacy of Shohei Ohtani

Where Is Missouri? The Midwestern Heartland Anchoring America’s Center

