Define the Sexual Reproduction: The Precision of Nature’s Evolutionary Engine
Define the Sexual Reproduction: The Precision of Nature’s Evolutionary Engine
Sexual reproduction, a fundamental biological process shared across countless species, enables the creation of genetically unique offspring through the fusion of male and female gametes. Unlike its asexual counterpart, this intricate mechanism harnesses diversity through chromosomal recombination and meiotic divisions, ensuring each generation carries a blend of parental traits. The process is not merely a biological mechanism but a dynamic force driving evolutionary adaptation and resilience in ecosystems worldwide.
Defining sexual reproduction requires examining its core biological steps: the formation of specialized reproductive cells, the fusion of gametes during fertilization, and the subsequent development of a multicellular zygote. Each stage is governed by precise molecular instructions that minimize errors while maximizing genetic variation. This balance between stability and change positions sexual reproduction as the cornerstone of complex life forms across animals, plants, fungi, and many microorganisms.
The StAGES OF Sexual Reproduction: From Gametes to Zygote
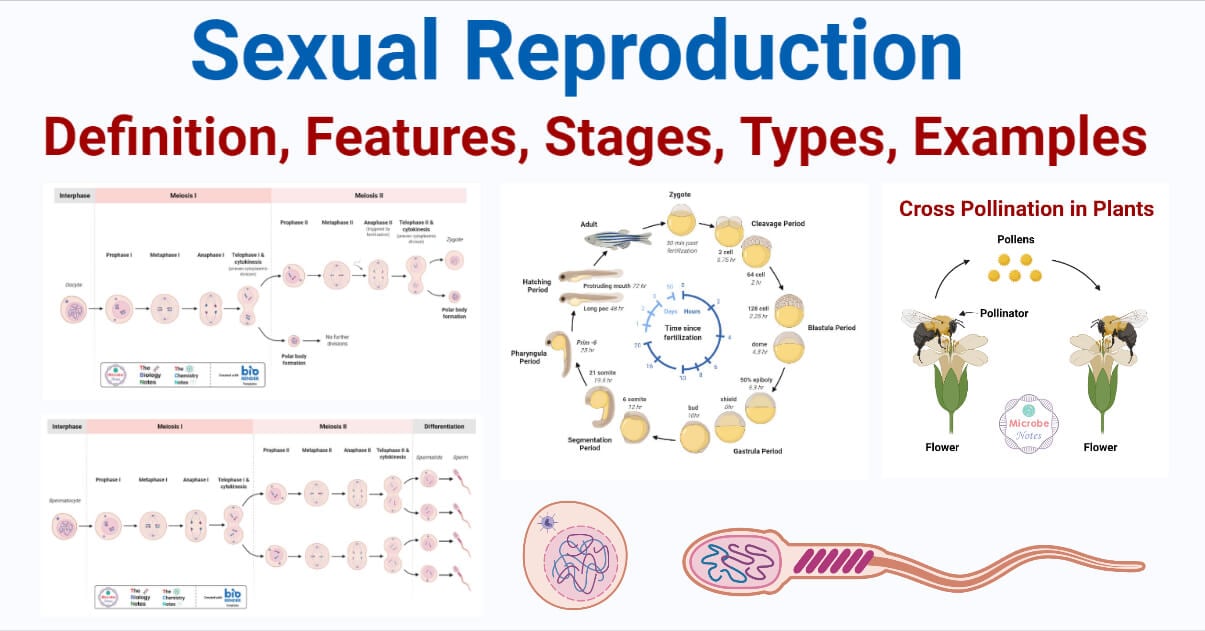
Sexual reproduction unfolds in several well-defined phases, beginning with gametogenesis—the production of sperm and egg cells. In mammals, this process involves meiosis, a specialized cell division that halves the chromosome number, ensuring offspring inherit half the genetic material from each parent. "Meiosis is nature’s architect of variation," notes geneticist Dr.Elena Torres, "as it shuffles genetic deck cards through crossing over and independent assortment." Once mature gametes are formed—spermatozoa in males and oocytes in females—they condense unique patterns of chromosomes, mRNA, and organelles. These cells travel toward each other in a process guided by chemical signals and biological triggers. Fertilization, the pivotal fusion event, merges the sperm’s single strand of DNA with the egg’s, restoring a full chromosomal complement.
This moment reconstitutes the full genetic blueprint of a new organism, laying the foundation for development. From the fertilized egg, or zygote, a cascade of cellular divisions called cleavage begins, rapidly forming an embryo. As years of research reveal, regulation of these phases is critical—disruptions in gamete formation or fusion can lead to developmental failure or genetic disorders.
Yet across species, evolutionary fine-tuning has produced remarkably reliable systems. In humans, fertilization typically occurs in the fallopian tube; in plants like maize, pollination precedes ovule fusion, each pathway adapted to ecological niches. Key Mechanisms Ensuring Genetic Diversity What sets sexual reproduction apart is its unparalleled capacity to generate genetic diversity—vital for survival in changing environments.
This variation arises primarily through two evolutionary tools embedded in meiosis: - **Crossing Over:** During prophase I, homologous chromosomes exchange segments, creating novel combinations of alleles. - **Independent Assortment:** Chromosomes align randomly along the cell plate, producing gametes with countless random combinations. Biologist David Chen explains, "These processes are nature’s randomizers—each generation gains a genetic fingerprint distinct from its parents." The outcome is not chaos but a structured stratagem for adaptation.
Offspring inherit a mosaic of traits, enhancing the likelihood that some individuals will possess advantageous mutations capable of thriving under stress. Genetic drift, recombination, and sexual selection collectively reinforce this adaptive advantage. Over millennia, these mechanisms have shaped speciation and extinction patterns, underpinning biodiversity across the biosphere.
From bacteria to primates, sexual reproduction remains central to life’s evolutionary rhythm. Biological Requirement vs. Evolutionary Advantage While sexual reproduction imposes energetic and logistical costs—requiring mate-finding, gamete production, and complex developmental timing—it delivers enduring benefits that far outweigh its challenges.
In stable environments, asexual reproduction may offer speed and efficiency, but sexual reproduction excels in fluctuating conditions where variability promotes resilience. "Organisms using sex are better equipped to respond to pathogens, climate shifts, and competitive pressures," asserts evolutionary biologist Dr. Priya Mehta.
"The genome becomes a toolkit rather than a blueprint." This adaptive flexibility explains the overwhelming prevalence of sexual reproduction among eukaryotes, despite its biological complexity. Examples abound: flowering plants rely on sexual reproduction to adapt to pollinator shifts, while animals use genetic diversity to combat epidemics. Even in parasitic organisms, such as some barnacles, cross-fertilization counters genetic bottlenecks, maintaining population viability.
In medical and agricultural contexts, understanding sexual reproduction enables breakthroughs—improving crop breeding, controlling disease vectors, and advancing genetic therapies. Scientific mastery over reproductive biology continues to unlock new frontiers in health and sustainability. Through its disciplined fusion of gametes, sexual reproduction shapes the very essence of life—not as a mere biological necessity, but as Nature’s masterful innovation for survival.
By blending precision with unpredictability, it sustains the endless complexity of living systems, ensuring evolution remains an unceasing force. The process remains, in essence, the most powerful mechanism for generating variation in nature—one elegant dance of chromosomes, gametes, and time, defining the continuity and diversity of life on Earth.



Related Post

70mai Omni: Master The Voice Commands — Unlock Seamless Control Through Precision & Strategy

Hugh Laurie Wife A Deep Dive Into the Life of Jo Green: Unveiling the Quiet Strength Behind the Icon

Ipse Ennise Silvia: A Deep Dive into a Rising Catalyst of Cultural and Intellectual Repercussion

