Decoding Molecular Accuracy: How Bh3 Formal Charge Reveals the Hidden Truth in Lewis Structures
Decoding Molecular Accuracy: How Bh3 Formal Charge Reveals the Hidden Truth in Lewis Structures
In the intricate world of chemical bonding, identifying the most energetically stable molecular arrangements demands precision. The Bh3 Formal Charge, a calculated metric rooted in valence electron distribution, stands as a cornerstone tool for chemists seeking to decode molecular stability. More than a mere calculation, Bh3 Formal Charge exposes electron density discrepancies, offering a window into favorable bonding patterns and atomic roles within a molecule.
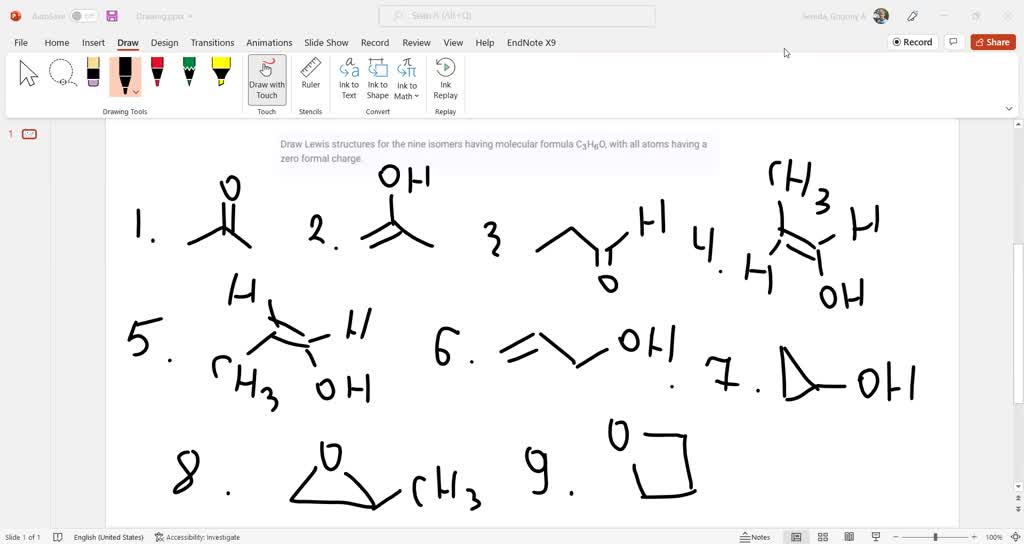
This quantitative probe transforms abstract electron configurations into tangible insights, enabling scientists to predict molecular geometry, reactivity, and reactivity ratios with greater confidence—especially in boron-based compounds. _formal charge and its role in validating Lewis structures_ At the heart of molecular analysis lies the formal charge—a hypothetical charge assigned to each atom in a Lewis structure based on electron sharing. The Bh3 formal charge specifically assesses electron allocation in boron trifluoride (BF₃), a prototypical molecule with a trigonal planar structure.
Boron, in this compound, shares three valence electrons with three fluorine atoms, forming three covalent bonds. Unlike typical tetrahedral molecules where formal charges often reveal electron imbalances, BF₃ presents a striking zero formal charge across all atoms. This balance confirms the molecule’s structural simplicity and stability, as no atom bears an excess or deficit of electrons.
According to classical bonding theory, such electron neutrality supports BF₃’s classification as a strong Lewis acid, capable of accepting electron pairs with minimal energetic resistance.
Quantifying electron integrity with Bh3 formal charge_ Calculating formal charge requires a precise formula: Formal Charge = (Valence Electrons) – (Lone Pair Electrons + Half of Bonding Electrons). For BF₃, boron has five valence electrons.
With three bonds to fluorine and zero lone pairs, its formal charge is computed as 5 – (0 + 3) = 0. Fluorine atoms, each starting with seven valence electrons and forming a single bond (sharing one electron), carry a formal charge of –1 (7 – 6 – 0 = +1 minus shared electrons, net –1). Although boron holds zero formal charge, fluorine’s –1 charge reflects its electron deficiency, a key factor in BF₃’s ability to act as an electron acceptor.
This systematic accounting confirms structural validity and highlights why BF₃ is often employed as a catalyst in organic synthesis. _formal charge’s predictive power in chemical behavior_ Beyond structural validation, Bh3 formal charge enables chemists to anticipate molecular interactions. In reactive systems, atoms with nonzero formal charges serve as hotspots for electrophilic attack or nucleophilic donation.
BF₃’s neutral structure situates boron in a middle ground—neither electron-rich nor depleted—making it selective in reactivity. For instance, when BF₃ encounters a fluoride ion, the negative formal charge on fluorine destabilizes the complex, driving acid-base reactions. Conversely, in catalytic contexts, BF₃’s balance prevents unwanted side reactions, preserving selectivity.
This dual insight into stability and reactivity underscores the practical value of Bh3 formal charge in materials design, pharmaceuticals, and industrial chemistry.
- Electron Distribution Clarity: Bh3 formal charge eliminates ambiguity by quantifying electron loss or gain per atom. Unlike resonant forms or speculative structures, this metric delivers a definitive fingerprint of electron arrangement.
- Predictive Reactivity Models: By highlighting formal charge disparities, chemists anticipate reaction pathways and design reagents accordingly.
BF₃’s neutral charge exemplifies such predictability, guiding its use in synthetic mechanisms.
- Educational and Research Utility: Bh3 formal charge serves as a teaching tool to illustrate fundamental concepts of electron counting and formal charge optimization, while also supporting advanced studies in coordination chemistry.


Related Post

Decoding Pink Headers: The Hidden Language Behind Social Media Visibility
Chris Stuckmann Net Worth and Earnings

How Many Innings Define a Baseball Game? The Definitive Breakdown

